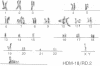Abstract
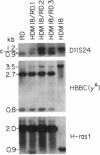
The identification of acquired homozygosity in human cancers implies locations of tumor suppressor genes without providing functional evidence. The localization of a defect in embryonal rhabdomyosarcomas to chromosomal region 11p15 provides one such example. In this report, we show that transfer of a normal human chromosome 11 into an embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cell line elicited a dramatic loss of the proliferative capacity of the transferrants. Indeed, the majority of the viable microcell hybrids had either eliminated genetic information on the short arm of the transferred chromosome 11 or increased the copy number of the rhabdomyosarcoma-derived chromosomes 11. Cells that possessed only the long arm of chromosome 11 also demonstrated a decreased growth rate. In contrast, all microcell hybrids retained the ability to form tumors upon inoculation into animals. These functional data support molecular studies indicating loss of genetic information on chromosome 11p15 during the development of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. In addition, our studies demonstrate the existence of a second gene on the long arm, previously unrecognized by molecular analyses, which negatively regulates the growth of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Boehm C. D., Giardina P. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr Nonrandom association of polymorphic restriction sites in the beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict W. F., Weissman B. E., Mark C., Stanbridge E. J. Tumorigenicity of human HT1080 fibrosarcoma X normal fibroblast hybrids: chromosome dosage dependency. Cancer Res. 1984 Aug;44(8):3471–3479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonetta L., Kuehn S. E., Huang A., Law D. J., Kalikin L. M., Koi M., Reeve A. E., Brownstein B. H., Yeger H., Williams B. R. Wilms tumor locus on 11p13 defined by multiple CpG island-associated transcripts. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):994–997. doi: 10.1126/science.2173146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Call K. M., Glaser T., Ito C. Y., Buckler A. J., Pelletier J., Haber D. A., Rose E. A., Kral A., Yeger H., Lewis W. H. Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at the human chromosome 11 Wilms' tumor locus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):509–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90601-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. L., Chen Y. M., Bookstein R., Lee W. H. Genetic mechanisms of tumor suppression by the human p53 gene. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1576–1580. doi: 10.1126/science.2274789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diller L., Kassel J., Nelson C. E., Gryka M. A., Litwak G., Gebhardt M., Bressac B., Ozturk M., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5772–5781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ege T., Ringertz N. R., Hamberg H., Sidebottom E. Preparation of microcells. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;15:339–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier R. E., Ruddle F. H. Microcell-mediated transfer of murine chromosomes into mouse, Chinese hamster, and human somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):319–323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Qian J., Hinrichs S. H., Benedict W. F. Structural evidence for the authenticity of the human retinoblastoma gene. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1657–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.2885916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessler M., Poustka A., Cavenee W., Neve R. L., Orkin S. H., Bruns G. A. Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):774–778. doi: 10.1038/343774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. F., Cavenee W. K. Genetics of cancer predisposition. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5518–5527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hamilton S. R., Hedge P., Markham A. Identification of a gene located at chromosome 5q21 that is mutated in colorectal cancers. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1366–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.1848370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koi M., Morita H., Yamada H., Satoh H., Barrett J. C., Oshimura M. Normal human chromosome 11 suppresses tumorigenicity of human cervical tumor cell line SiHa. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(1):12–21. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koi M., Shimizu M., Morita H., Yamada H., Oshimura M. Construction of mouse A9 clones containing a single human chromosome tagged with neomycin-resistance gene via microcell fusion. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1989 May;80(5):413–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1989.tb02329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koufos A., Grundy P., Morgan K., Aleck K. A., Hadro T., Lampkin B. C., Kalbakji A., Cavenee W. K. Familial Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome and a second Wilms tumor locus both map to 11p15.5. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):711–719. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koufos A., Hansen M. F., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Lampkin B. C., Cavenee W. K. Loss of heterozygosity in three embryonal tumours suggests a common pathogenetic mechanism. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):330–334. doi: 10.1038/316330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koufos A., Hansen M. F., Lampkin B. C., Workman M. L., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Cavenee W. K. Loss of alleles at loci on human chromosome 11 during genesis of Wilms' tumour. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):170–172. doi: 10.1038/309170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugoh H. M., Hashiba H., Shimizu M., Oshimura M. Suggestive evidence for functionally distinct, tumor-suppressor genes on chromosomes 1 and 11 for a human fibrosarcoma cell line, HT1080. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1637–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugo T. G., Handelin B., Killary A. M., Housman D. E., Fournier R. E. Isolation of microcell hybrid clones containing retroviral vector insertions into specific human chromosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2814–2820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Melnyk J., Finkelstein J. Z., Adams E. C., Jr, Gardner M. B. Cultivation in vitro of cells derived from a human rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer. 1969 Sep;24(3):520–526. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196909)24:3<520::aid-cncr2820240313>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen T., Cavenee W. K. Suppressors of the malignant phenotype. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Apr;1(4):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra B. C., Srivatsan E. S. Localization of HeLa cell tumor-suppressor gene to the long arm of chromosome II. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):565–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Kitayama H., Matsuzaki T., Sugimoto Y., Okayama H., Bassin R. H., Ikawa Y. Detection of genes with a potential for suppressing the transformed phenotype associated with activated ras genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):162–166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. Mechanisms of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2203–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Genetic analysis of indefinite division in human cells: identification of four complementation groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6042–6046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve A. E., Sih S. A., Raizis A. M., Feinberg A. P. Loss of allelic heterozygosity at a second locus on chromosome 11 in sporadic Wilms' tumor cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1799–1803. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi V. M., Sujansky E., Smith A. C., Francke U. Chromosomal imbalance in the Aniridia-Wilms' tumor association: 11p interstitial deletion. Pediatrics. 1978 Apr;61(4):604–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager R. Tumor suppressor genes: the puzzle and the promise. Science. 1989 Dec 15;246(4936):1406–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.2574499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrable H. J., Witte D. P., Lampkin B. C., Cavenee W. K. Chromosomal localization of the human rhabdomyosarcoma locus by mitotic recombination mapping. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):645–647. doi: 10.1038/329645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrable H., Witte D., Shimada H., Seemayer T., Sheng W. W., Soukup S., Koufos A., Houghton P., Lampkin B., Cavenee W. Molecular differential pathology of rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1989 Sep;1(1):23–35. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu M., Yokota J., Mori N., Shuin T., Shinoda M., Terada M., Oshimura M. Introduction of normal chromosome 3p modulates the tumorigenicity of a human renal cell carcinoma cell line YCR. Oncogene. 1990 Feb;5(2):185–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo-Avila C., Gooch W. M., 3rd Neoplasms associated with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Perspect Pediatr Pathol. 1976;3:255–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S., Zou Z. Q., Pirollo K., Blattner W., Chang E. H. Germ-line transmission of a mutated p53 gene in a cancer-prone family with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):747–749. doi: 10.1038/348747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J. Mycoplasma detection-an obligation to scientific accuracy. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):563–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Stanbridge E. J., McBride H. L., Meese E. U., Casey G., Araujo D. E., Witkowski C. M., Nagle R. B. Tumorigenicity in human melanoma cell lines controlled by introduction of human chromosome 6. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.2300817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viskochil D., Buchberg A. M., Xu G., Cawthon R. M., Stevens J., Wolff R. K., Culver M., Carey J. C., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90252-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman B. E., Saxon P. J., Pasquale S. R., Jones G. R., Geiser A. G., Stanbridge E. J. Introduction of a normal human chromosome 11 into a Wilms' tumor cell line controls its tumorigenic expression. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):175–180. doi: 10.1126/science.3031816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]