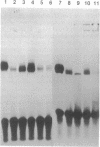
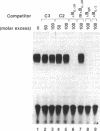
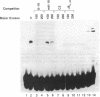
Abstract
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is an important immunoregulatory protein that is expressed usually only in large granular lymphocytes and T cells. The gene encoding IFN-gamma was previously found to contain an intronic enhancer element that was not tissue-specific in its activity, despite the restricted expression of the intact IFN-gamma-encoding gene. Using nuclear extracts from the human T-cell line Jurkat, we have now identified two protein-binding regions in this intronic enhancer element. One of the protected regions has strong partial identify to the NF-kappa B site present in the promoter region of the human interleukin 2-encoding gene. Based on this observation and recent reports of the interaction of the c-rel protooncogene product (c-Rel) with NF-kappa B sites, we determined whether c-Rel could interact with the intronic enhancer element in the human IFN-gamma genomic DNA. Most surprisingly, gel-shift analysis, using c-Rel expressed in Escherichia coli established that c-Rel binds specifically to the IFN-gamma intronic DNA but not to the interleukin 2-like NF-kappa B site. Additional studies with antibodies prepared against c-Rel peptides verified specificity of the interaction of c-Rel with this binding site. In addition, using an affinity-purified p50 subunit of the NF-kappa B complex, we observed that the p50 protein did not bind to this additional c-Rel-binding site. Furthermore, nucleotide sequence analysis of this DNA region revealed a strong similarity of the additional c-Rel-binding site to a previously identified IFN-stimulable response element. These data show that c-Rel can interact with DNA regions distinct from that recognized by NF-kappa B and may, in fact, be involved in transcriptional regulation of the IFN-stimulable genes via the IFN-stimulable response element.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrill A. M., Reid L. E., Gilbert C. S., Gewert D. R., Porter A. C., Lewin A. R., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Differential response of the human 6-16 and 9-27 genes to alpha and gamma interferons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):591–598. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Nelson F. B., Reinherz E. L., Diamond D. J. The human interferon-gamma gene contains an inducible promoter that can be transactivated by tax I and II. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Aug;21(8):1879–1885. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Mittereder N., Rice N. R. A human rel proto-oncogene cDNA containing an Alu fragment as a potential coding exon. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Transcriptional induction of the murine c-rel gene with serum and phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5239–5243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Morley K. L., Hoekstra M. F., Hunter T., Verma I. M. The mouse c-rel protein has an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal transcriptional transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5473–5485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia J. C., Wedrychowicz T., Young H. A., Hardy K. J. A model of human cytokine regulation based on transfection of gamma interferon gene fragments directly into isolated peripheral blood T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):661–664. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarone V. C., Chrivia J., Hardy K. J., Young H. A. Identification of enhancer-like elements in human IFN-gamma genomic DNA. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):725–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Belin D., Vassalli J. D., de Kossodo S., Vassalli P. Gamma interferon enhances macrophage transcription of the tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin 1, and urokinase genes, which are controlled by short-lived repressors. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2113–2118. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn P., DaSilva L., Martarano L., Derse D. Equine infectious anemia virus tat: insights into the structure, function, and evolution of lentivirus trans-activator proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1616–1624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1616-1624.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. S., Bond B. L., Parslow T. G. Estrogen regulates the IFN-gamma promoter. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4362–4367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R. J., Gerondakis S. Murine c-rel transcription is rapidly induced in T-cells and fibroblasts by mitogenic agents and the phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Aug;1(8):345–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R. J., Gerondakis S. The murine c-rel proto-oncogene encodes two mRNAs the expression of which is modulated by lymphoid stimuli. Oncogene Res. 1990;5(4):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L. Regulation of cellular gene expression by interferon-gamma: involvement of multiple pathways. Int J Cell Cloning. 1990 Jan;8 (Suppl 1):92–102. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530080709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Temin H. M. The v-rel oncogene encodes a cell-specific transcriptional activator of certain promoters. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Temin H. M. Transactivation of gene expression by nuclear and cytoplasmic rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4323–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. J., Manger B., Newton M., Stobo J. D. Molecular events involved in regulating human interferon-gamma gene expression during T cell activation. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2353–2358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. J., Peterlin B. M., Atchison R. E., Stobo J. D. Regulation of expression of the human interferon gamma gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8173–8177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos B., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Siekevitz M., Greene W. C. Kappa B-specific DNA binding proteins: role in the regulation of human interleukin-2 gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):457–460. doi: 10.1126/science.2497518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara T., Hooks J. J., Dougherty S. F., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 2-mediated immune interferon (IFN-gamma) production by human T cells and T cell subsets. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1784–1789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. The control of interferon-inducible gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 22;285(2):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80802-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice N. R., Copeland T. D., Simek S., Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. Detection and characterization of the protein encoded by the v-rel oncogene. Virology. 1986 Mar;149(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., Gilmore T. D. vRel is an inactive member of the Rel family of transcriptional activating proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3122–3130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3122-3130.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Poteat H., Tan T. H., Kawakami K., Roeder R., Haseltine W., Rosen C. A. Cellular transcription factors and regulation of IL-2 receptor gene expression by HTLV-I tax gene product. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.2838905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of multiple nuclear factors that bind to the TAX-inducible enhancer within the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1733–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Hardy K. J. Interferon-gamma: producer cells, activation stimuli, and molecular genetic regulation. Pharmacol Ther. 1990;45(1):137–151. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90012-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Ortaldo J. R. One-signal requirement for interferon-gamma production by human large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]