Abstract
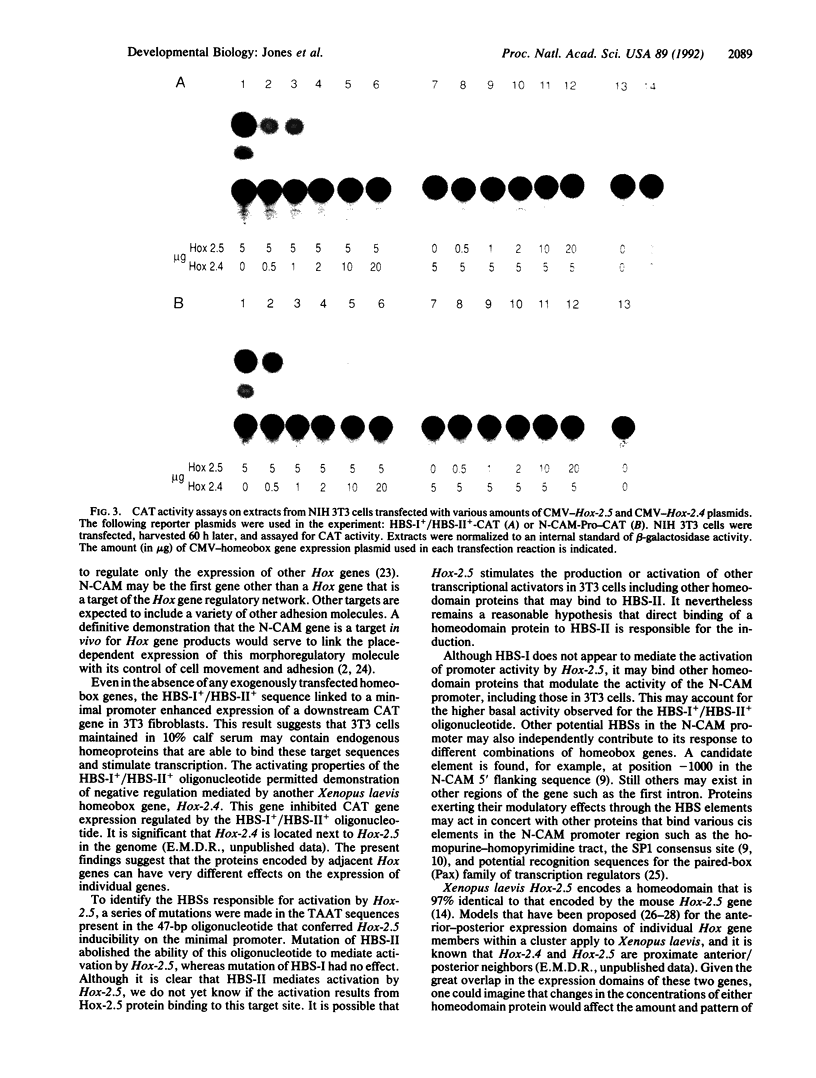
In an effort to determine whether homeobox genes modulate the activity of the promoter of the mouse neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) gene, we have carried out a series of cotransfection experiments using NIH 3T3 cells. Plasmids were constructed containing Xenopus laevis Hox-2.5 and -2.4 coding sequences linked to a human cytomegalovirus promoter (CMV-Hox-2.5 and CMV-Hox-2.4). A 4.9-kilobase DNA fragment containing 5' flanking and first exon sequences of the mouse N-CAM gene was linked to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene (N-CAM-Pro-CAT). Cotransfection with CMV-Hox-2.5 and N-CAM-Pro-CAT resulted in a strong induction of CAT activity. The N-CAM promoter contained two potential homeodomain binding sites (sites I and II) within a 47-base-pair segment (512-559 base pairs upstream of the ATG codon in the first exon of the N-CAM gene). This segment was linked to a minimal promoter (simian virus 40 early) and a downstream CAT gene. Although this construct was transcriptionally active at a low level in NIH 3T3 cells, cotransfection of CMV-Hox-2.5 resulted in CAT activity that was greatly elevated. Mutational studies revealed that it was the homeodomain binding site II sequence that was required for this regulation. In contrast, cotransfection with CMV-Hox-2.4 eliminated the CAT activity that was driven by the CMV-Hox-2.5 construct. Thus, the products of two related Hox genes, which are located adjacent to each other in the Hox-2 complex, can differentially modulate transcription from the promoter of a cell adhesion molecule gene. The results suggest that the N-CAM gene is likely to be a target for regulation by Hox gene products.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boncinelli E., Somma R., Acampora D., Pannese M., D'Esposito M., Faiella A., Simeone A. Organization of human homeobox genes. Hum Reprod. 1988 Oct;3(7):880–886. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a136802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Fritsch R., Fickenscher H., Deutsch U., Goulding M., Gruss P. The molecular basis of the undulated/Pax-1 mutation. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):873–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90434-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. S., Reyes A., Akeson R. Transcription initiation sites and structural organization of the extreme 5' region of the rat neural cell adhesion molecule gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3314–3324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., Goetz J., Wright C. V., Fritz A., Hardwicke J., De Robertis E. M. Differential utilization of the same reading frame in a Xenopus homeobox gene encodes two related proteins sharing the same DNA-binding specificity. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2139–2149. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03053.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuong C. M., Edelman G. M. Expression of cell-adhesion molecules in embryonic induction. I. Morphogenesis of nestling feathers. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1009–1026. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuong C. M., Oliver G., Ting S. A., Jegalian B. G., Chen H. M., De Robertis E. M. Gradients of homeoproteins in developing feather buds. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1021–1030. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Crossin K. L. Cell adhesion molecules: implications for a molecular histology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Morphoregulation. Dev Dyn. 1992 Jan;193(1):2–10. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001930103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Embryonic induction--molecular prospects. Development. 1987 Mar;99(3):285–306. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.3.285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. R., Gaugler L., Deagostini-Bazin H., Bally-Cuif L., Goridis C. Identification of positive and negative regulatory elements governing cell-type-specific expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1959–1968. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Crossin K. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Identification and characterization of the promoter for the cytotactin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Gruss P. Murine developmental control genes. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):374–379. doi: 10.1126/science.1974085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi G., Crossin K. L., Edelman G. M. Expression sequences and distribution of two primary cell adhesion molecules during embryonic development of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2359–2372. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Garbern J., Arnheiter H., Tournier-Lasserve E., Lazzarini R. A. The Hox-1.3 homeo box protein is a sequence-specific DNA-binding phosphoprotein. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):158–172. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prediger E. A., Hoffman S., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Four exons encode a 93-base-pair insert in three neural cell adhesion molecule mRNAs specific for chicken heart and skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9616–9620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. P., Tamkun J. W., Hartzell G. W., 3rd The structure and function of the homeodomain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 28;989(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Morita E. A., Wilkin D. J., De Robertis E. M. The Xenopus XIHbox 6 homeo protein, a marker of posterior neural induction, is expressed in proliferating neurons. Development. 1990 May;109(1):225–234. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.1.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zappavigna V., Renucci A., Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Urier G., Peschle C., Duboule D. HOX4 genes encode transcription factors with potential auto- and cross-regulatory capacities. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4177–4187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]