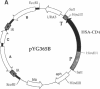
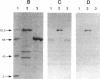
Abstract
Due to its remarkably long half-life, together with its wide in vivo distribution and its lack of enzymatic or immunological functions, human serum albumin (HSA) represents an optimal carrier for therapeutic peptides/proteins aimed at interacting with cellular or molecular components of the vascular and interstitial compartments. As an example, we designed a genetically engineered HSA-CD4 hybrid aimed at specifically blocking the entry of the human immunodeficiency virus into CD4+ cells. In contrast with CD4, HSA-CD4 is correctly processed and efficiently secreted by Kluyveromyces yeasts. In addition, its CD4 moiety exhibits binding and antiviral in vitro properties similar to those of soluble CD4. Finally, the elimination half-life of HSA-CD4 in a rabbit experimental model is comparable to that of control HSA and 140-fold higher than that of soluble CD4. These results indicate that the genetic fusion of bioactive peptides to HSA is a plausible approach toward the design and recovery of secreted therapeutic HSA derivatives with appropriate pharmacokinetic properties.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV infection. Lancet. 1988 Jun 4;1(8597):1285–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV infection. Lancet. 1988 Jun 4;1(8597):1285–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthos J., Deen K. C., Chaikin M. A., Fornwald J. A., Sathe G., Sattentau Q. J., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., McDougal J. S., Pietropaolo C. Identification of the residues in human CD4 critical for the binding of HIV. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90922-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Chaudhary V. K., Clouse K. A., Jaraquemada D., Nicholas J. A., Rubino K. L., Fitzgerald D. J., Pastan I., Moss B. Recombinant CD4-Pseudomonas exotoxin hybrid protein displays HIV-specific cytotoxicity without affecting MHC class II-dependent functions. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Jun;6(6):795–804. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrn R. A., Mordenti J., Lucas C., Smith D., Marsters S. A., Johnson J. S., Cossum P., Chamow S. M., Wurm F. M., Gregory T. Biological properties of a CD4 immunoadhesin. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):667–670. doi: 10.1038/344667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chamow S. M., Mordenti J., Marsters S. A., Gregory T., Mitsuya H., Byrn R. A., Lucas C., Wurm F. M., Groopman J. E. Designing CD4 immunoadhesins for AIDS therapy. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):525–531. doi: 10.1038/337525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chams V., Jouault T., Fenouillet E., Gluckman J. C., Klatzmann D. Detection of anti-CD4 autoantibodies in the sera of HIV-infected patients using recombinant soluble CD4 molecules. AIDS. 1988 Oct;2(5):353–361. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198810000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. J., Bianchi M. M., Suda K., Fukuhara H. The host range of the pKD1-derived plasmids in yeast. Curr Genet. 1989 Aug;16(2):95–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00393401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. J., Saliola M., Falcone C., Bianchi M. M., Fukuhara H. Sequence organization of the circular plasmid pKD1 from the yeast Kluyveromyces drosophilarum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4471–4481. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar E. S., Li X. L., Moudgil T., Ho D. D. High concentrations of recombinant soluble CD4 are required to neutralize primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6574–6578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcone C., Saliola M., Chen X. J., Frontali L., Fukuhara H. Analysis of a 1.6-micron circular plasmid from the yeast Kluyveromyces drosophilarum: structure and molecular dimorphism. Plasmid. 1986 May;15(3):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90044-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleer R., Yeh P., Amellal N., Maury I., Fournier A., Bacchetta F., Baduel P., Jung G., L'Hôte H., Becquart J. Stable multicopy vectors for high-level secretion of recombinant human serum albumin by Kluyveromyces yeasts. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Oct;9(10):968–975. doi: 10.1038/nbt1091-968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friguet B., Chaffotte A. F., Djavadi-Ohaniance L., Goldberg M. E. Measurements of the true affinity constant in solution of antigen-antibody complexes by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Mar 18;77(2):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. L., Kahn J. O., Kaplan L. D., Groopman J. E., Volberding P. A., Amman A. J., Arri C. J., Bouvier L. M., Mordenti J., Izu A. E. Phase 1 study of recombinant human CD4-immunoglobulin G therapy of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2580–2586. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsy J., Meyer M., Tateno M., Clarkson S., Levy J. A. The Fc and not CD4 receptor mediates antibody enhancement of HIV infection in human cells. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1357–1360. doi: 10.1126/science.2786647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idziorek T., Klatzmann D. Functional expression of the CD4 protein after cross-linking to red blood cells with a bifunctional reagent. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 11;1062(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson V. A., Barlow M. A., Chou T. C., Fisher R. A., Walker B. D., Hirsch M. S., Schooley R. T. Synergistic inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) replication in vitro by recombinant soluble CD4 and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):837–844. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouault T., Chapuis F., Olivier R., Parravicini C., Bahraoui E., Gluckman J. C. HIV infection of monocytic cells: rôle of antibody-mediated virus binding to Fc-gamma receptors. AIDS. 1989 Mar;3(3):125–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. O., Allan J. D., Hodges T. L., Kaplan L. D., Arri C. J., Fitch H. F., Izu A. E., Mordenti J., Sherwin J. E., Groopman J. E. The safety and pharmacokinetics of recombinant soluble CD4 (rCD4) in subjects with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. A phase 1 study. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Feb 15;112(4):254–261. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D. R., McDougal J. S., Maddon P. J. The CD4 molecule and HIV infection. Immunodefic Rev. 1990;2(1):43–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Cort S. P., Kennedy M. S., Mawle A. C. Binding of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV/ARV/HIV to the CD4 (T4) molecule: conformation dependence, epitope mapping, antibody inhibition, and potential for idiotypic mimicry. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2937–2944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Griffiths P. D., Weiss R. A. HIV susceptibility conferred to human fibroblasts by cytomegalovirus-induced Fc receptor. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):659–661. doi: 10.1038/343659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogino T., Inoue M., Ando Y., Awai M., Maeda H., Morino Y. Chemical modification of superoxide dismutase. Extension of plasma half life of the enzyme through its reversible binding to the circulating albumin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1988 Aug;32(2):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1988.tb00675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Seed B. Genetic analysis of monoclonal antibody and HIV binding sites on the human lymphocyte antigen CD4. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):65–72. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poznansky M. J., Halford J., Taylor D. Growth hormone-albumin conjugates. Reduced renal toxicity and altered plasma clearance. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):18–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poznansky M. J. Soluble enzyme--albumin conjugates: new possibilities for enzyme replacement therapy. Methods Enzymol. 1988;137:566–574. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)37052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson N. E., Brown N. R., Hussey R. E., Vaid A., Matthews T. J., Bolognesi D. P., Reinherz E. L. Binding site for human immunodeficiency virus coat protein gp120 is located in the NH2-terminal region of T4 (CD4) and requires the intact variable-region-like domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6102–6106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Antibody-dependent enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Lancet. 1988 Apr 9;1(8589):790–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91657-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M., Prince A. M., Alter H. J., Dreesman G. R., Eichberg J. W. Antibody-dependent enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in vitro by serum from HIV-1-infected and passively immunized chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4710–4714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. E., Kwong P. D., Truneh A., Porter T. G., Arthos J., Rosenberg M., Dai X. P., Xuong N. H., Axel R., Sweet R. W. Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):419–426. doi: 10.1038/348419a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley R. T., Merigan T. C., Gaut P., Hirsch M. S., Holodniy M., Flynn T., Liu S., Byington R. E., Henochowicz S., Gubish E. Recombinant soluble CD4 therapy in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. A phase I-II escalating dosage trial. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Feb 15;112(4):247–253. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-4-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz O., Henin Y., Marechal V., Montagnier L. A rapid and simple colorimetric test for the study of anti-HIV agents. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Dec;4(6):441–448. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda A., Tuazon C. U., Ennis F. A. Antibody-enhanced infection by HIV-1 via Fc receptor-mediated entry. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):580–583. doi: 10.1126/science.2972065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teppler H., Lee S. H., Rieber E. P., Gordon S. Murine immunoglobulin G anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies bind to primary human monocytes and macrophages through Fc receptors as well as authentic CD4. AIDS. 1990 Jul;4(7):627–632. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199007000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiriart C., Goudsmit J., Schellekens P., Barin F., Zagury D., De Wilde M., Bruck C. Antibodies to soluble CD4 in HIV-1-infected individuals. AIDS. 1988 Oct;2(5):345–351. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198810000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traunecker A., Schneider J., Kiefer H., Karjalainen K. Highly efficient neutralization of HIV with recombinant CD4-immunoglobulin molecules. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):68–70. doi: 10.1038/339068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Yan Y. W., Garrett T. P., Liu J. H., Rodgers D. W., Garlick R. L., Tarr G. E., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L., Harrison S. C. Atomic structure of a fragment of human CD4 containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):411–418. doi: 10.1038/348411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesolowski-Louvel M., Tanguy-Rougeau C., Fukuhara H. A nuclear gene required for the expression of the linear DNA-associated killer system in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Yeast. 1988 Mar;4(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/yea.320040108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]