Figure 5. Cross-individual variability is lost in rutabaga mutants.
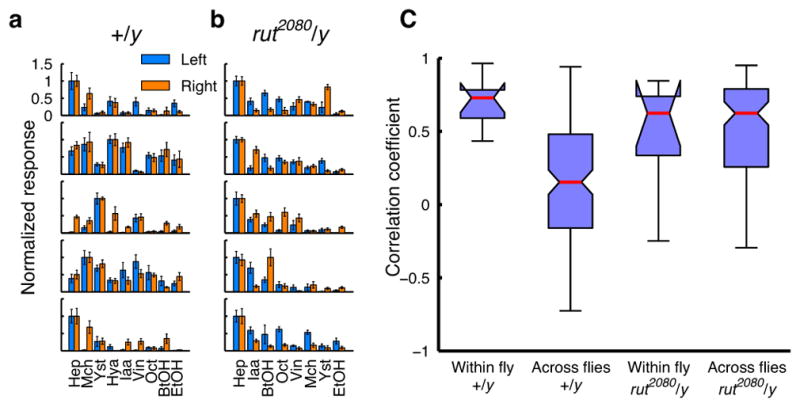
a, Odor tuning of a pair of α2sc neurons on the left and right hemispheres in the same fly, recorded with GCaMP5 imaging (mean ± SEM). Data from five wild-type males. b, Same as a but rut2080 males. c, Control males show higher variability across flies than within flies (n = 9 flies, p < 10−4, Tukey’s post hoc test following two-way ANOVA). This difference is lost in rut2080 hemizygous males, which show similar levels of variability both within and across flies (n = 8 flies, p > 0.995, Tukey’s post hoc test). Interactions between the genotypes and comparison types (within versus across flies) were significant (p < 0.005, two-way ANOVA). Within-fly tuning correlations were not statistically different between the two genotypes (p > 0.65, Tukey’s post hoc test).
