Abstract
Mutations of SOD-1 have recently been associated with autosomal dominant familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). A patient is described with a 20 year duration of motor neuron disease, with clinical features of ALS, who was heterozygous for a point mutation ATT to ACT leading to substitution of isoleucine for threonine at codon 113 in exon 4 of SOD-1. This mutation has previously been described in two families with ALS and three apparently sporadic cases of ALS. The patient described here had a family history suggestive of autosomal dominant inheritance of this genetic mutation; other members of the family having a more typical disease duration. Unusual pathological features included neurofibrillary tangles in neurons of the globus pallidus, substantia nigra, locus coeruleus, and inferior olivary nuclei, and absence of ubiquitin immunoreactive inclusions in motor neurons. This may reflect the slow progression of the neurodegeneration associated with the SOD-1 mutation in this patient. The prolonged survival, of over 20 years, with other family members having a more typical survival of two to three years, has important implications for genetic counselling in families with ALS in addition to the fundamental biological questions concerning the influence of these mutations on disease expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki M., Ogasawara M., Matsubara Y., Narisawa K., Nakamura S., Itoyama Y., Abe K. Familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in Japan associated with H46R mutation in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene: a possible new subtype of familial ALS. J Neurol Sci. 1994 Oct;126(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki M., Ogasawara M., Matsubara Y., Narisawa K., Nakamura S., Itoyama Y., Abe K. Mild ALS in Japan associated with novel SOD mutation. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):323–324. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum J. S., Roos R. P., Salazar-Grueso E. F., Buchman A., Iannaccone S., Glantz R., Siddique T., Maselli R. Intrafamilial heterogeneity in hereditary motor neuron disease. Neurology. 1992 Aug;42(8):1488–1492. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.8.1488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey-Wilson J. E., Plato C. C., Elston R. C., Garruto R. M. Potential role of an additive genetic component in the cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia in the western Pacific. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jan 1;45(1):68–76. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320450118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowling A. C., Schulz J. B., Brown R. H., Jr, Beal M. F. Superoxide dismutase activity, oxidative damage, and mitochondrial energy metabolism in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem. 1993 Dec;61(6):2322–2325. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb07478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J., Lantos P., Stratton M., Roques P., Rossor M. Familial progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 May;56(5):473–476. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.5.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. Proximal axonal enlargement in motor neuron disease. Neurology. 1968 Sep;18(9):841–851. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.9.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Griffin J. W., Choy C., Padula C. A., Price D. L. Pathology of motor neurons in accelerated hereditary canine spinal muscular atrophy. Lab Invest. 1982 Jan;46(1):89–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté F., Collard J. F., Julien J. P. Progressive neuronopathy in transgenic mice expressing the human neurofilament heavy gene: a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90158-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H. X., Hentati A., Tainer J. A., Iqbal Z., Cayabyab A., Hung W. Y., Getzoff E. D., Hu P., Herzfeldt B., Roos R. P. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and structural defects in Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase. Science. 1993 Aug 20;261(5124):1047–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.8351519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figlewicz D. A., Garruto R. M., Krizus A., Yanagihara R., Rouleau G. A. The Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene in ALS and parkinsonism-dementia of Guam. Neuroreport. 1994 Jan 31;5(5):557–560. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199401000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson M. H., Martin J. B. Cerebral lesions in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 1973 Nov 5;26(3):237–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00684433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. G., Szakál-Quin G., Priest J. W., Anthony D. C. In vitro evidence that covalent crosslinking of neurofilaments occurs in gamma-diketone neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4979–4982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. W., Hoffman P. N., Clark A. W., Carroll P. T., Price D. L. Slow axonal transport of neurofilament proteins: impairment of beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile administration. Science. 1978 Nov 10;202(4368):633–635. doi: 10.1126/science.81524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiroy D. C., Miyazaki M., Multhaup G., Fischer P., Garruto R. M., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L., Simms G., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Amyloid of neurofibrillary tangles of Guamanian parkinsonism-dementia and Alzheimer disease share identical amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2073–2077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney M. E., Pu H., Chiu A. Y., Dal Canto M. C., Polchow C. Y., Alexander D. D., Caliendo J., Hentati A., Kwon Y. W., Deng H. X. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 1994 Jun 17;264(5166):1772–1775. doi: 10.1126/science.8209258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRANO A., ZIMMERMAN H. M. Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes. A topographic study. Arch Neurol. 1962 Sep;7:227–242. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210030065009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Donnenfeld H., Sasaki S., Nakano I. Fine structural observations of neurofilamentous changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 Sep;43(5):461–470. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198409000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Malamud N., Elizan T. S., Kurland L. T. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam. Further pathologic studies. Arch Neurol. 1966 Jul;15(1):35–51. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1966.00470130039004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson A. J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its association with dementia, parkinsonism and other neurological disorders: a review. Brain. 1981 Jun;104(2):217–247. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T., Brock D. J., Chancellor A. M., Warlow C. P., Swingler R. J. Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) mutations and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet. 1993 Oct 23;342(8878):1050–1051. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)92905-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Hirano A. Involvement of the brain stem reticular formation in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Neuropathol. 1992 Jan-Feb;11(1):41–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. K., Marszalek J. R., Cleveland D. W. A mutant neurofilament subunit causes massive, selective motor neuron death: implications for the pathogenesis of human motor neuron disease. Neuron. 1994 Oct;13(4):975–988. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
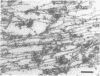
- Lowe J. New pathological findings in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1994 Jul;124 (Suppl):38–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetto V., Perry G., Tabaton M., Mulvihill P., Fried V. A., Smith H. T., Gambetti P., Autilio-Gambetti L. Ubiquitin is associated with abnormal cytoplasmic filaments characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4501–4505. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa H., Matsumoto S., Yen S. H., Hirano A., Rojas-Corona R. R., Donnenfeld H. Focal accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilaments within anterior horn cell in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;79(1):37–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00308955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris F., Shepherd R., Denys E., U K., Mukai E., Elias L., Holden D., Norris H. Onset, natural history and outcome in idiopathic adult motor neuron disease. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Aug;118(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olanow C. W. A radical hypothesis for neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Nov;16(11):439–444. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrell R. W., deBelleroche J. S. Superoxide dismutase and ALS. Lancet. 1994 Dec 17;344(8938):1651–1652. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pramatarova A., Goto J., Nanba E., Nakashima K., Takahashi K., Takagi A., Kanazawa I., Figlewicz D. A., Rouleau G. A. A two basepair deletion in the SOD 1 gene causes familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Nov;3(11):2061–2062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberecht W., Sapp P., Viaene M. K., Rosen D., McKenna-Yasek D., Haines J., Horvitz R., Theys P., Brown R., Jr Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase activity in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem. 1994 Jan;62(1):384–387. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62010384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen D. R., Siddique T., Patterson D., Figlewicz D. A., Sapp P., Hentati A., Donaldson D., Goto J., O'Regan J. P., Deng H. X. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):59–62. doi: 10.1038/362059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer D., Autilio-Gambetti L., Chiò A., Gambetti P., Giordana M. T., Gullotta F., Migheli A., Vigliani M. C. Ubiquitin in motor neuron disease: study at the light and electron microscope. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1991 Jul;50(4):463–473. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199107000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. P., Emser W., Heimes C. Familial occurrence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, parkinsonism, and dementia. Ann Neurol. 1984 Dec;16(6):642–648. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar S. K., Yanagihara R., Garruto R. M., Grundke-Iqbal I., Kosik K. S., Gajdusek D. C. Immunocytochemical characterization of neurofibrillary tangles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and parkinsonism-dementia of Guam. Ann Neurol. 1989 Feb;25(2):146–151. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddique T., Figlewicz D. A., Pericak-Vance M. A., Haines J. L., Rouleau G., Jeffers A. J., Sapp P., Hung W. Y., Bebout J., McKenna-Yasek D. Linkage of a gene causing familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis to chromosome 21 and evidence of genetic-locus heterogeneity. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1381–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi H., Oyanagi K., Ikuta F., Tanaka M., Yuasa T., Miyatake T. Widespread multiple system degeneration in a patient with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Dec 1;120(1):15–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90018-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troncoso J. C., Hoffman P. N., Griffin J. W., Hess-Kozlow K. M., Price D. L. Aluminum intoxication: a disorder of neurofilament transport in motor neurons. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 2;342(1):172–175. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91369-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z., Cork L. C., Griffin J. W., Cleveland D. W. Increased expression of neurofilament subunit NF-L produces morphological alterations that resemble the pathology of human motor neuron disease. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90157-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waegh S. M., Lee V. M., Brady S. T. Local modulation of neurofilament phosphorylation, axonal caliber, and slow axonal transport by myelinating Schwann cells. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90183-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]