Abstract
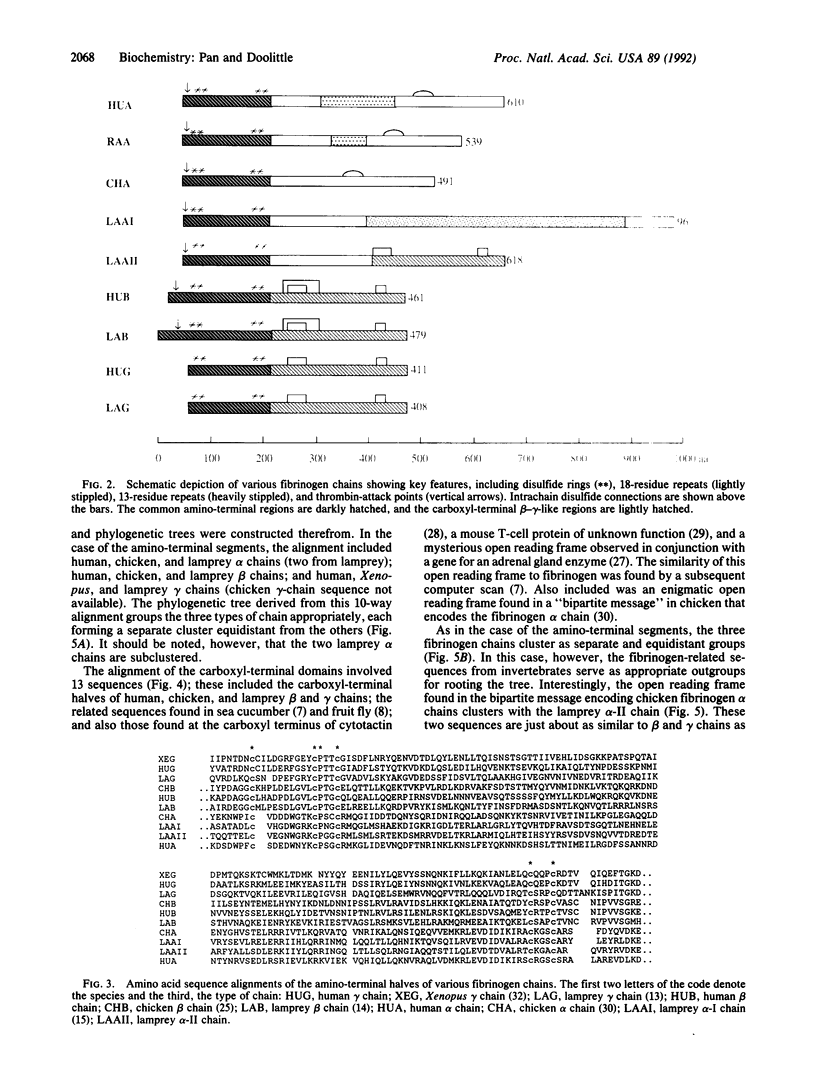
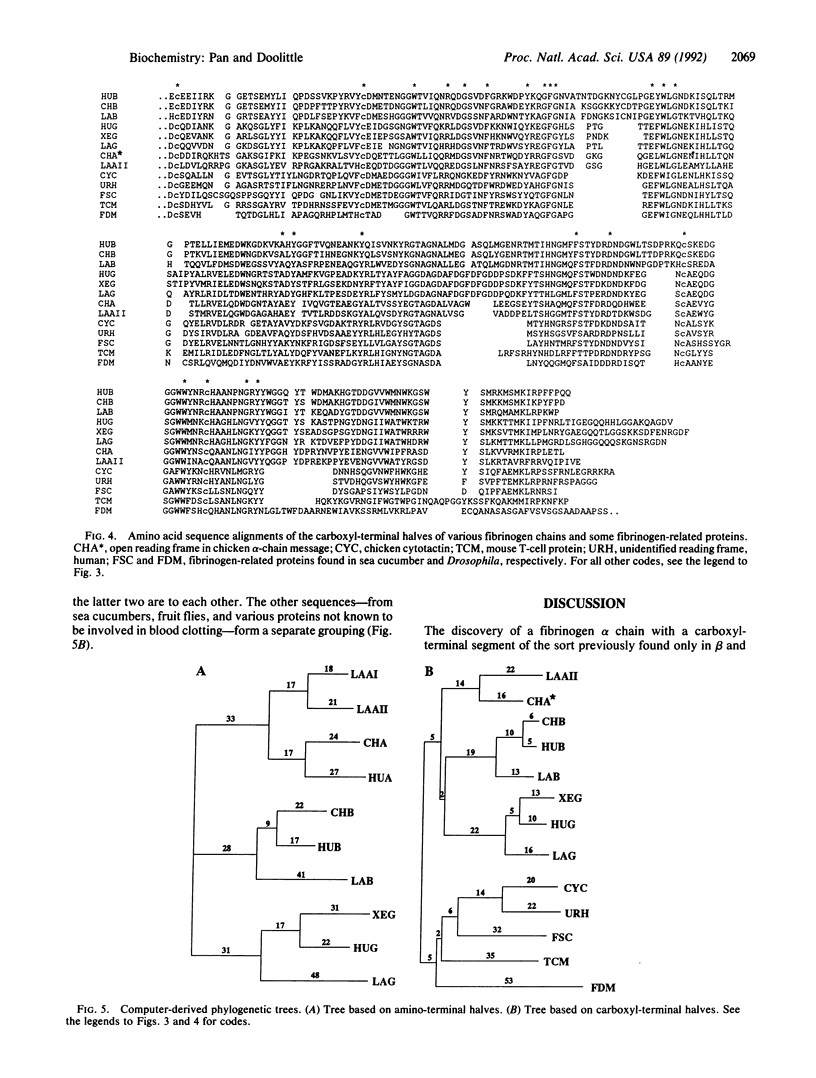
The message for a second fibrinogen alpha chain has been cloned from a lamprey liver cDNA library. The sequence is unique in that the amino-terminal half is homologous to all other known alpha chains, including another from lamprey, but its carboxyl-terminal half is homologous to the carboxyl-terminal portions of beta and gamma chains, segments that compose the distal globular regions of fibrinogen. The structural pattern of this newly discovered alpha chain suggests that it could be a direct descendant of the archetypal chain that existed prior to the gene duplications that led to unique beta and gamma chains and before the dislocating events that gave rise to contemporary alpha chains.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker N. E., Mlodzik M., Rubin G. M. Spacing differentiation in the developing Drosophila eye: a fibrinogen-related lateral inhibitor encoded by scabrous. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1370–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.2175046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K., Hunter I., Engel J. Structure and function of laminin: anatomy of a multidomain glycoprotein. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):148–160. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohonus V. L., Doolittle R. F., Pontes M., Strong D. D. Complementary DNA sequence of lamprey fibrinogen beta chain. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 21;25(21):6512–6516. doi: 10.1021/bi00369a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell B. A., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequences of lamprey fibrinopeptides A and B and characterizations of the junctions split by lamprey and mammalian thrombins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 22;453(2):426–438. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOOLITTLE R. F. CHARACTERIZATION OF LAMPREY FIBRINOPEPTIDES. Biochem J. 1965 Mar;94:742–750. doi: 10.1042/bj0940742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F. Nearest neighbor procedure for relating progressively aligned amino acid sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:659–669. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Watt K. W., Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Riley M. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):464–468. doi: 10.1038/280464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Wooding G. L. The subunit structure of lamprey fibrinogen and fibrin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive alignment and phylogenetic tree construction of protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:375–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschen A., Lottspeich F. Sequence homology between gamma-chain and beta-chain in human fibrin. Thromb Res. 1977 Dec;11(6):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Frischauf A. M. Isolation of genomic DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:180–183. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Burgoon M. P., Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. A cDNA clone for cytotactin contains sequences similar to epidermal growth factor-like repeats and segments of fibronectin and fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2186–2190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama T., Hall L. R., Haser W. G., Tonegawa S., Saito H. Structure of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-specific gene shows a strong homology to fibrinogen beta and gamma chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Hynes R. O. The structure of human thrombospondin, an adhesive glycoprotein with multiple calcium-binding sites and homologies with several different proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1635–1648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel Y., Bristow J., Gitelman S. E., Miller W. L. Transcript encoded on the opposite strand of the human steroid 21-hydroxylase/complement component C4 gene locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6582–6586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastori R. L., Moskaitis J. E., Smith L. H., Jr, Schoenberg D. R. Estrogen regulation of Xenopus laevis gamma-fibrinogen gene expression. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 13;29(10):2599–2605. doi: 10.1021/bi00462a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong D. D., Moore M., Cottrell B. A., Bohonus V. L., Pontes M., Evans B., Riley M., Doolittle R. F. Lamprey fibrinogen gamma chain: cloning, cDNA sequencing, and general characterization. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):92–101. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence of the carboxy-terminal cyanogen bromide peptide of the human fibrinogen beta-chain: homology with the corresponding gamma-chain peptide and presence in fragment D. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 29;386(2):617–622. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. Z., Patterson J., Gray J. E., Yu C., Cottrell B. A., Shimizu A., Graham D., Riley M., Doolittle R. F. Complete sequence of the lamprey fibrinogen alpha chain. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 12;28(25):9801–9806. doi: 10.1021/bi00451a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt K. W., Takagi T., Doolittle R. F. Amino acid sequence of the beta chain of human fibrinogen: homology with the gamma chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach L., Grieninger G. Bipartite mRNA for chicken alpha-fibrinogen potentially encodes an amino acid sequence homologous to beta- and gamma-fibrinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5198–5202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach L., Oddoux C., Procyk R., Grieninger G. The beta chain of chicken fibrinogen contains an atypical thrombin cleavage site. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3290–3294. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Doolittle R. F. Presence of a vertebrate fibrinogen-like sequence in an echinoderm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2097–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




