Abstract
The inhibitory glycine receptor (GlyR) is a member of the ligand-gated ion channel receptor superfamily. Glycine activation of the receptor is antagonized by the convulsant alkaloid strychnine. Using in vitro mutagenesis and functional analysis of the cDNA encoding the alpha 1 subunit of the human GlyR, we have identified several amino acid residues that form the strychnine-binding site. These residues were identified by transient expression of mutated cDNAs in mammalian (293) cells and examination of resultant [3H]strychnine binding, glycine displacement of [3H]strychnine, and electrophysiological responses to the application of glycine and strychnine. This mutational analysis revealed that residues from two separate domains within the alpha 1 subunit form the binding site for the antagonist strychnine. The first domain includes the amino acid residues Gly-160 and Tyr-161, and the second domain includes the residues Lys-200 and Tyr-202. These results, combined with analyses of other ligand-gated ion channel receptors, suggest a conserved tertiary structure and a common mechanism for antagonism in this receptor superfamily.
Full text
PDF
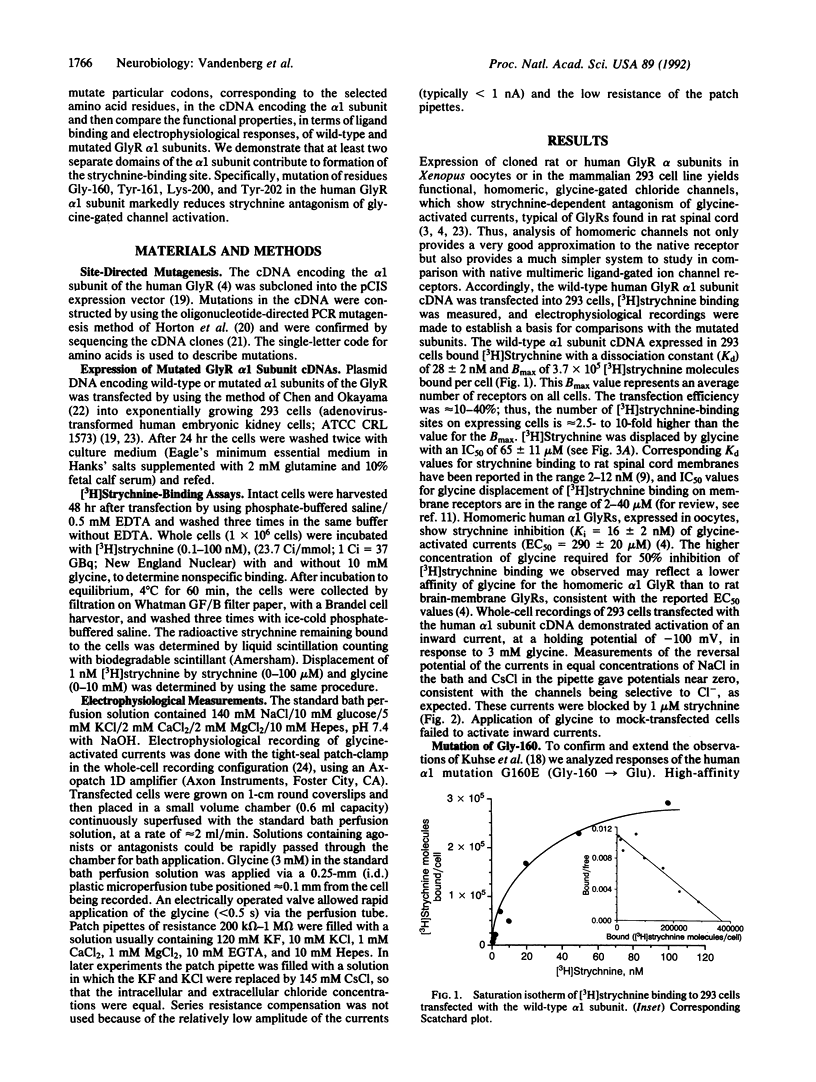
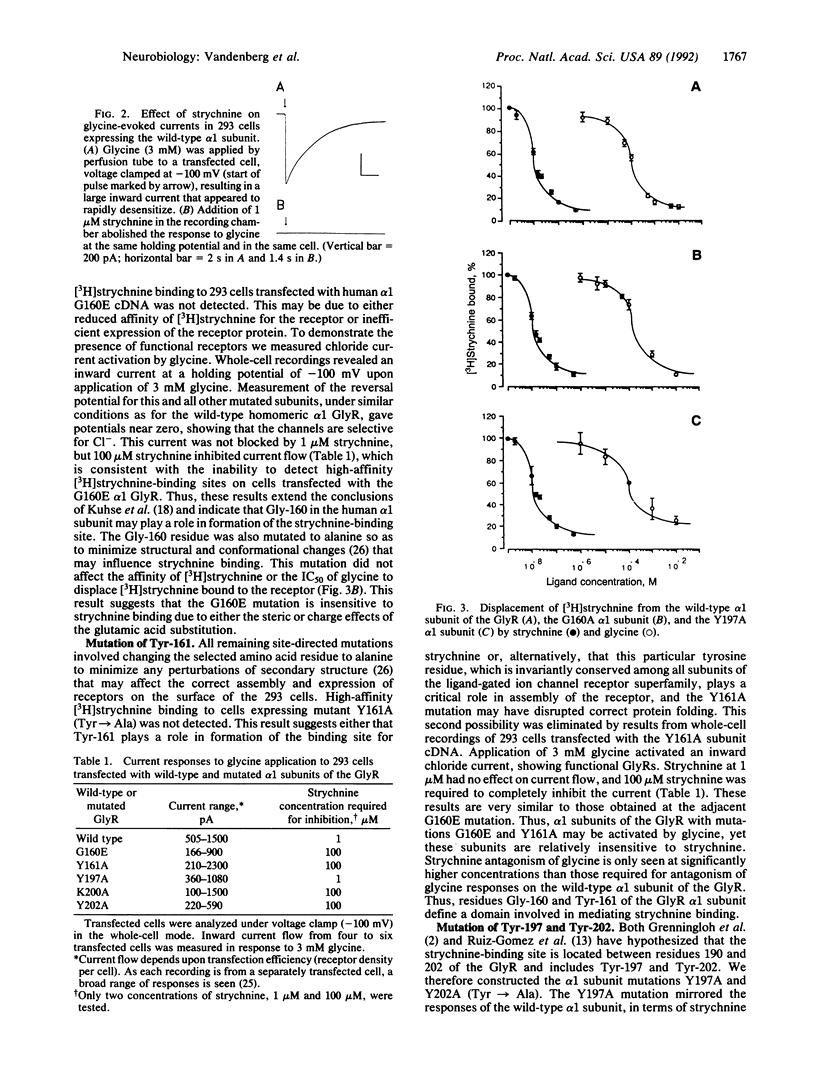


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker C. M., Hoch W., Betz H. Glycine receptor heterogeneity in rat spinal cord during postnatal development. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3717–3726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03255.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz H. Homology and analogy in transmembrane channel design: lessons from synaptic membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 17;29(15):3591–3599. doi: 10.1021/bi00467a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1081–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.2471267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A., Johnston I. H. The hyperpolarization of spinal motoneurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;5(3):235–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00238666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M., Giraudat J., Kotzyba-Hibert F., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Chang J. Y., Lazure C., Chrétien M., Changeux J. P. Amino acids of the Torpedo marmorata acetylcholine receptor alpha subunit labeled by a photoaffinity ligand for the acetylcholine binding site. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2346–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Revah F., Black D., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Changeux J. P. Identification of a novel amino acid alpha-tyrosine 93 within the cholinergic ligands-binding sites of the acetylcholine receptor by photoaffinity labeling. Additional evidence for a three-loop model of the cholinergic ligands-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10430–10437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Revah F., Bouet F., Ménez A., Goeldner M., Hirth C., Changeux J. P. Allosteric transitions of the acetylcholine receptor probed at the amino acid level with a photolabile cholinergic ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5051–5055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Pfeiffer F., Betz H. Photoaffinity-labelling of the glycine receptor of rat spinal cord. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Gundelfinger E., Schmitt B., Betz H., Darlison M. G., Barnard E. A., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H. Glycine vs GABA receptors. Nature. 1987 Nov 5;330(6143):25–26. doi: 10.1038/330025b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Pribilla I., Prior P., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Taleb O., Betz H. Cloning and expression of the 58 kd beta subunit of the inhibitory glycine receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90149-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Schmieden V., Schofield P. R., Seeburg P. H., Siddique T., Mohandas T. K., Becker C. M., Betz H. Alpha subunit variants of the human glycine receptor: primary structures, functional expression and chromosomal localization of the corresponding genes. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):771–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhse J., Schmieden V., Betz H. A single amino acid exchange alters the pharmacology of neonatal rat glycine receptor subunit. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):867–873. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90346-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marvizón J. C., García Calvo M., Vázquez J., Mayor F., Jr, Ruíz Gómez A., Valdiviesco F., Benavides J. Activation and inhibition of 3H-strychnine binding to the glycine receptor by Eccles' anions: modulatory effects of cations. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;30(6):598–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H. gamma-Aminobutyric acid type A receptor point mutation increases the affinity of compounds for the benzodiazepine site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1421–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Sontheimer H., Gorman C. M., Kettenmann H., Seeburg P. H., Schofield P. R. Transient expression shows ligand gating and allosteric potentiation of GABAA receptor subunits. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1306–1308. doi: 10.1126/science.2848320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz Gómez A., Fernández-Shaw C., Valdivieso F., Mayor F., Jr Chemical modification of the glycine receptor with fluorescein isothiocyanate specifically affects the interaction of glycine with its binding site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 14;160(1):374–381. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91666-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Gómez A., Morato E., García-Calvo M., Valdivieso F., Mayor F., Jr Localization of the strychnine binding site on the 48-kilodalton subunit of the glycine receptor. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 31;29(30):7033–7040. doi: 10.1021/bi00482a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmieden V., Grenningloh G., Schofield P. R., Betz H. Functional expression in Xenopus oocytes of the strychnine binding 48 kd subunit of the glycine receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):695–700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontheimer H., Becker C. M., Pritchett D. B., Schofield P. R., Grenningloh G., Kettenmann H., Betz H., Seeburg P. H. Functional chloride channels by mammalian cell expression of rat glycine receptor subunit. Neuron. 1989 May;2(5):1491–1497. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Snyder S. H. Strychnine binding associated with glycine receptors of the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2832–2836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



