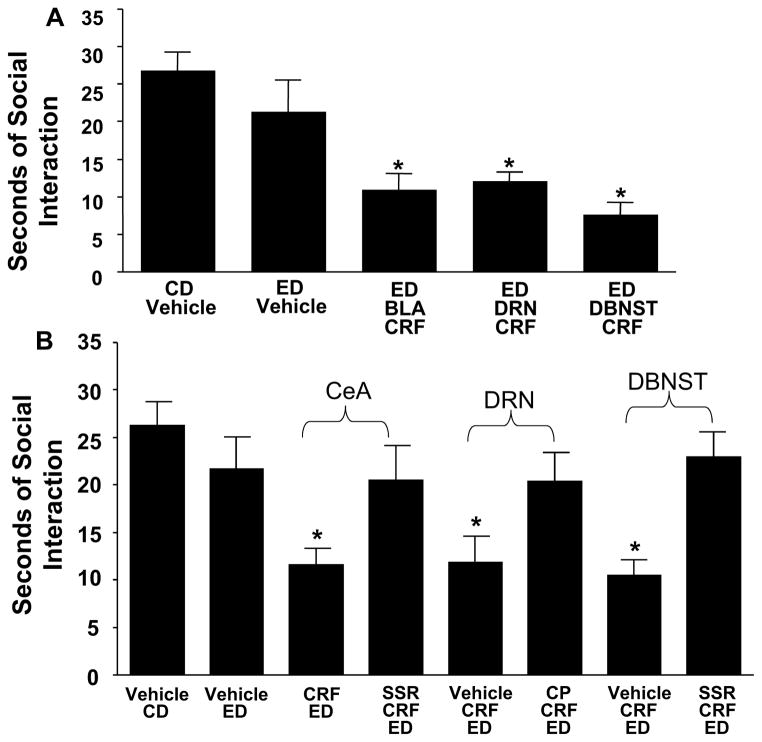
Fig. 4.
Fig. 4A. Effects of repeated corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) into the basolateral amygdala (BLA), dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), and dorsolateral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (d-BNST) before exposure to chronic alcohol liquid diet reduces social interaction (SI) behaviors during withdrawal. CRF (0.5 μg/0.5 μL) was microinjected twice, once per week, into the BLA, DRN, or d-BNST before exposure to 5 days of 4.5% ethanol (alcohol) liquid diet (ED). In the Control Diet (CD)-vehicle and ED-vehicle groups, vehicle was administered into each of the brain sites (n = 3–4 for each site), and data for these vehicle injections were combined because a significant difference in SI across sites was not observed across these groups. No significant difference was found for the SI between the CD-vehicle and ED-vehicle groups (p > 0.05). A group that received CRF and was on CD only was not included for each of the present sites because previous data demonstrated that intracerebroventricular administration of CRF to rats that received CD sensitize SI deficits (Overstreet et al., 2004), and the repeated CRF in the CeA of control diet-treated animals likewise did not sensitize withdrawal-induced anxiety. SI was measured 5 to 6 h after the ED removal. *Significantly different from CD-vehicle and ED-vehicle [F(4,42) = 9.227, p < 0.001].
Fig. 4B. CRF-1 receptor antagonist blockade of CRF-sensitized alcohol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior when CRF is injected into the central amygdala, dorsal raphe, or dorsolateral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. A 10 mg/kg dose of the CRF-1 receptor antagonist, SSR125543 (SSR), was administered i.p. 15 min before the microinjection of CRF (0.5 μg) into either the central amygdala or the d-BNST followed by the 5 days of ethanol (alcohol) diet. Another CRF-1 receptor antagonist CP154526 (CP; 10 mg/kg i.p.) was administered 15 min before each of the CRF (0.5 μg) microinjections into the dorsal raphe. CRF in these brain sites sensitized social interaction deficits (reduced SI), and this effect was prevented by the CRF-1 receptor antagonists. SI was measured 5 to 6 h after the removal of ED. In the CD-vehicle group and the ED-vehicle group, vehicle was administered into each of the brain sites (n = 4–6 for each site), and data were combined because a significant change across sites was not observed. No significant difference in SI (p > 0.05) was observed when the CD-vehicle group was compared with the ED-vehicle group. *p < 0.01 compared with vehicle CD- and vehicle ED-treated groups and the groups that received the SSR125543 systemically [F(7,76) = 3.005, p < 0.01]. Adapted from Huang et al., 2010.