Abstract
Objective
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) is a pleiotropic cytokine having diverse roles in vascular morphogenesis, homeostasis, and pathogenesis. Altered activity of and signaling through TGF-β has been implicated in thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections, conditions characterized by a reduced structural integrity of the wall that associates with altered biomechanics and mechanobiology. We quantify and contrast the passive and active biaxial biomechanical properties of the ascending and proximal descending thoracic aorta in a mouse model of altered TGF-β signaling, with and without treatment with rapamycin.
Approach and Results
Postnatal disruption of the gene (Tgfbr2) that codes the type II TGF-β receptor compromises vessel-level contractility and elasticity. Daily treatment with rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor that protects against aortic dissection in these mice, largely preserves or restores the contractile function while the passive properties remain compromised. Importantly, this increased smooth muscle contractility protects an otherwise vulnerable aortic wall from pressure-induced intramural delaminations in vitro.
Conclusions
Notwithstanding the protection afforded by rapamycin in vivo and in vitro, the residual mechanical dysfunctionality suggests a need for caution if rapamycin is to be considered as a potential therapeutic. There is a need for in vivo evaluations in cases of increased hemodynamic loading, including hypertension or extreme exercise, which could unduly stress a structurally vulnerable aortic wall. Given these promising early results, however, such studies are clearly warranted.
Keywords: aorta, stiffness, strength, aneurysm, transforming growth factor-beta, rapamycin
Introduction
Vascular cells must establish and then maintain an extracellular matrix (ECM) that endows the aortic wall with appropriate compliance and resilience, but also sufficient strength. Decreased compliance can lead to hemodynamic consequences that are implicated in diverse hypertension- and aging-related conditions, including heart attack, stroke, and kidney failure1. In contrast, decreased strength can lead to catastrophic aortic rupture or dissection2. Frank rupture is most common in aneurysms of the infrarenal aorta, whereas dissection tends to occur in the ascending and proximal descending thoracic aorta in the presence or absence of aneurysm. It is not clear why the thoracic aorta is particularly vulnerable to dissection3, but different embryonic lineages of intramural cells, their differential responses to cytokines such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) or hormones such as angiotensin-II, and the distinct pooling of mucoid material have been suggested4-6.
Altered activation of or signaling through TGF-β has also been linked to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections (TAADs). Such alterations have been reported in Marfan syndrome, Loeys-Dietz syndrome, and familial TAADs, including those due to ACTA2 and MYH11 mutations7. Mouse models have been developed to study effects of altered TGF-β, its receptors, and downstream signaling in arterial morphogenesis, homeostasis, and TAAD progression8-11. Such studies provide insight into molecular- and cellular-level mechanisms, but there has yet to be any rigorous study of vessel-level changes in the wall mechanics. It is the biomechanical mechanisms that largely dictate the ultimate fate – dissection and/or rupture – of the aortic wall.
We study a conditional knockout mouse model wherein the gene (Tgfbr2) coding the TGF-β type II receptor, an essential ligand binding component of the receptor complex, can be inactivated postnatally in vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs) under tamoxifen control11. Of particular note, this model suggests that basal TGF-β signaling in aortic SMCs promotes postnatal wall homeostasis and impedes early progression to TAADs. An additional finding is that rapamycin, an inhibitor of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates cell proliferation and protein synthesis, protects against the development of intramural hematoma in the thoracic aorta of mice in which Tgfbr2 is disrupted postnatally. Given that the material properties and structural integrity of the aortic wall are fundamental to its long-term biomechanical functionality, including resistance to TAADs, we assessed, for the first time, active and passive biaxial mechanical behaviors of the ascending and proximal descending thoracic aorta in these mice, without and with rapamycin treatment.
Methods
See Online Supplemental Material
Results
Table 1 shows that 52 male mice were studied at approximately 8 weeks of age across three groups: 17 controls (Ctrl), 19 Tgfbr2 disrupted via tamoxifen-induction at 4 weeks of age (Tmx), and 16 treated daily with rapamycin for 4 weeks following Tgfbr2 disruption at 4 weeks of age (Tmx+Rapa). Of these, 30 were used for passive biaxial evaluation and histological examination, 17 for active biaxial evaluation, and 5 for final hypothesis testing.
Table 1.
Group composition, age, body mass, and occurrence of aortic dissections in Tgfbr2f/f mice that were untreated (Ctrl), treated with tamoxifen to disrupt TGF-β type II receptor signaling (Tmx), and additionally treated with rapamycin (Tmx + Rapa).
| Ctrl | Tmx | Tmx + Rapa | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
| n | 17 | 19 | 16 |
| Age (weeks) | 8.2 ± 0.1 | 8.5 ± 0.2 | 8.4 ± 0.1 |
| Body Mass (grams) | 22.8 ± 0.5 | 22.0 ± 0.5 | 16.4 ± 0.4* |
| % Dissected | 0% | 42%* | 0% |
p<0.05 versus Ctrl.
Consistent with prior findings11, loss of SMC specific TGF-β signaling at 4 weeks of age resulted in an ∼42% incidence of thoracic aortic dissections at 8 weeks of age – with lesions arising in the ascending thoracic aorta (ATA) and/or proximal descending thoracic aorta (DTA) – while daily treatment with rapamycin prevented dissection but resulted in a lower body mass on average (Table 1). ATAs from the Tmx group exhibited diverse gross phenotypes: some vessels appeared normal, some exhibited mild dilatation and fibrosis, and some had varying degrees of intramural hematoma in the absence of a clear intimal flap (Supplemental Figure II). In contrast, many DTAs from the Tmx group appeared normal, save some proximal intramural hematomas (Figure II). Figure 1 shows histological images for some of these phenotypes at both aortic locations, with Tmx+Dis indicating vessels in which Tgfbr2 disruption led to an accumulation of blood within the medial layer in vivo. Consistent with prior findings in aortas that had not undergone in vitro biomechanical testing (Figure 2f-g in11), medial and adventitial cross-sectional areas were larger in dissected vessels (Figure III). Calculating the percentage of total area that was occupied by media versus adventitia revealed slight adventitial thickening in the Tmx+Rapa group (Figures 1 and III). The amount of elastin appeared to be preserved, which means that its area fraction tended to be lower with dissection or treatment with rapamycin due to increases in adventitial collagen (Figure III). Measurements of residual-stress relieving opening angles revealed marked differences due to Tgfbr2 disruption that were not prevented with rapamycin treatment (Figure IV, Table I). Opening angles reflect transmural distributions in elastic fibers and fibrillar collagens; the differences were consistent with an increase in adventitial collagen in Tgfbr2 disruption11. Finally, focal accumulations of mucoid material were observed in the media of some dissected vessels, not necessarily at the site of dissection (Figure V). Henceforth, the term dissection will indicate the presence of an intramural accumulation of blood independent of its source; the term delamination will signify intramural separations (usually within the media) without evidence of associated blood.
Figure 1.
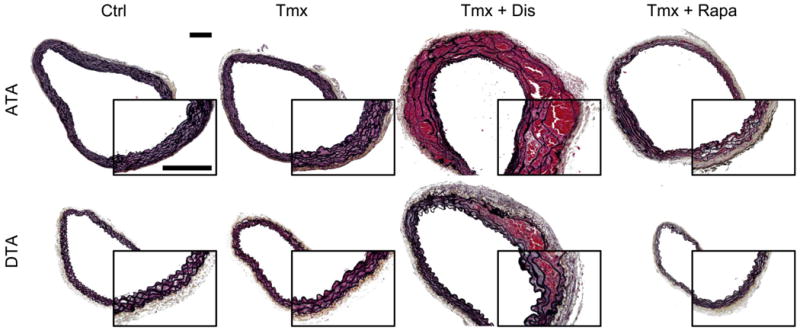
[Color]. Representative Movat-stained images of ascending thoracic aortas (ATA – top row) and descending thoracic aortas (DTA – bottom row) reveal microstructural composition and organization in the three groups (Table 1). Vessels in which Tgfbr2 disruption led to dissection with accumulated blood within the media (Tmx+Dis) were delineated from non-dissected specimens (Tmx). Ctrl and Tmx vessels had similar composition and wall structure, but Tmx+Dis DTAs had increased collagen content as well as increased medial and adventitial areas; trends were similar in the ATA (Figure III). In contrast, Tmx+Rapa DTAs were smaller in caliber with respect to Ctrl and Tmx (Table II), while displaying a moderate increase in adventitial area (p < 0.1) despite an unchanged medial area (Figure III). Tmx+Rapa ATAs were not smaller, but displayed trends similar to DTAs without reaching statistical significance. Overall, treatment with rapamycin caused the adventitia to occupy a significantly higher fraction of the cross-section (Figure III). Insets show magnified views; scale bars represent 200 μm.
Figure 2.
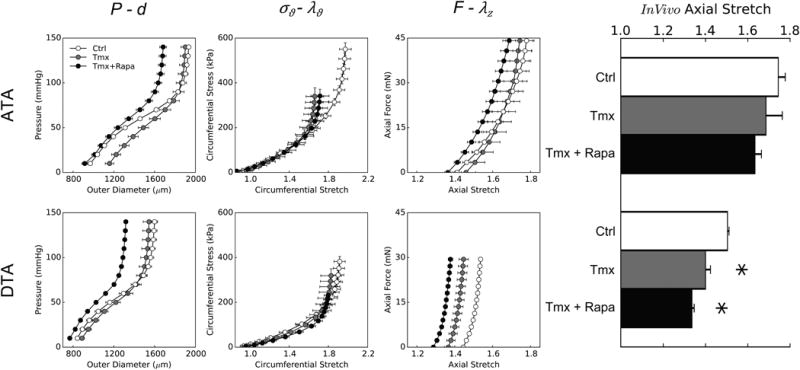
Passive biaxial mechanical behaviors from ascending (ATA – top row) and descending (DTA – bottom row) thoracic aortas: mean pressure–diameter data (first column) and associated circumferential Cauchy stress–stretch data (second column) for cyclic P-d tests plus mean axial force–length data for cyclic f-l tests performed at 100 mmHg (third column) and individual values of the in vivo axial stretch (bar plot – fourth column). Data are shown for three groups: controls (Ctrl), tamoxifen-induced disruption of Tgfbr2 without dissection (Tmx), and tamoxifen-induced disruption with daily treatment with rapamycin (Tmx+Rapa). Disrupted TGF-β signaling caused differential effects in the two aortic locations: loss of distensibility (with normal extensibility) in ATAs and loss of extensibility (with normal distensibility) in DTAs. Rapamycin neither prevented nor improved the passive biomechanical changes, despite reducing the diameter with respect to Tmx. * indicates p < 0.05 with respect to Ctrl samples from similar aortic locations.
Geometrical and biomechanical metrics are listed in Table I for all specimens that survived passive biaxial testing. That is, to focus on the potentially vulnerable, but not dissected, aortic wall, we excluded Tmx+Dis samples from quantitative comparisons of passive mechanical properties (Figure VI). Figure 2 shows pressure–diameter (structural) and associated circumferential stress–stretch (material) behaviors as well as axial force–stretch responses for the three groups and both regions. Note that ATAs and DTAs from control mice (white symbols) exhibit the usual highly nonlinear and compliant behavior; the initial non-zero slope in the stress–stretch response indicates a normal elastin-dominated behavior at low pressure. This low-pressure behavior was similar in vessels from Tmx and Tmx+Rapa groups, consistent with histological evidence of nearly preserved elastin. Yet, the subsequent characteristic stiffening usually ascribed to the recruitment of previously undulated collagen fibers differed with Tgfbr2 disruption. Tmx and Tmx+Rapa ATAs exhibited qualitatively similar stress–stretch behaviors with a loss of distensibility despite axial properties similar to controls (Figure 2, top row). In contrast, Tmx and Tmx+Rapa DTAs were circumferentially indistinguishable from controls (despite the latter having smaller diameters) while displaying a progressive loss of axial extensibility (Figure 2, bottom row). Finally, dissected DTAs had nearly normal circumferential behaviors (away from the site of dissection), while dissected ATAs showed circumferential dilation, a further loss of distensibility, and loss of extensibility (Figure VI). Further examination of passive data revealed that Tgfbr2 disruption did not affect the biaxial material stiffness (Table I), though biaxial stresses were lower at in vivo conditions (Figure 2).
Changes in elastic energy storage due to disrupted TGF-β signaling in the SMCs are shown in Figure 3. Consistent with data in Figure 2 and with respect to controls, iso-energetic contours were compressed along the ordinate (indicating lower distensibility) for ATAs and especially along the abscissa (indicating lower extensiblity) for DTAs for both the Tmx and Tmx+Rapa groups. Albeit not shown, control ATAs and DTAs displayed similar energy storage and degrees of anisotropy as wild-type mice12. Importantly, the reduced overall energy stored elastically in ATAs and DTAs of mice with Tgfbr2 disruption compromises their primary mechanical function (i.e., storage of elastic energy during systole that can be used to work on the blood during diastole to augment flow), and rapamycin neither prevented this reduction nor restored it towards normal (it actually worsened it in the DTA). There was some improvement in terms of a reduced energy dissipation (i.e., intrinsic losses of elastic energy during cyclic loading), however (Table I).
Figure 3.
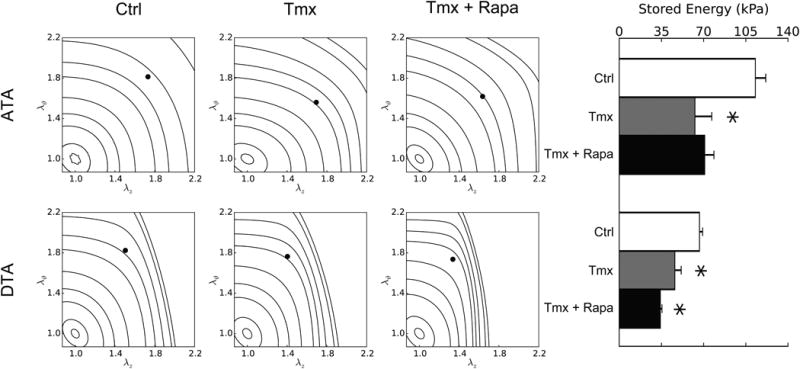
Passive elastic energy storage during biaxial mechanical testing of ascending (ATA – top row) and descending (DTA – bottom row) thoracic aortas for three groups: Ctrl (first column), Tmx (second column), and Tmx+Rapa (third column). Iso-energetic contour plots highlight biaxial strain dependencies whereas individual values reveal in vivo states (bar plot – fourth column). Each iso-energy level is indicated as a curve (with values of 0.1, 1, 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 100, 250, and 500 kPa), while in vivo values are shown as filled circles. ATAs normally store more energy than DTAs due to a higher elastin content and nearly equi-biaxial loading. Loss of TGF-β signaling decreased energy storage in both regions and rapamycin neither prevented nor restored this function (in ATAs, Tmx+Rapa energy storage is lower than Ctrl at p < 0.1 while being not significantly different from Tmx). * indicates p < 0.05 with respect to Ctrl samples from similar aortic locations.
Figure 4 shows an unexpected, but striking, observation in passively loaded DTAs from Tgfbr2 disrupted mice, both Tmx (1 of 9) and Tmx+Rapa (6 of 11). In this subset of specimens (7 of 20, or 35%), grossly normally appearing specimens often delaminated during passive mechanical testing, beginning during the initial period of static loading (acclimation) and progressing during subsequent mechanical testing (Figure 4a). In all cases, the P-d and f-l protocols were completed because the apparently intact adventitia allowed pressurization (Figures 4b and VI); as noted above, however, we excluded data from these specimens in the quantitative assessments in Figures 2 and 3 and Table I. Nevertheless, by comparing raw P-d data between intact and delaminated DTAs, we observed dilatation and increased hysteresis (i.e., energy dissipation, as revealed by different loading and unloading curves) in delaminated samples (Figure 4b). The latter likely resulted from an accumulation of physiologic solution within the delaminated wall, which would increase intramural viscous dissipation during cyclic loading. As seen in Figure 4c-d, using both in vitro imaging via optical coherence tomography and normal histology, the intramural delaminations were extensive and involved multiple medial lamellar units. Some of the delaminations may have initiated near branch sites in the DTAs, which necessarily were not present within the tested regions of the ATAs.
Figure 4.
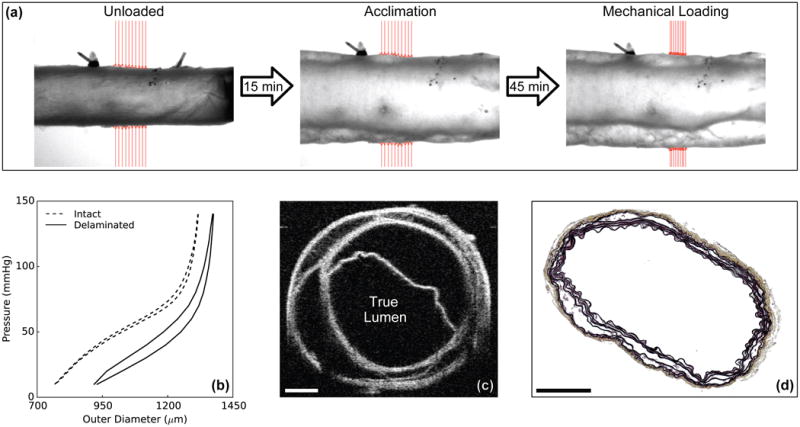
Illustrative data for mechanical testing under passive conditions of a rapamycin-treated, Tgfbr2 disrupted DTA (Tmx+Rapa). Video-images (a) reveal the initiation of an intramural delamination (separation of wall layers) upon static pressurization (acclimation), with progression during cyclic pressurization (mechanical loading from 10 to 140 mmHg repeated four times) despite the grossly normal appearance prior to loading (unloaded). Shown, too, are associated pressure-diameter data (b), an optical coherence tomographic image collected during testing (c), and a histological image obtained after testing (d). The cross-sectional images reveal complex, extensive separation of medial elastic layers with an otherwise intact adventitia (which allowed pressurization during mechanical testing). Mechanical data showed that delamination was associated with circumferential dilation (higher outer diameter) and increased hysteresis (higher energy dissipation), both consistent with the accumulation of interstitial fluid following delamination. Scale bars represent 200 μm.
Active biaxial tests on the DTA revealed that daily treatment with rapamycin largely preserved or improved the contractile function that was otherwise diminished due to Tgfbr2 disruption. In particular, we measured changes in outer diameter upon stimulation with 80 mM KCl while monitoring changes in axial force. For each vessel, we adjusted the fixed value of axial stretch so that changes in axial force (total minus passive) varied from positive (tensile) to negative (compressive) due to contraction (Figure VII). We defined an active in vivo axial stretch as that value at which no change in transducer-measured axial force occurs upon contraction, assuming that this would be a “preferred” (homeostatic) value under physiologic conditions. When contracted at individual active in vivo stretches and 70 mmHg transmural pressure, changes in outer diameter were: -250±22 μm (Ctrl), -163±21 μm (Tmx), and -223±25 μm (Tmx+Rapa) (Figure 5). Hence, rapamycin either nearly preserved or restored towards normal the active circumferential properties of DTAs in Tgfbr2 disrupted mice. Values of the active in vivo stretches were yet statistically lower for Tmx (1.38±0.03) and Tmx+Rapa (1.41±0.01), relative to Ctrl (1.52±0.02), similar to the lower passive in vivo stretches (Table I) for Tmx (1.40) and Tmx+Rapa (1.34) relative to Ctrl (1.50). These findings suggest that the axial direction is controlled largely by passive properties and rapamycin neither prevented nor reversed the decreased axial stretch due to disrupted TGF-β signaling (Fig 2, right). A decreased axial stretch can unload the wall biaxially, which could be protective in many cases of altered hemodynamic loading or genetic mutations13.
Figure 5.
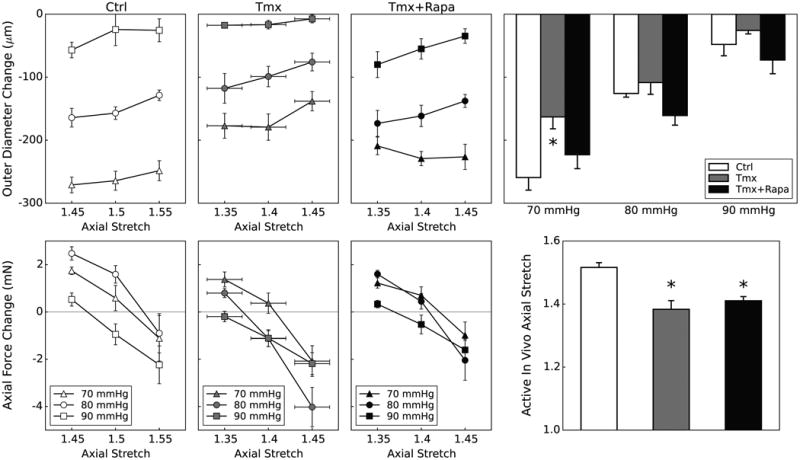
Active biaxial mechanical data from descending thoracic aortas (DTA) contracted via 80 mM KCl for three groups: Ctrl (first column), Tmx (second column), and Tmx+Rapa (third column). Data in the first three columns show contraction-induced changes in outer diameter (top row) following 15 minutes of SMC activation and changes in axial force (bottom row), at three isobaric (70, 80, and 90 mmHg) and three axially isometric (around the vessel-specific in vivo stretch) conditions, thus yielding 9 different active states. The active in vivo axial stretch is calculated individually for each vessel at the three pressures as the value at which axial force remains constant upon contraction. Data in the far right columns summarize the primary biaxial findings: contraction-stimulated decreases in outer diameter (top) and values of active in vivo axial stretch (bottom). Passive and active in vivo axial stretches were indistinguishable (Table II) for each group. Tgfbr2 disruption diminishes SMC contraction at 70 mmHg, but rapamycin treatment tends to restore or augment this contractility at all pressures though without recovery of the preferred axial stretch. * indicates p < 0.05 with respect to Ctrl samples from similar aortic locations.
Anecdotally, in contrast to observations under passive conditions (Figure 4), none of the DTA specimens exhibited intramural delaminations while tested under active conditions. We thus tested the hypothesis that increased SMC contractility could protect an otherwise structurally vulnerable aortic wall from intramural delamination. Figure 6 shows illustrative results from a series of experiments on Tmx+Rapa DTAs. None of the specimens exhibited a visible or optical coherence tomographic-detected intramural delamination when pressurized while actively contracted with 80 mM KCl at 70 mmHg (Figure 6, top). In stark contrast, a sub-set of vessels (2 of 5) began to delaminate at the same pressure soon after being rendered passive by washing out the high K+ Krebs with a normal Hanks solution (Figure 6, middle); indeed, these specimens delaminated further upon cyclic pressurization over physiologic ranges (Figure 6, bottom). Table II shows calculated reductions in wall stress in circumferential and axial directions when the vessels were contracted. This reduction resulted, in large part, by decreasing the inner radius and increasing wall thickness (Figure 6) and may have protected the wall from damage.
Figure 6.
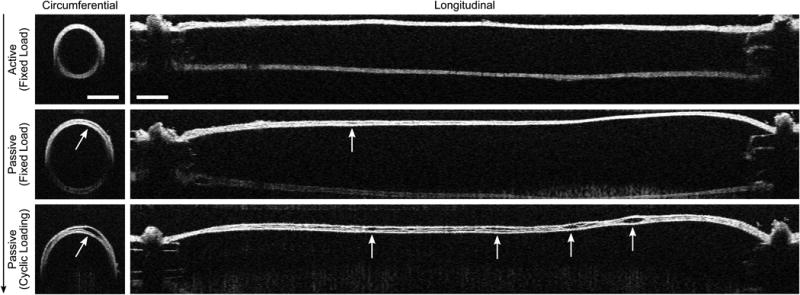
Optical coherence tomographic images of circumferential (left) and longitudinal (right) sections of a representative cannulated artery. Images were collected sequentially (vertical arrow) during biaxial mechanical tests on a rapamycin-treated, Tgfbr2 disrupted (Tmx+Rapa) descending thoracic aorta (DTA) exposed to a 70 mmHg luminal pressure at the in vivo axial stretch. The artery was first contracted via 80 mM of KCl (top row), then fully relaxed for 40 minutes via multiple washouts of HBSS (middle row), and finally pressurized cyclically from 10 to 140 mmHg under passive conditions (bottom row). Intramural delaminations nucleated locally upon SMC relaxation and propagated along the length and circumference. This phenomenon never occurred in control samples regardless of contractility (Ctrl – 0/5 active, 0/7 passive), it occurred in only one Tgfbr2 disrupted sample (Tmx – 0/5 active, 1/7 passive), but manifested itself with the highest frequency in rapamycin-treated, Tgfbr2 disrupted specimens (Tmx+Rapa – 0/10 active, 6/11 passive). White arrows show initiation and spatial progression of intramural delaminations; dark arrows indicate temporal progression. Scale bars represent 400 μm.
Discussion
Data from patients demonstrate that mutations to the gene (TGFBR2) that codes the TGF-β type II receptor predispose to TAADs14,15. Among other cellular-level effects, these mutations lead to a decreased expression of contractile proteins in medial SMCs; indeed, cultured mutant SMCs fail to elaborate or organize increased contractile proteins in response to exogenous TGF-β16. Importantly, mutations to genes that encode SMC contractile proteins (e.g., ACTA2 and MYH11) and associated molecules (e.g., MLCK and PRKG1) similarly predispose to TAADs17-20. There is, therefore, increasing evidence that dysfunctional SMC contractility plays important roles in humans presenting with TAADs21,22.
There are three main findings of this study. First, postnatal disruption of Tgfbr2 in SMCs compromises both active (contractile) and passive (structural) biaxial biomechanical properties in the murine thoracic aorta. Second, daily in vivo treatment with rapamycin largely preserves or restores biaxial contractile properties, but not passive structural properties. Third, stimulated in vitro contraction of SMCs in DTAs from rapamycin-treated mice with postnatal disruption of Tgfbr2 prevents pressure-induced intramural delamination (0 of 11) whereas in vitro inactivation of SMCs allows delaminations (6 of 11 total, or 55%). Indeed, delaminations initiated even at a modest transmural pressure (70 mmHg or lower) in a sub-set of rapamycin treated vessels (2 of 5, or 40%) immediately after the contracted vessel was rendered passive.
Postnatal disruption of Tgfbr2 reduced the contractile range of the DTA by ∼37% (at transmural pressures of 70 and 80 mmHg and in vivo axial stretches), and fundamentally changed its biaxial character (Figure VII). Because of circumferential-axial coupling, contraction at a fixed pressure and axial stretch just above the in vivo value typically results in positive (i.e., tensile) axial force generation in normal vessels23. DTAs from Tgfbr2 disrupted mice exhibited weak or negative changes in axial force, which was either prevented or reversed by rapamycin treatment. As noted in Supplemental Materials, these differences may allow Tmx+Rapa vessels to increase wall thickness upon contraction similar to controls. Related to this, unloaded wall thickness was not different between Ctrl and Tmx DTAs, but it was ∼11% greater in Tmx+Rapa DTAs (Table I). Both contraction-induced and intrinsic increases in thickness can reduce wall stress (Table II), which together may have kept active Tmx+Rapa vessels from exceeding threshold levels for delamination.
The compromised vessel-level contractility in Tgfbr2 disrupted aortas is consistent with our prior findings that there is decreased contractile protein gene expression (e.g., Acta2 and Myh11), decreased phosphorylation of myosin light chain (p-MLC), and decreased cell-induced compaction in a collagen gel assay11. The present data reveal further, however, that rapamycin largely protects against or reverses vessel-level contractile deficits. This finding is consistent with reports that rapamycin promotes SMC differentiation from a synthetic to contractile phenotype24. Indeed, rapamycin did not protect against or reverse the marked changes in passive biaxial properties, which may require adequate synthesis of ECM to ensure structural integrity. Tgfbr2 disruption, with or without treatment with rapamycin, resulted in a significant decrease in elastic energy storage (Figure 3), which marks decreased mechanical functionality12. Although circumferential material stiffness was not affected significantly by Tgfbr2 disruption, or its treatment with rapamycin, there was a trend in the ATA and significance in the DTA toward a decrease in the passive in vivo axial stretch (Figure 2), which likely contributed to the overall decreases in wall stress (Figure 2). Notwithstanding slightly lower blood pressures in the Tmx mice11 and near normalized pressures in the Tmx+Rapa mice, lower passive wall stresses could be either protective or detrimental. Lower stresses typically reduce the risk of a structural failure; yet, lower than normal stresses can also signal an atrophic mechanobiological response25. The latter could contribute to diminished wall integrity provided that the intramural cells can sense the wall stress. Mechanosensing and mechanoregulation of ECM requires functional actomyosin activity22, however, which may have been compromised similar to the diminished vessel-level contractility caused by the Tgfbr2 disruption. Given that remodeling responses to decreased wall stress tend to take much longer to manifest on a tissue-level than responses to increased wall stress25, rapamycin could possibly improve passive properties by improving mechanosensing and mechanoregulation of ECM if vessels were treated for a longer period (> 4 weeks). Future studies will be needed in this regard.
Rapamycin inhibits the mTOR pathway that serves as an important node for cell signaling26. Amongst its diverse actions, rapamycin is a strong attenuator of cell proliferation, particularly T-cells, which contributes to its potent immunosuppression27. Interestingly, T-cells play important roles in structurally stiffening the murine aorta in an angiotensin-II model of hypertension, primarily by increasing collagen deposition in the adventitia28. Angiotensin-II also plays important roles in TAADs29,30 and there is considerable cross-talk between angiotensin-II and TGF-β signaling, both of which promote ECM production. Our results in normotensive mice showed, however, that rapamycin (which presumably blocked T-cell activity) associated with a slight increase in adventitial area in the Tgfbr2 disrupted mice due to a modest increase in collagen and a slight decrease in medial area (Figure III). The latter may have resulted from a reduction in SMC number since rapamycin attenuates proliferation11. Recalling that rapamycin largely preserved or improved biaxial contractility in the DTAs of the Tgfbr2 mice (and that ATAs were not studied under active conditions since they never delaminated in vitro), note that increased contractility typically associates with decreased proliferation and decreased protein synthesis. Indeed, rapamycin decreases angiotensin-II / mechanical stress mediated protein synthesis31. Our results are thus consistent with an increased contractility and decreased proliferation/synthesis by medial SMCs, with less apparent effects on adventitial fibroblasts. Indeed, a logical mechanobiological response by adventitial fibroblasts in cases of medial atrophy would be to increase ECM deposition, but there is a need to delineate medial and adventitial biomechanics to address this expectation32. The situation could also be different in patients having TGBFR2 mutations. Tgfbr2 disruption in the current mouse model is both SMC-specific and postnatal, whereas adventitial (myo)fibroblasts in TGFBR2 patients may have reduced contractile protein expression and decreased mechanosensing and mechanoregulation capability16.
That rapamycin increased vessel-level contractility and prevented in vivo dissection in all mice with tamoxifen-induced Tgfbr2 disruption is consistent with the emerging concept that decreased SMC contractility predisposes to TAADs21,33. Three possibilities seem tenable. First, increased contractility could off-load some stress from an otherwise mechanically vulnerable ECM34. Second, increased actomyosin activity could improve the SMC mechanosensing and mechanoregulation of the ECM that is fundamental to maintaining mechanical functionality and structural integrity22. Third, increased microvascular tone could decrease both flow within and permeability of a vasa vasorum, if present (i.e., although a stimulated vasa vasorum and associated angiogenic progression in murine arteries remains controversial, an invading pathologic vasa vasorum could enable entry of blood into the outer medial layers (Figure 1) and increased microvascular contractility could attenuate this possibility).
Although each of these effects could contribute to the in vivo protection afforded by rapamycin, it is particularly noteworthy that in vitro pressurization to physiologic levels resulted in gross delaminations in vessels under passive, but never active, conditions (Figure 6). This observation supports the hypothesis that improved SMC tone may help to stress shield an otherwise mechanically vulnerable ECM (Table II). If true, there is a pressing need to determine if such shielding would remain sufficient in cases of increased intramural stress, as in extreme exercise or hypertension, both of which are risk factors for aortic dissection3. There is similarly motivation to determine if adverse effects of calcium channel blocking in mice and patients predisposed to TAADs35 might be due, in part, to the loss of otherwise beneficial stress shielding due to SMC contraction. Indeed, increased vessel-level contractility could not only stress shield the ECM, it could attenuate a localized accumulation of interstitial fluid (cf. Figure 4) that could otherwise follow from an increased pooling of glycosaminoglycans or increased permeability of vasa vasorum. Additional, potential roles of rapamycin in these other cases are noted in the Supplemental Discussion.
In conclusion, this study confirms that rapamycin protects against intramural hematoma in vivo in mice with postnatal Tgfbr2 disruption11. Although reasons for this therapeutic benefit remain unknown, rapamycin preserved or restored SMC contractility toward control values and reduced localized pooling of mucoid material, both of which may have been protective6,22. Nevertheless, rapamycin did not restore the passive biaxial mechanical properties to normal; axial stretch and axial stiffness tended to remain reduced as did overall elastic energy storage. Because blood pressure is normal or slightly lower than normal in mice with Tgfbr2 disruption, the lower than normal stresses may not have been high enough to exploit the apparent underlying structural vulnerability that was revealed via in vitro mechanical testing under passive conditions. Given that uncontrolled hypertension and acute increases in blood pressure (e.g., exercise related) pose significant risks for aortic dissection, we caution against the therapeutic use of rapamycin until further investigation can elucidate the protective mechanisms and potential trade-offs are considered carefully. Indeed, although there is no obvious vascular phenotype in Myh11R247C/R247C mice under normal hemodynamic loading, induced hypertension results in both rupture-related, pre-mature deaths and evident aortic fragility during mechanical testing32. There is, therefore, a need for further study of the potential role of ECM vulnerability under increased hemodynamic loads. Nevertheless, the potentially protective role of vessel-level contractility against dissection of a vulnerable thoracic aorta emphasizes the need for further biomechanical studies to complement molecular findings.
Supplementary Material
Significance.
The present results represent the first observation of spontaneous in vitro delaminations under physiologic loading of a structurally vulnerable thoracic aorta in a mouse model predisposed to aortic dissection. Importantly, induced SMC contractility afforded 100% protection against intramural delamination, which could be an initiator of dissection. Calculations suggest that contraction markedly reduces intramural wall stresses and thereby may stress shield a vulnerable ECM. Pharmacologic treatments should thus balance the need to reduce hemodynamic loads while preserving SMC contractility in large arteries.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge expert assistance by the Yale Histology Service.
Source of Funding: This work was supported by grants from the NIH (R01 HL105297, U01 HL116323) and National Marfan Foundation.
Abbreviations
- ATA
ascending thoracic aorta
- DTA
descending thoracic aorta
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- mTOR
mechanistic target of rapamycin
- SMC
smooth muscle cell
- TAAD
thoracic aortic aneurysm and dissection
- TGF-β
transforming growth factor beta
- Tgfbr2
murine gene coding the TGF-β type II receptor
- Tmx
tamoxifen
- Rapa
rapamycin
Footnotes
Disclosures: None.
References
- 1.Laurent S, Boutouyrie P. The structural factor of hypertension: large and small artery alterations. Circ Res. 2015;116:1007–1021. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Martufi G, Gasser TC, Appoo JJ, Di Martino ES. Mechano-biology in the thoracic aortic aneurysm: A review and case study. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2014;13:917–928. doi: 10.1007/s10237-014-0557-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Elefteriades JA, Farkas EA. Thoracic aortic aneurysm: Clinically pertinent controversies and uncertainties. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55:841–857. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.08.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ruddy JM, Jones JA, Spinale FG, Ilonomidis JS. Regional heterogeneity within the aorta: Relevance to aneurysm disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;136:1123–1130. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2008.06.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.El-Hamamsy I, Yacoub MH. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of thoracic aortic aneurysms. Nature Rev–Cardiol. 2009;6:771–786. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2009.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Humphrey JD. Possible roles of glycosaminoglycans in aortic dissections, with implications to dysfunctional TGF-b. J Vasc Res. 2013;50:1–10. doi: 10.1159/000342436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Doyle JJ, Gerber EE, Dietz HC. Matrix-dependent perturbation of TGFβ signaling and disease. FEBS Letters. 2012;586:2003–2015. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Choudhary B, Zhou J, Li P, Thomas S, Kaartinen V, Sucov HM. Absence of TGFβ signaling in embryonic vascular smooth muscle leads to reduced lysyl oxidase expression, impaired elastogenesis, and aneurysm. Genetics. 2009;7:115–121. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Langlois D, Hneino M, Bouazza L, Parlakian A, Sasaki T, Bricca G, Li JY. Conditional inactivation of TGF-b type II receptor in smooth muscle cells and epicardium causes lethal aortic and cardiac defects. Transgen Res. 2010;19:1069–1082. doi: 10.1007/s11248-010-9379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jaffe M, Sesti C, Washington IM, Du L, Dronadula N, Chin MT, Stolz DB, Davis EC, Dichek DA. Transforming growth factor-β signaling in myogenic cells regulates vascular morphogenesis, differentiation, and matrix synthesis. Arterioscl Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:e1–11. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.238410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li W, Li Q, Jiao Y, Qin L, Ali R, Zhou J, Ferruzzi J, Kim RW, Geirsson A, Dietz HC, Offermanns S, Humphrey JD, Tellides G. Tgfbr2 disruption in postnatal smooth muscle impairs aortic wall homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:755–767. doi: 10.1172/JCI69942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ferruzzi J, Bersi MR, Uman S, Yanagisawa H, Humphrey JD. Decreased energy storage, not increased material stiffness, characterizes central artery dysfunction in fibulin-5 deficiency independent of sex. J Biomech Engr. 2015;137 doi: 10.1115/1.4029431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Humphrey JD, Eberth JF, Dye WW, Gleason RL. Fundamental role of axial stress in compensatory adaptations by arteries. J Biomech. 2009;42:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2008.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Loeys BL, Chen J, Neptune ER, et al. A syndrome of altered cardiovascular, craniofacial, neurocognitive and skeletal development caused by mutations in TGFBR1 or TGFBR2. Nat Genet. 2005;37:275–281. doi: 10.1038/ng1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pannu H, Fadulu VT, Chung J, et al. Mutations in transforming growth factor-beta receptor type II cause familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Circulation. 2005;112:513–520. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.537340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Inamoto S, Kwartler CS, Lafont AL, et al. TGFBR2 mutations alter smooth muscle cell phenotype and predispose to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;88:520–529. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhu L, Vranckx R, Khau van Kien P, et al. Mutations in myosin heavy chain 11 cause a syndrome associating thoracic aortic aneurysm/aortic dissection and patent ductus arteriosus. Nat Genet. 2006;38:343–349. doi: 10.1038/ng1721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guo DC, Pannu H, Papke CL, et al. Mutations in smooth muscle α-actin (ACTA2) lead to thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1488–1493. doi: 10.1038/ng.2007.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang L, Guo D-C, Cao J, Gong L, Kamm KE, Regalado E, Li L, Shete S, He W-Q, Zhu M-S, Offermanns S, Gilchrest D, Elefteriades J, Stull JT, Milewicz DM. Mutations in myosin light chain kinase cause familial aortic dissections. Am J Hum Genet. 2010;87:701–707. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.10.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guo DC, Regalado E, Casteel DE, et al. Recurrent gain-of-function mutation in PRKG1 causes thoracic aortic aneurysms and acute aortic dissections. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;93:398–404. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.06.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Milewicz DM, Gou DC, Fadulu VT, Lafont AL, Papke CL, Inamoto S, Kwartler CS, Pannu Genetic basis of thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections: Focus on smooth muscle cell contractile dysfunction. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2008;9:283–302. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.8.080706.092303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Humphrey JD, Tellides G, Schwartz MA, Milewicz DM. Role of mechanotransduction in vascular biology: Focus on thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections. Circ Res. 2015;116:1448–1461. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.304936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Murtada S-I, Ferruzzi J, Yanagisawa H, Humphrey JD. Reduced biaxial contractility in the descending thoracic aorta of fibulin-5 deficient mice. J Biomech Engr. 2016 doi: 10.1115/1.4032938. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Martin KA, Rzucidlo EM, Merenick BL, Fingar DC, Brownn DJ, Wagner RJ, Powell RJ. The mTOR/p70 S6K1 pathway regulates vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation. Am J Physiol. 2004;286:C507–517. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00201.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Humphrey JD. Cardiovascular Solid Mechanics: Cells, Tissues, and Organs. Springer: NY: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dobashi Y, Watanabe Y, Miwa C, Suzuki S, Koyama S. Mammalian target of rapamycin: a central node of complex signaling cascades. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011;4:476–495. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yi T, Cuchara L, Wang Y, et al. Human allograft arterial injury is ameliorated by sirolimus and cyclosporine and correlates with suppression of interferon-gamma. Transplantation. 2006;81:559–566. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000198737.12507.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wu J, Thabet SR, Kirabo A, et al. Inflammation and mechanical stretch promote aortic stiffening in hypertension through activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Circ Res. 2014;114:616–625. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pannu H, Fadulu VT, Papke C, et al. MYH11 mutations result in a distinct vascular pathology driven by insulin-like growth factor 1 and angiotensin II. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:2453–2462. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huang J, Yamashiro Y, Papke C, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme-induced activation of local angiotensin signaling is required for ascending aortic aneurysms in fibulin-4-deficient mice. Sci Trans Med. 2013;5 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005025. 183ra58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Govindarajan G, Eble DM, Lucchesi PA, Samarel AM. Focal adhesion kinase is involved in angiotensin-II mediated protein synthesis in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 2000;87:710–716. doi: 10.1161/01.res.87.8.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bellini C, Wang S, Milewicz DM, Humphrey JD. Mhy11R247C/R247C mutations increase thoracic aortic vulnerability to intramural damage despite a general biomechanical adaptivity. J Biomech. 2015;48:113–121. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2014.10.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lindsay ME, Dietz HC. Lessons on the pathogenesis of aneurysm from heritable conditions. Nature. 2011;473:308–316. doi: 10.1038/nature10145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Humphrey JD, Wilson E. A potential role of smooth muscle tone in early hypertension: A theoretical study. J Biomech. 2003;36:1595–1601. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9290(03)00178-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Doyle JJ, Doyle AJ, Wilson NK, et al. A deleterious gene-by-environment interaction imposed by calcium channel blockers in Marfan syndrome. eLife. 2015;4:e08648. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


