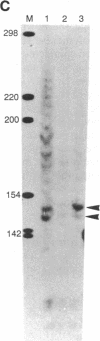
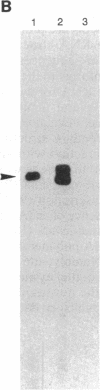
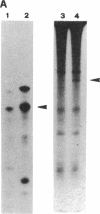
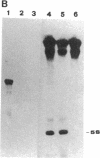
Abstract
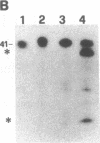
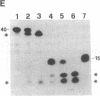
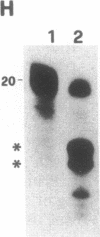
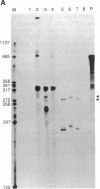
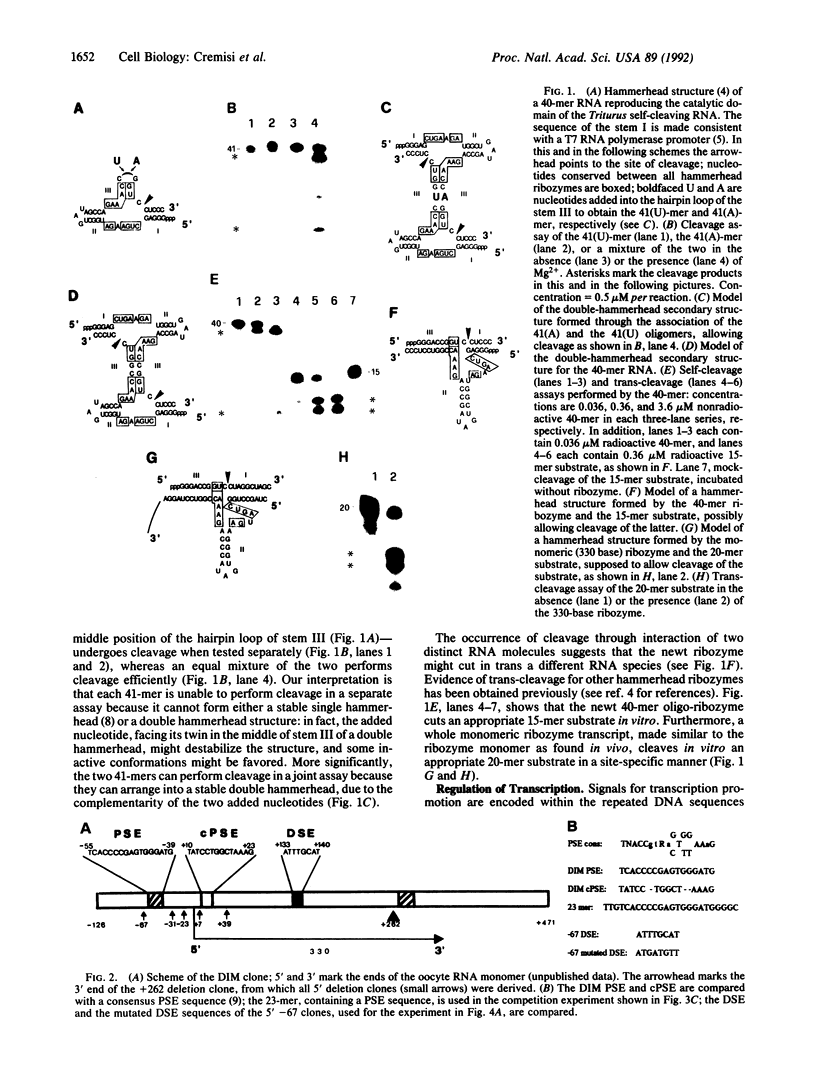
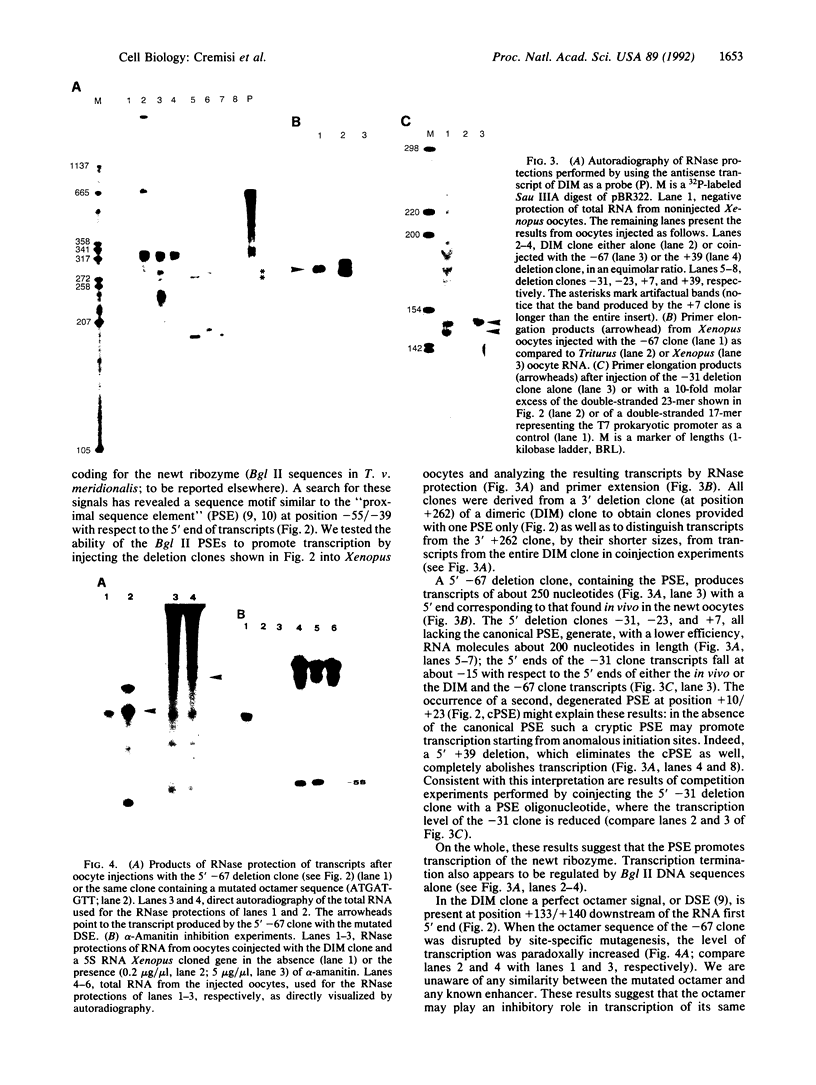
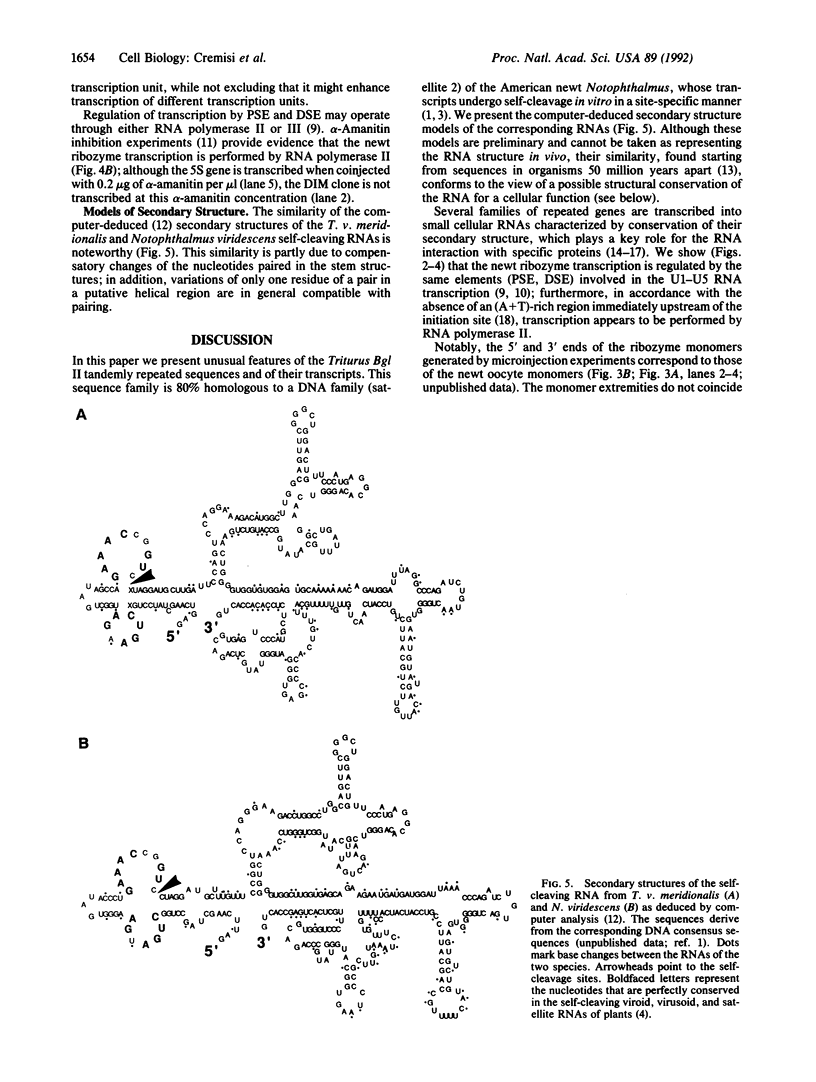
We analyzed the cleavage properties and the transcription regulation of the newt (Triturus vulgaris meridionalis) self-cleaving RNA. In vitro self-cleavage of model oligoribonucleotides occurs within a double hammerhead structure. In addition, an entire ribozyme molecule, as well as its catalytic domain, "trans-cleaves" in vitro appropriate oligoribonucleotide substrates. Signals encoded within the ribozyme DNA sequences regulate the ribozyme transcription, which is RNA polymerase II dependent. Finally, the deduced secondary structure of the self-cleaving RNA appears to be conserved in evolutionarily distant newt species. These features suggest that the newt ribozyme could play some role in the cell, possibly related to its cleavage properties.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burton F. H., Loeb D. D., Voliva C. F., Martin S. L., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Conservation throughout mammalia and extensive protein-encoding capacity of the highly repeated DNA long interspersed sequence one. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. M., Gall J. G. Self-cleaving transcripts of satellite DNA from the newt. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. M., Mahon K. A., Gall J. G. Transcription of a satellite DNA in the newt. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1137–1144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Davies C., Sheldon C. C., Jeffries A. C., Symons R. H. Self-cleaving viroid and newt RNAs may only be active as dimers. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):265–267. doi: 10.1038/334265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Liu J. S., Pace N. R. The secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA, the catalytic element of a ribonucleoprotein enzyme. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen C., Stebbins-Boaz B., Gerbi S. A. Nucleotide sequence determination and secondary structure of Xenopus U3 snRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2127–2148. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Zeller R. Xenopus laevis U2 snRNA genes: tandemly repeated transcription units sharing 5' and 3' flanking homology with other RNA polymerase II transcribed genes. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1883–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Groebe D. R., Witherell G. W., Uhlenbeck O. C. Oligoribonucleotide synthesis using T7 RNA polymerase and synthetic DNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8783–8798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Moorefield B., Pieler T. Common mechanisms of promoter recognition by RNA polymerases II and III. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon C. C., Symons R. H. RNA stem stability in the formation of a self-cleaving hammerhead structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5665–5677. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Self-cleavage of RNA in the replication of small pathogens of plants and animals. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Nov;14(11):445–450. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley J. M., Macgregor H. C., Nardi I., Andrews C., Erba H. P. Cytological evidence of transcription of highly repeated DNA sequences during the lampbrush stage in Triturus cristatus carnifex. Chromosoma. 1980;80(3):289–307. doi: 10.1007/BF00292686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]