Abstract
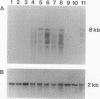
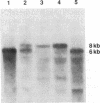
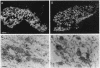
Microtubule-associated protein tau consists in brain of a series of isoforms of 48- to 67-kDa apparent molecular mass that are encoded by mRNAs of approximately 6 kilobases (kb) and that are generated from a single gene by alternative splicing. Previously, a tau-like protein of 110-kDa apparent molecular mass was described in peripheral ganglia and in peripheral neuronlike cell lines. We now report the cloning and sequencing of a rat cDNA encoding this big tau. The corresponding protein contains sequence identical to the longest of the previously cloned small tau isoforms but with an additional 254 amino acid insert in the amino-terminal half. Big tau is produced from an 8-kb mRNA generated by alternative splicing from the same gene that encodes small tau. Production of big tau from the cloned sequence gives a protein of 110-kDa apparent molecular mass that aligns on SDS/PAGE with big tau protein extracted from peripheral ganglia. RNA blots show that in peripheral ganglia from adult rats only the 8-kb mRNA band corresponding to big tau is found, whereas in ganglia from newborn rats both 6- and 8-kb tau mRNA bands are found. In tissues from the central nervous system only the 6-kb mRNA band can be detected. Big tau protein is therefore produced specifically in the peripheral nervous system, and it will be interesting to see whether further molecular differences between the two major divisions of the vertebrate nervous system will be discovered.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa H., Kawasaki H., Murofushi H., Kotani S., Suzuki K., Sakai H. A common amino acid sequence in 190-kDa microtubule-associated protein and tau for the promotion of microtubule assembly. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5885–5890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butner K. A., Kirschner M. W. Tau protein binds to microtubules through a flexible array of distributed weak sites. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):717–730. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Kosik K. S. Inhibition of neurite polarity by tau antisense oligonucleotides in primary cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):461–463. doi: 10.1038/343461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmore J. H., Solomon F. Inhibition of MAP2 expression affects both morphological and cell division phenotypes of neuronal differentiation. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):817–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Feinstein S. C., Shooter E. M., Kirschner M. W. Nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells involves the coordinate induction of microtubule assembly and assembly-promoting factors. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1799–1807. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D., Kobayashi S., Kellogg D., Kirschner M. Regulation of microtubule protein levels during cellular morphogenesis in nerve growth factor-treated PC12 cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1583–1591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D., Kobayashi S., Kirschner M. Association of tau protein with microtubules in living cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;466:257–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennulat D. J., Liem R. K., Hashim G. A., Shelanski M. L. Two separate 18-amino acid domains of tau promote the polymerization of tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5327–5330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgieff I. S., Liem R. K., Mellado W., Nunez J., Shelanski M. L. High molecular weight tau: preferential localization in the peripheral nervous system. J Cell Sci. 1991 Sep;100(Pt 1):55–60. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Crowther R. A., Garner C. C. Molecular characterization of microtubule-associated proteins tau and MAP2. Trends Neurosci. 1991 May;14(5):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Jakes R. Expression of separate isoforms of human tau protein: correlation with the tau pattern in brain and effects on tubulin polymerization. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4225–4230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Jakes R., Rutherford D., Crowther R. A. Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90210-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Spillantini M. G., Potier M. C., Ulrich J., Crowther R. A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding an isoform of microtubule-associated protein tau containing four tandem repeats: differential expression of tau protein mRNAs in human brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):393–399. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M., Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Walker J. E., Klug A. Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4051–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A., Drechsel D., Kirschner M. W., Martin D. W., Jr Tau consists of a set of proteins with repeated C-terminal microtubule-binding domains and variable N-terminal domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1381–1388. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmler A. Structure of the bovine tau gene: alternatively spliced transcripts generate a protein family. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1389–1396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Takemura R., Oshima T., Mori H., Ihara Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Hirokawa N. Expression of multiple tau isoforms and microtubule bundle formation in fibroblasts transfected with a single tau cDNA. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1173–1184. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Orecchio L. D., Bakalis S., Neve R. L. Developmentally regulated expression of specific tau sequences. Neuron. 1989 Apr;2(4):1389–1397. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G., Neve R. L., Kosik K. S. The microtubule binding domain of tau protein. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1615–1624. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A. Microtubule-associated proteins: their potential role in determining neuronal morphology. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:29–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Stein M., Beach D. The product of the mei3+ gene, expressed under control of the mating-type locus, induces meiosis and sporulation in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):729–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Harris P., Kosik K. S., Kurnit D. M., Donlon T. A. Identification of cDNA clones for the human microtubule-associated protein tau and chromosomal localization of the genes for tau and microtubule-associated protein 2. Brain Res. 1986 Dec;387(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblinger M. M., Argasinski A., Wong J., Kosik K. S. Tau gene expression in rat sensory neurons during development and regeneration. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2453–2459. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02453.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Oberkanins C., Himmler A. Molecular structure and function of microtubule-associated proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;124:217–273. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61528-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]