Abstract
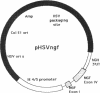
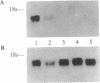
Sympathetic neurons in the superior cervical ganglion (SCG) of adult rats depend on target-derived nerve growth factor (NGF) for maintenance of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) levels and the noradrenergic neurotransmitter system. Axotomy of a SCG results in NGF deprivation, causing a decline in TH activity; continuous local application of NGF can prevent this decline in TH activity. We now report that injection of a defective herpes simplex virus 1 vector that expresses NGF (pHSVngf) into a SCG can prevent the decline in TH activity that follows axotomy. SCG of adult rats were injected with either pHSVngf virus or pNFlac virus, which expresses Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase. Analysis of RNA from pHSVngf-infected SCG indicated that the NGF gene was efficiently transcribed and processed. Furthermore, 4 days after pHSVngf injection animals underwent axotomy of the virus-injected SCG. After another 10 days, animals were sacrificed and both the injected-axotomized and contralateral control ganglia were assayed for TH activity. Axotomy of SCG injected with pNFlac virus produced a 50% decline in TH activity relative to control ganglia (P = 0.02). In contrast, SCG injected with pHSVngf virus did not show a decline in TH activity following axotomy; instead, these ganglia manifested an 18% increase in TH levels relative to control ganglia. These data demonstrate that herpes simplex virus 1 vectors can be used to modify neuronal physiology in vivo; specifically, expression of a critical gene product by neural cells that do not normally produce it has potential applications for gene therapy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apfel S. C., Lipton R. B., Arezzo J. C., Kessler J. A. Nerve growth factor prevents toxic neuropathy in mice. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jan;29(1):87–90. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1525–1534. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothman D. A., Geller A. I., Pardee A. B. Expression of the E. coli Lac Z gene from a defective HSV-1 vector in various human normal, cancer-prone and tumor cells. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 20;258(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81640-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibner M. D., Black I. B. The effect of taget organ removal on the development of sympathetic neurons. Brain Res. 1976 Feb 13;103(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A. T., Margolis T. P., Sedarati F., Stevens J. G., Feldman L. T. A latent, nonpathogenic HSV-1-derived vector stably expresses beta-galactosidase in mouse neurons. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90171-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Selby M. J., Mobley W. C., Weinrich S. L., Hruby D. E., Rutter W. J. Processing and secretion of nerve growth factor: expression in mammalian cells with a vaccinia virus vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2456–2464. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federoff H. J., Grabczyk E., Fishman M. C. Dual regulation of GAP-43 gene expression by nerve growth factor and glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19290–19295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freese A., Geller A. I., Neve R. HSV-1 vector mediated neuronal gene delivery. Strategies for molecular neuroscience and neurology. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 15;40(10):2189–2199. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90711-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Armstrong D. M., Williams L. R., Varon S. Morphological response of axotomized septal neurons to nerve growth factor. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Mar 1;269(1):147–155. doi: 10.1002/cne.902690112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Wictorin K., Fischer W., Williams L. R., Varon S., Bjorklund A. Retrograde cell changes in medial septum and diagonal band following fimbria-fornix transection: quantitative temporal analysis. Neuroscience. 1986 Sep;19(1):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Breakefield X. O. A defective HSV-1 vector expresses Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase in cultured peripheral neurons. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1667–1669. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Freese A. Infection of cultured central nervous system neurons with a defective herpes simplex virus 1 vector results in stable expression of Escherichia coli beta-galactosidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1149–1153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller A. I., Keyomarsi K., Bryan J., Pardee A. B. An efficient deletion mutant packaging system for defective herpes simplex virus vectors: potential applications to human gene therapy and neuronal physiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8950–8954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Otten U., Thoenen H. Biochemical effects of antibodies against nerve growth factor on developing and differentiated sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 9;148(1):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorin P. D., Johnson E. M., Jr Effects of long-term nerve growth factor deprivation on the nervous system of the adult rat: an experimental autoimmune approach. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 29;198(1):27–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90341-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Hartikka J., Knusel B. Function of neurotrophic factors in the adult and aging brain and their possible use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):515–533. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F. Nerve growth factor promotes survival of septal cholinergic neurons after fimbrial transections. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2155–2162. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02155.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellweg R., Hartung H. D. Endogenous levels of nerve growth factor (NGF) are altered in experimental diabetes mellitus: a possible role for NGF in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Jun;26(2):258–267. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A. The effects of axotomy on the development of the rat superior cervical ganglion. Brain Res. 1975 Jun 13;90(2):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer M. M., Barde Y. A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor prevents neuronal death in vivo. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):261–262. doi: 10.1038/331261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn A., Leibrock J., Bailey K., Barde Y. A. Identification and characterization of a novel member of the nerve growth factor/brain-derived neurotrophic factor family. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):339–341. doi: 10.1038/344339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jr, Gorin P. D., Brandeis L. D., Pearson J. Dorsal root ganglion neurons are destroyed by exposure in utero to maternal antibody to nerve growth factor. Science. 1980 Nov 21;210(4472):916–918. doi: 10.1126/science.7192014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Black I. B. The effects of nerve growth factor (NGF) and antiserum to NGF on the development of embryonic sympathetic neurons in vivo. Brain Res. 1980 May 5;189(1):157–168. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Black I. B. The role of axonal transport in the regulation of enzyme activity in sympathetic ganglia of adult rats. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 10;171(3):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)91046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibrock J., Lottspeich F., Hohn A., Hofer M., Hengerer B., Masiakowski P., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):149–152. doi: 10.1038/341149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay R. M., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Placode and neural crest-derived sensory neurons are responsive at early developmental stages to brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Dev Biol. 1985 Dec;112(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. B., Friedmann T., Robertson R. C., Tuszynski M., Wolff J. A., Breakefield X. O., Gage F. H. Grafting genetically modified cells to the damaged brain: restorative effects of NGF expression. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.3201248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Aebersold P., Cornetta K., Kasid A., Morgan R. A., Moen R., Karson E. M., Lotze M. T., Yang J. C., Topalian S. L. Gene transfer into humans--immunotherapy of patients with advanced melanoma, using tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes modified by retroviral gene transduction. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 30;323(9):570–578. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008303230904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Goeddel D. V., Nguyen T., Lewis M., Shih A., Laramee G. R., Nikolics K., Winslow J. W. Primary structure and biological activity of a novel human neurotrophic factor. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):767–773. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90203-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. E., Modert C. W., Yip H. K., Johnson E. M., Jr Retrograde axonal transport of intravenously administered 125I-nerve growth factor in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetes. 1983 Jul;32(7):654–663. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.7.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H. The human growth hormone gene family: nucleotide sequences show recent divergence and predict a new polypeptide hormone. DNA. 1982;1(3):239–249. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1982.1.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Edwards R., Sharp F., Rutter W. J. Mouse nerve growth factor gene: structure and expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3057–3064. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D., Johnson E. M., Jr Neurotrophic molecules. Ann Neurol. 1989 Oct;26(4):489–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöckli K. A., Lottspeich F., Sendtner M., Masiakowski P., Carroll P., Götz R., Lindholm D., Thoenen H. Molecular cloning, expression and regional distribution of rat ciliary neurotrophic factor. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):920–923. doi: 10.1038/342920a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Bandtlow C., Heumann R. The physiological function of nerve growth factor in the central nervous system: comparison with the periphery. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;109:145–178. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Physiology of nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1284–1335. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D., Richter-Landsberg C., Short M. P., Cepko C., Breakefield X. O. Retrovirus-mediated gene transfer of beta-nerve growth factor into mouse pituitary line AtT-20. Mol Biol Med. 1988 Feb;5(1):43–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]