Abstract
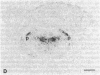
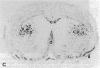
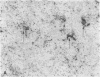
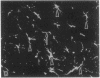
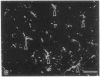
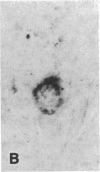
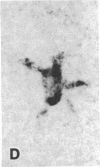
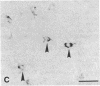
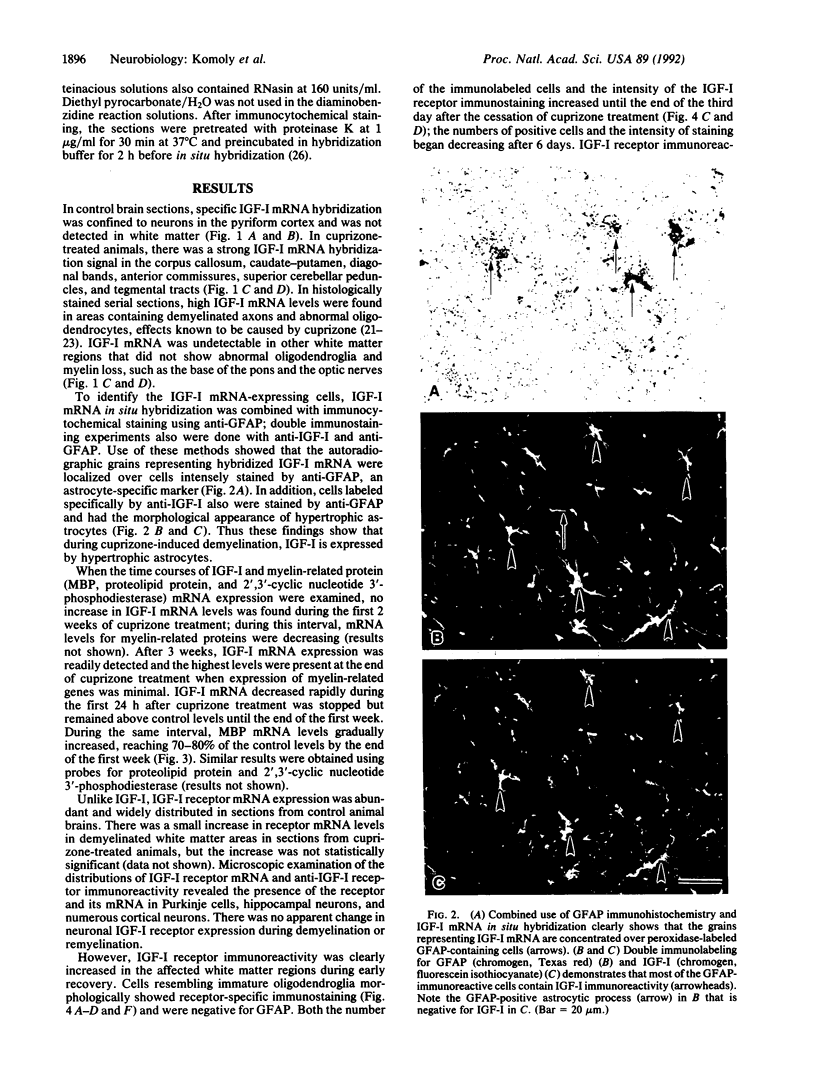
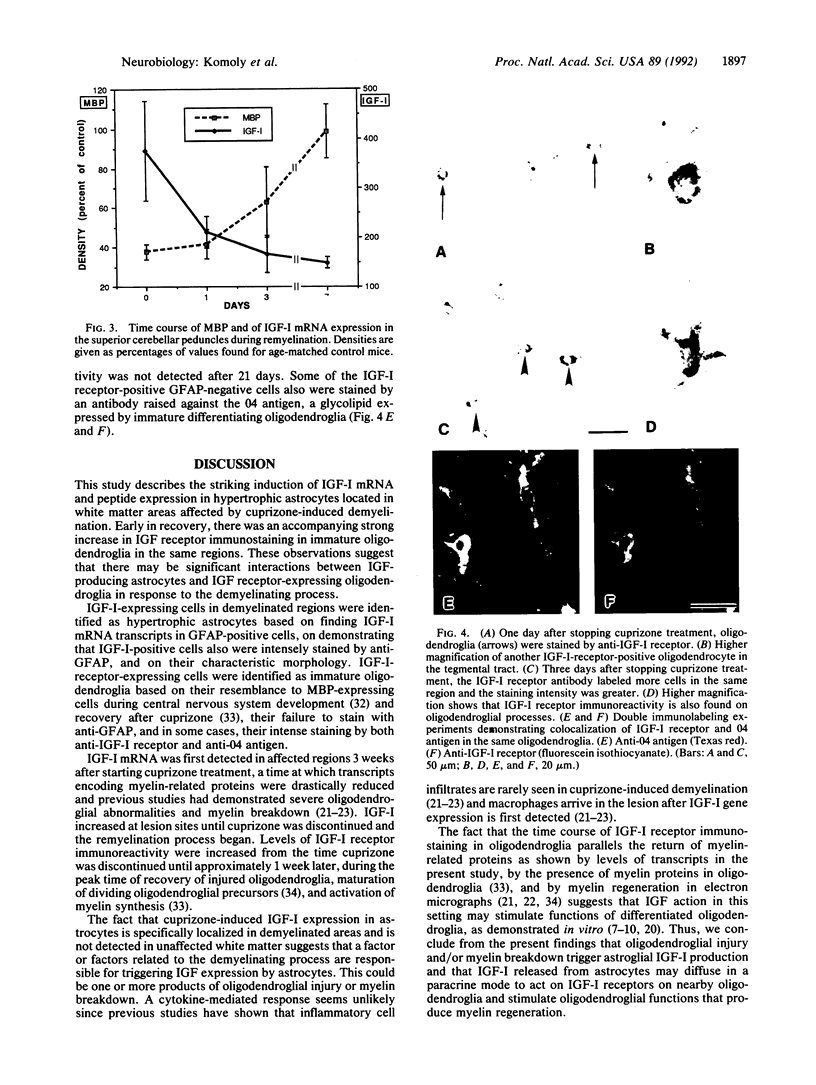
To investigate insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-I receptor gene expression during experimental demyelination and myelin regeneration, young mice were fed cuprizone (( bis(cyclohexanone) oxaldihydrazone )). This copper-chelating agent produces demyelination in the corpus callosum and superior cerebellar peduncles, and when treatment is stopped, there is rapid remyelination. At intervals during cuprizone treatment and recovery, brain sections were hybridized with specific probes and immunostained with antibodies to determine the localization and relative amounts of IGF-I and IGF-I receptor mRNAs and peptides. In untreated littermates, IGF-I and IGF-I receptor mRNAs and peptides were not detected in white matter. In cuprizone-treated mice, high levels of both IGF-I mRNA and peptide were expressed by astrocytes in areas of myelin breakdown. Astrocyte IGF-I expression decreased rapidly during recovery and oligodendroglial expression of myelin-related genes increased. In severely demyelinated areas, immature oligodendroglia exhibited a transient increase in IGF-I receptor mRNA and peptide immunoreactivity during early recovery. This highly specific pattern of IGF-I induction in astrocytes during demyelination and the expression of the IGF-I receptor in regenerating oligodendrocytes during recovery suggest that IGF-I functions in the regulation of oligodendrocyte and myelin metabolism in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizenman Y., de Vellis J. Brain neurons develop in a serum and glial free environment: effects of transferrin, insulin, insulin-like growth factor-I and thyroid hormone on neuronal survival, growth and differentiation. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 17;406(1-2):32–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90766-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almazan G., Honegger P., Matthieu J. M., Guentert-Lauber B. Epidermal growth factor and bovine growth hormone stimulate differentiation and myelination of brain cell aggregates in culture. Brain Res. 1985 Aug;353(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90214-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. C., Harvath L., Dubois-Dalcq M. E. Type 1 astrocytes and oligodendrocyte-type 2 astrocyte glial progenitors migrate toward distinct molecules. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Nov;27(3):400–407. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer-le Lievre C., Ståhlbom P. A., Sara V. R. Expression of IGF-I and -II mRNA in the brain and craniofacial region of the rat fetus. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):105–115. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. A., Shen-Orr Z., Lowe W. L., Jr, Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor I mRNA levels are developmentally regulated in specific regions of the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Apr;10(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker D. A., Ludwin S. K. Blood-brain barrier permeability during Cuprizone-induced demyelination. Implications for the pathogenesis of immune-mediated demyelinating diseases. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Apr;78(2):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Van Evercooren A., Olichon-Berthe C., Kowalski A., Visciano G., Van Obberghen E. Expression of IGF-I and insulin receptor genes in the rat central nervous system: a developmental, regional, and cellular analysis. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Feb;28(2):244–253. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490280212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore W. F. Observations on oligodendrocyte degeneration, the resolution of status spongiosus and remyelination in cuprizone intoxication in mice. J Neurocytol. 1972 Dec;1(4):413–426. doi: 10.1007/BF01102943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A. Transient IGF-I gene expression during the maturation of functionally related central projection neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3442–3455. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A., Werner H., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Cellular pattern of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and type I IGF receptor gene expression in early organogenesis: comparison with IGF-II gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1386–1398. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-9-1386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroni P., Grandes P. Nerve sprouting in innervated adult skeletal muscle induced by exposure to elevated levels of insulin-like growth factors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1307–1317. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene structures, serum, and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 1989 Feb;10(1):68–91. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-1-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco-Bloom E., Black I. B. Insulin growth factors regulate the mitotic cycle in cultured rat sympathetic neuroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4066–4070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factors I and II. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 5;190(3):445–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoly S., Jeyasingham M. D., Pratt O. E., Lantos P. L. Decrease in oligodendrocyte carbonic anhydrase activity preceding myelin degeneration in cuprizone induced demyelination. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Jun;79(1-2):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90268-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoly S., Liu Y., Webster H. D., Chan K. F. Distribution of protein kinase C isozymes in rat optic nerves. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Jul;29(3):379–389. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490290313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennard P. R. Image analysis for all. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):103–104. doi: 10.1038/347103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwin S. K. An autoradiographic study of cellular proliferation in remyelination of the central nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jun;95(3):683–696. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwin S. K. Central nervous system demyelination and remyelination in the mouse: an ultrastructural study of cuprizone toxicity. Lab Invest. 1978 Dec;39(6):597–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwin S. K., Sternberger N. H. An immunohistochemical study of myelin proteins during remyelination in the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;63(3):240–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00685250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Hynes M. A., Simmons J. G., Jansen M., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-II mRNAs in rat fetal and adult tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14539–14544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Hammer R. E., Behringer R. R., D'Ercole A. J., Bell G. I., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Growth enhancement of transgenic mice expressing human insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1988 Dec;123(6):2827–2833. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-6-2827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMorris F. A., Dubois-Dalcq M. Insulin-like growth factor I promotes cell proliferation and oligodendroglial commitment in rat glial progenitor cells developing in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Oct-Dec;21(2-4):199–209. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490210212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMorris F. A., Smith T. M., DeSalvo S., Furlanetto R. W. Insulin-like growth factor I/somatomedin C: a potent inducer of oligodendrocyte development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):822–826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Glial cell diversification in the rat optic nerve. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1450–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.2648568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. The nature and regulation of the receptors for insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:425–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Rechler M. M., Ishii D. N. Effects of insulin, insulin-like growth factor-II, and nerve growth factor on neurite formation and survival in cultured sympathetic and sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1211–1219. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01211.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Burgess S. K., Milbrandt J. D., Krause J. E. Differential expression of insulin-like growth factor genes in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):265–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saneto R. P., Low K. G., Melner M. H., de Vellis J. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor I and other epigenetic modulators of myelin basic protein expression in isolated oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Oct-Dec;21(2-4):210–219. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490210213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger N. H., Itoyama Y., Kies M. W., Webster H. D. Myelin basic protein demonstrated immunocytochemically in oligodendroglia prior to myelin sheath formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2521–2524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Mezey E., Siegel R. E. Vasopressin and oxytocin mRNAs in adrenalectomized and Brattleboro rats: analysis by quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry. Brain Res. 1986 Dec;387(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ferra F., Engh H., Hudson L., Kamholz J., Puckett C., Molineaux S., Lazzarini R. A. Alternative splicing accounts for the four forms of myelin basic protein. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Pal R. H., Koper J. W., van Golde L. M., Lopes-Cardozo M. Effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) on oligodendrocyte-enriched glial cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Apr;19(4):483–490. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490190412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]