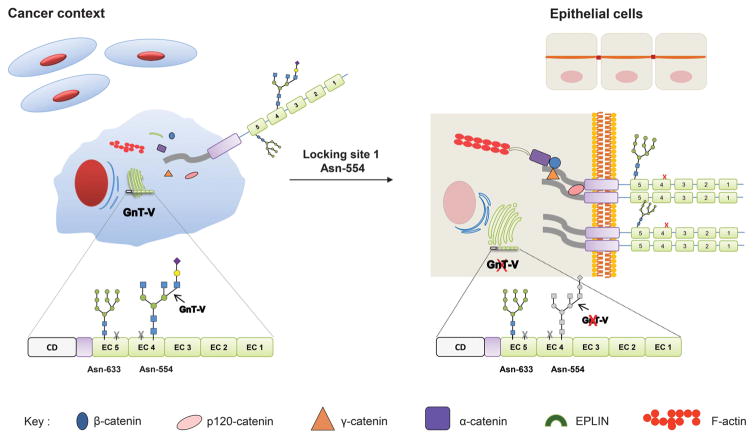
Figure 6.
Proposing model for the site-specific E-cadherin N-glycosylation in cancer context. The site-specific occupancy of E-cadherin Asn-554 with β1, 6 GlcNAc-branched structures catalyzed by GnT-V impairs its biological functions leading to a decreased E-cadherin cis-dimerization capability, a decreased cellular aggregation and an impairment of the molecular assembly of adherens junctions. Locking this site-specific modification either by Asn-554 mutation or by GnT-V silencing recovers the biological functions of E-cadherin by increasing E-cadherin cis-dimerization, aggregation and the stability of the E-cadherin–catenin complex.