Abstract
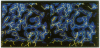
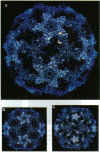
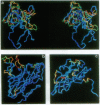
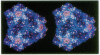
Theiler murine encephalomyelitis virus strains are categorized into two groups, a neurovirulent group that rapidly kills the host, and a demyelinating group that causes a generally nonlethal infection of motor neurons followed by a persistent infection of the white matter with demyelinating lesions similar to those found in multiple sclerosis. The three-dimensional structure of the DA strain, a member of the demyelinating group, has been determined at 2.8 A resolution. As in other picornaviruses, the icosahedral capsid is formed by the packing of wedge-shaped eight-stranded antiparallel beta barrels. The surface of Theiler virus has large star-shaped plateaus at the fivefold axes and broad depressions spanning the twofold axes. Several unusual structural features are clustered near one edge of the depression. These include two finger-like loops projecting from the surface (one formed by residues 78-85 of VP1, and the other formed by residues 56-65 of VP3) and a third loop containing three cysteines (residues 87, 89, and 91 of VP3), which appear to be covalently modified. Most of the sequence differences between the demyelinating and neurovirulent groups that could play a role in determining pathogenesis map to the surface of the star-shaped plateau. The distribution of these sequence differences on the surface of the virion is consistent with models in which the differences in the pathogenesis of the two groups of Theiler viruses are the result of differences in immunological or receptor-mediated recognition processes.
Full text
PDF
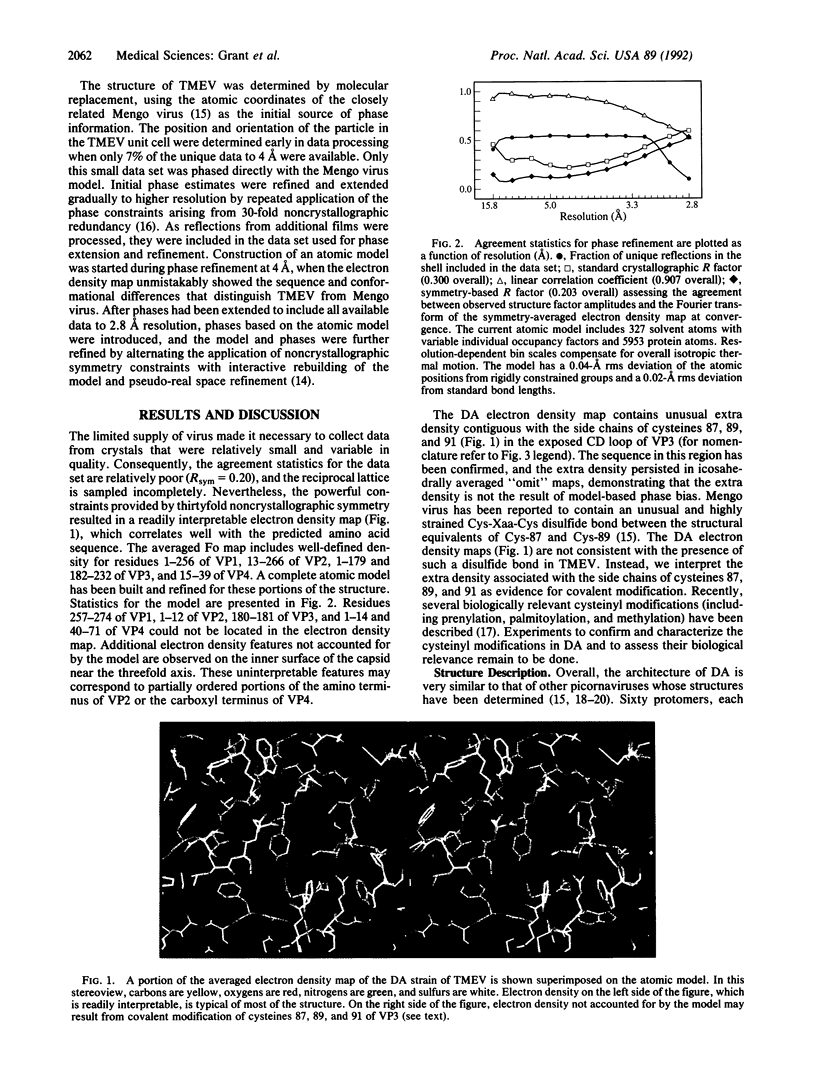
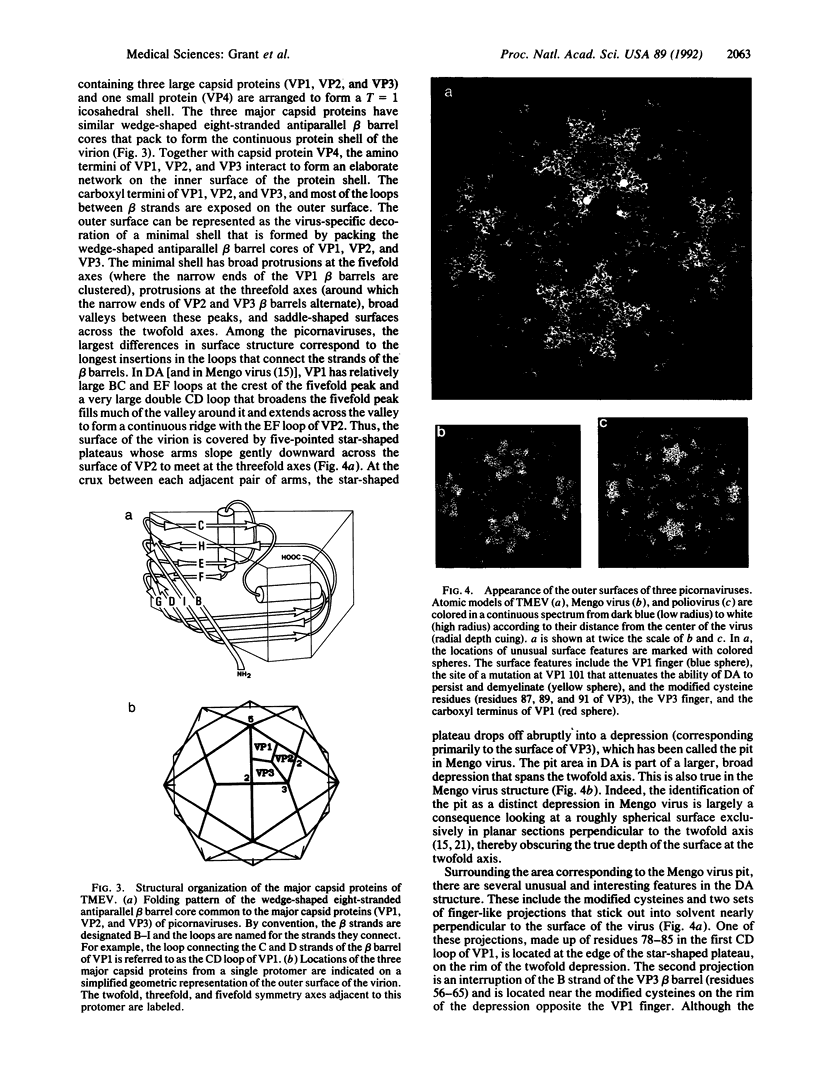


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acharya R., Fry E., Stuart D., Fox G., Rowlands D., Brown F. The three-dimensional structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):709–716. doi: 10.1038/337709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Antibodies against the chemically synthesized genome-linked protein of poliovirus react with native virus-specific proteins. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton S. R., Nelsen B., Kirkegaard K. Temperature-sensitive poliovirus mutant fails to cleave VP0 and accumulates provirions. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4067–4075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4067-4075.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Cox A. D. Isoprenoid modification and plasma membrane association: critical factors for ras oncogenicity. Cancer Cells. 1991 Sep;3(9):331–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. L., Stein S., Rosenstein L., Bodwell T., Routbort M., Semler B. L., Roos R. P. Neurovirulence determinants of genetically engineered Theiler viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4125–4129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J., Rodriguez M., Roos R. P. Strains from both Theiler's virus subgroups encode a determinant for demyelination. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6345–6348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6345-6348.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Kupsky W. J., Racaniello V. R. Reduced mouse neurovirulence of poliovirus type 2 Lansing antigenic variants selected with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90136-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Calenoff M., Bandyopadhyay P., Miller S. D., Dal Canto M. C., Gerety S., Jensen K. The 5' noncoding sequences from a less virulent Theiler's virus dramatically attenuate GDVII neurovirulence. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4370–4377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4370-4377.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C. Prediction of three-dimensional models for foot-and-mouth disease virus and hepatitis A virus. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo M., Vriend G., Kamer G., Minor I., Arnold E., Rossmann M. G., Boege U., Scraba D. G., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. The atomic structure of Mengo virus at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):182–191. doi: 10.1126/science.3026048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Wychowski C., Couderc T., Crainic R., Hogle J., Girard M. Engineering a poliovirus type 2 antigenic site on a type 1 capsid results in a chimaeric virus which is neurovirulent for mice. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister A., Tangy F., Aubert C., Brahic M. Genetic mapping of the ability of Theiler's virus to persist and demyelinate. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4252–4257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4252-4257.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Bradley J., Yang X. F., Wimmer E., Moss E. G., Racaniello V. R. Poliovirus host range is determined by a short amino acid sequence in neutralization antigenic site I. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):213–215. doi: 10.1126/science.2838906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara Y., Stein S., Fu J. L., Stillman L., Klaman L., Roos R. P. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of DA strain of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis viruses. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90642-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Borkowski J., Calenoff M., Oh C. K., Ostrowski B., Lipton H. L. Insights into Theiler's virus neurovirulence based on a genomic comparison of the neurovirulent GDVII and less virulent BeAn strains. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90652-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevear D. C., Calenoff M., Rozhon E., Lipton H. L. Analysis of the complete nucleotide sequence of the picornavirus Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus indicates that it is closely related to cardioviruses. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1507–1516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1507-1516.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C., Page G., Zhou H., Chow M. Identification of residues in VP2 that contribute to poliovirus neutralization antigenic site 3B. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90856-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M., Roos R. P. Pathogenesis of early and late disease in mice infected with Theiler's virus, using intratypic recombinant GDVII/DA viruses. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):217–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.217-225.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos R. P., Stein S., Routbort M., Senkowski A., Bodwell T., Wollmann R. Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus neutralization escape mutants have a change in disease phenotype. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4469–4473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4469-4473.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Pallansch M. A. Preparation and characterization of encephalomyocarditis (EMC) virus. Methods Enzymol. 1981;78(Pt A):315–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangy F., McAllister A., Aubert C., Brahic M. Determinants of persistence and demyelination of the DA strain of Theiler's virus are found only in the VP1 gene. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1616–1618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1616-1618.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeates T. O., Jacobson D. H., Martin A., Wychowski C., Girard M., Filman D. J., Hogle J. M. Three-dimensional structure of a mouse-adapted type 2/type 1 poliovirus chimera. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2331–2341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07772.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurbriggen A., Fujinami R. S. A neutralization-resistant Theiler's virus variant produces an altered disease pattern in the mouse central nervous system. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1505–1513. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1505-1513.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurbriggen A., Hogle J. M., Fujinami R. S. Alteration of amino acid 101 within capsid protein VP-1 changes the pathogenicity of Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2037–2049. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]