Abstract
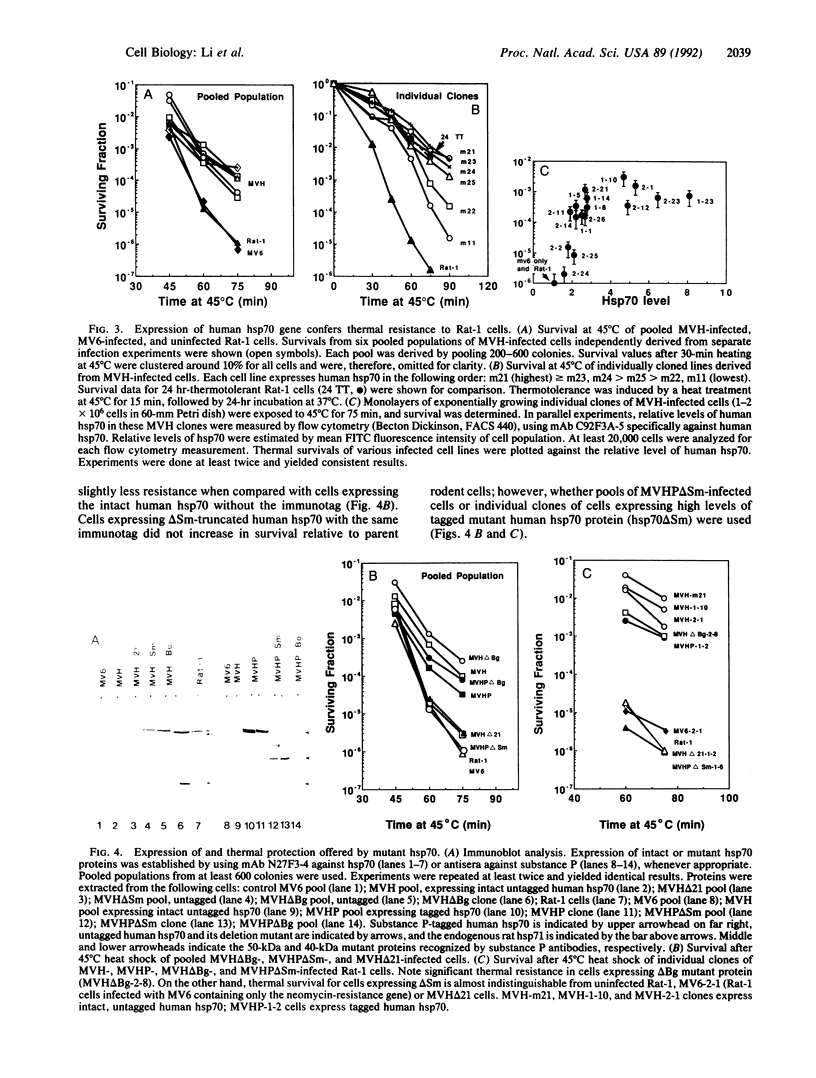
Retroviral-mediated gene transfer experiments show that rodent cells become heat resistant when stably and constitutively expressing a cloned human gene encoding an intact human 70-kDa heat shock protein (hsp70). Cells expressing higher levels of the hsp70 protein generally tolerate thermal stress better, whereas cells expressing either of two mutated hsp70-encoding genes, one with a 4-base pair out-of-frame deletion and one with an in-frame deletion of codons 438-618, are heat sensitive. These results provide strong evidence that expression of hsp70 leads directly to thermal tolerance. Surprisingly, cells expressing a mutant hsp70 of a human gene missing codons 120-428 are, nevertheless, heat resistant. Because the deleted region of this mutant contains the ATP-binding domain of human hsp70, this domain appears dispensable in the hsp70-mediated protection of cells from thermal stress.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiello L., Guilfoyle R., Huebner K., Weinmann R. Adenovirus 5 DNA sequences present and RNA sequences transcribed in transformed human embryo kidney cells (HEK-Ad-5 or 293). Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):460–469. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. L., Tao T. W., Hahn G. M. Membrane lipids of B16 melanoma cells and heat-resistant variants. Int J Radiat Biol. 1988 Nov;54(5):813–823. doi: 10.1080/09553008814552241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann R. P., Mizzen L. E., Welch W. J. Interaction of Hsp 70 with newly synthesized proteins: implications for protein folding and assembly. Science. 1990 May 18;248(4957):850–854. doi: 10.1126/science.2188360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edington B. V., Whelan S. A., Hightower L. E. Inhibition of heat shock (stress) protein induction by deuterium oxide and glycerol: additional support for the abnormal protein hypothesis of induction. J Cell Physiol. 1989 May;139(2):219–228. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerner E. W., Schneider M. J. Induced thermal resistance in HeLa cells. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):500–502. doi: 10.1038/256500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle K. J., Dethlefsen L. A. Heat fractionation and thermotolerance: a review. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):1843–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle K. J., Leeper D. B. Interaction of hyperthermia and radiation in CHO cells: recovery kinetics. Radiat Res. 1976 Jun;66(3):505–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschmeier P. T., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Perkins A. S., Weinstein I. B. Construction and characterization of a retroviral vector demonstrating efficient expression of cloned cDNA sequences. DNA. 1988 Apr;7(3):219–225. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Bernier D., Chrétien P., Nicole L. M., Tanguay R. M., Marceau N. Synthesis and degradation of heat shock proteins during development and decay of thermotolerance. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2457–2461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Chrétien P., Lambert H., Hickey E., Weber L. A. Heat shock resistance conferred by expression of the human HSP27 gene in rodent cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):7–15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo A., Li G. C. Heat-resistant variants of Chinese hamster fibroblasts altered in expression of heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8029–8033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Involvement of ATP in the nuclear and nucleolar functions of the 70 kd heat shock protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3137–3143. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C. Elevated levels of 70,000 dalton heat shock protein in transiently thermotolerant Chinese hamster fibroblasts and in their stable heat resistant variants. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985 Jan;11(1):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(85)90376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Li L. G., Liu Y. K., Mak J. Y., Chen L. L., Lee W. M. Thermal response of rat fibroblasts stably transfected with the human 70-kDa heat shock protein-encoding gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1681–1685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Werb Z. Correlation between synthesis of heat shock proteins and development of thermotolerance in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Morimoto R. I. Mutational analysis of the human HSP70 protein: distinct domains for nucleolar localization and adenosine triphosphate binding. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1947–1962. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. Use of peptide tagging to detect proteins expressed from cloned genes: deletion mapping functional domains of Drosophila hsp 70. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3087–3093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Hsp70 accelerates the recovery of nucleolar morphology after heat shock. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3095–3100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J. Heat shock is lethal to fibroblasts microinjected with antibodies against hsp70. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):433–436. doi: 10.1126/science.3175665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subjeck J. R., Sciandra J. J., Johnson R. J. Heat shock proteins and thermotolerance; a comparison of induction kinetics. Br J Radiol. 1982 Aug;55(656):579–584. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-55-656-579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Suhan J. P. Cellular and biochemical events in mammalian cells during and after recovery from physiological stress. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):2035–2052. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B., Hunt C., Morimoto R. Structure and expression of the human gene encoding major heat shock protein HSP70. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):330–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]