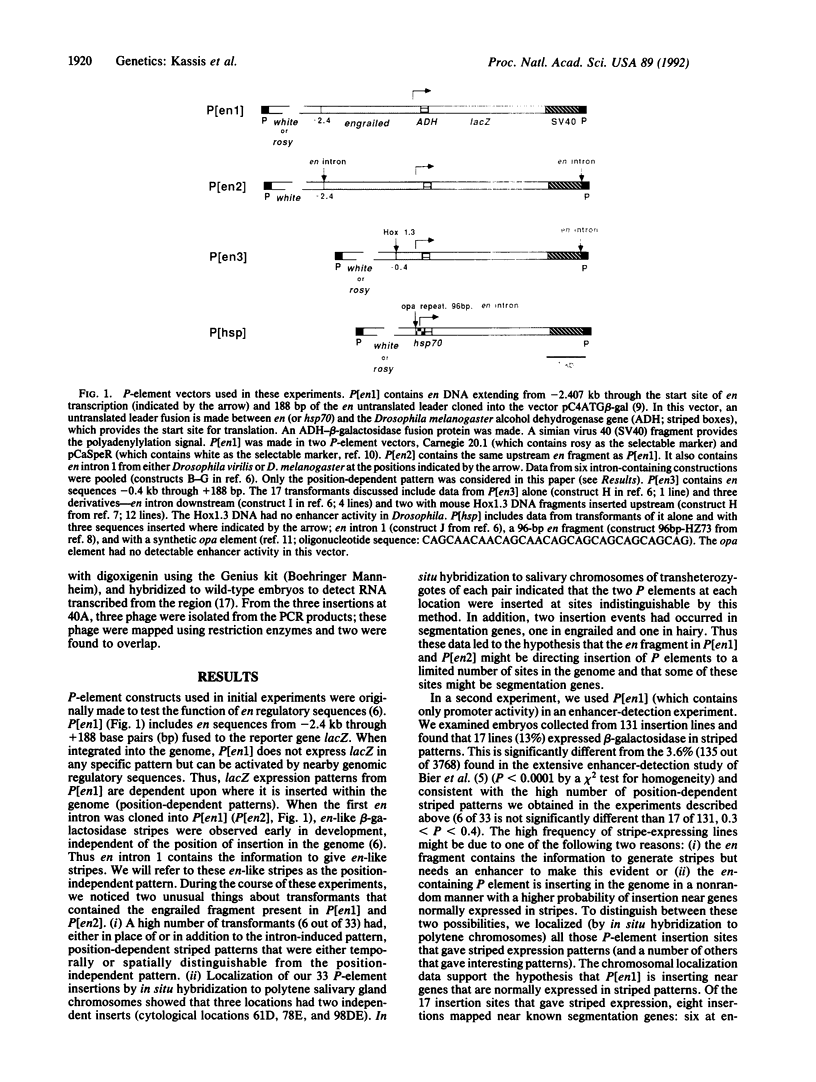
Abstract
Vectors derived from the Drosophila P element transposon are widely used to make transgenic Drosophila. Insertion of most P-element-derived vectors is nonrandom, but they exhibit a broad specificity of target sites. During experiments to identify cis-acting regulatory elements of the Drosophila segmentation gene engrailed, we identified a fragment of engrailed DNA that, when included within a P-element vector, strikingly alters the specificity of target sites. P-element vectors that contain this fragment of engrailed regulatory DNA insert at a high frequency near genes expressed in stripes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker N. E. Localization of transcripts from the wingless gene in whole Drosophila embryos. Development. 1988 Jun;103(2):289–298. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker N. E. Transcription of the segment-polarity gene wingless in the imaginal discs of Drosophila, and the phenotype of a pupal-lethal wg mutation. Development. 1988 Mar;102(3):489–497. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellen H. J., O'Kane C. J., Wilson C., Grossniklaus U., Pearson R. K., Gehring W. J. P-element-mediated enhancer detection: a versatile method to study development in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1288–1300. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier E., Vaessin H., Shepherd S., Lee K., McCall K., Barbel S., Ackerman L., Carretto R., Uemura T., Grell E. Searching for pattern and mutation in the Drosophila genome with a P-lacZ vector. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1273–1287. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. B., Laughon A., Thalley B. S. Expression, function, and regulation of the hairy segmentation protein in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):883–890. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Transfer RNA genes are genomic targets for de Novo transposition of the yeast retrotransposon Ty3. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):837–850. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hama C., Ali Z., Kornberg T. B. Region-specific recombination and expression are directed by portions of the Drosophila engrailed promoter. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1079–1093. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper K. L., Parkhurst S. M., Ish-Horowicz D. Spatial control of hairy protein expression during embryogenesis. Development. 1989 Nov;107(3):489–504. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs J. R., Hiromi Y., Patel N. H., Goodman C. S. Lineage, migration, and morphogenesis of longitudinal glia in the Drosophila CNS as revealed by a molecular lineage marker. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1625–1631. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis J. A. Spatial and temporal control elements of the Drosophila engrailed gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):433–443. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis J. A., VanSickle E. P., Sensabaugh S. M. A fragment of engrailed regulatory DNA can mediate transvection of the white gene in Drosophila. Genetics. 1991 Aug;128(4):751–761. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.4.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Nakanishi M., Ali Z., Drees B., Gustavson E., Theis J., Kauvar L., Kornberg T., O'Farrell P. H. Molecular cloning of engrailed: a gene involved in the development of pattern in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):309–316. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80126-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Kane C. J., Gehring W. J. Detection in situ of genomic regulatory elements in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9123–9127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Gerber A. S., Hartl D. L. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):621–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrimon N., Noll E., McCall K., Brand A. Generating lineage-specific markers to study Drosophila development. Dev Genet. 1991;12(3):238–252. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020120309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S. B., Hansen L. J., Chalker D. L. Integration specificity of retrotransposons and retroviruses. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. C., Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. Highly preferred targets for retrovirus integration. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kassis J. A., O'Farrell P. H. A synthetic homeodomain binding site acts as a cell type specific, promoter specific enhancer in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2573–2578. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Yedvobnick B., Finnerty V. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. opa: a novel family of transcribed repeats shared by the Notch locus and other developmentally regulated loci in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel M., Nusse R., Johnston P., Lawrence P. A. Distribution of the wingless gene product in Drosophila embryos: a protein involved in cell-cell communication. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]