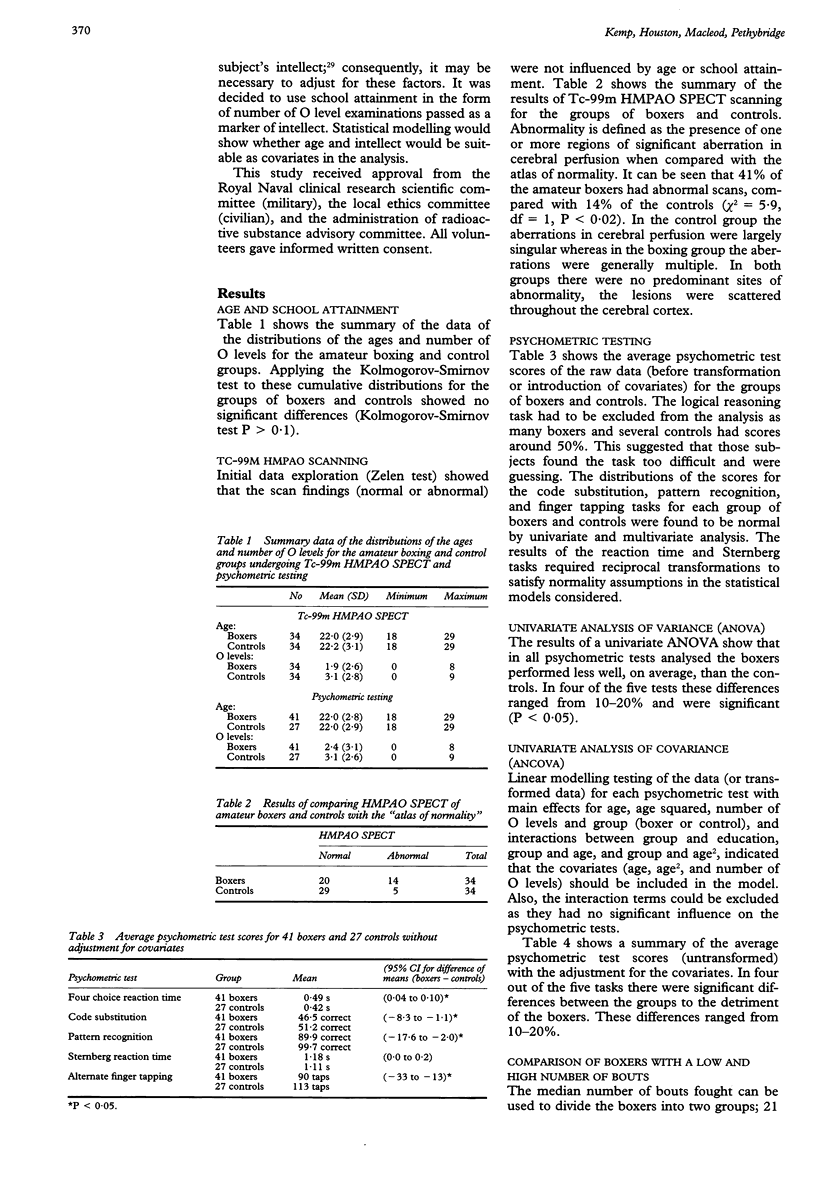
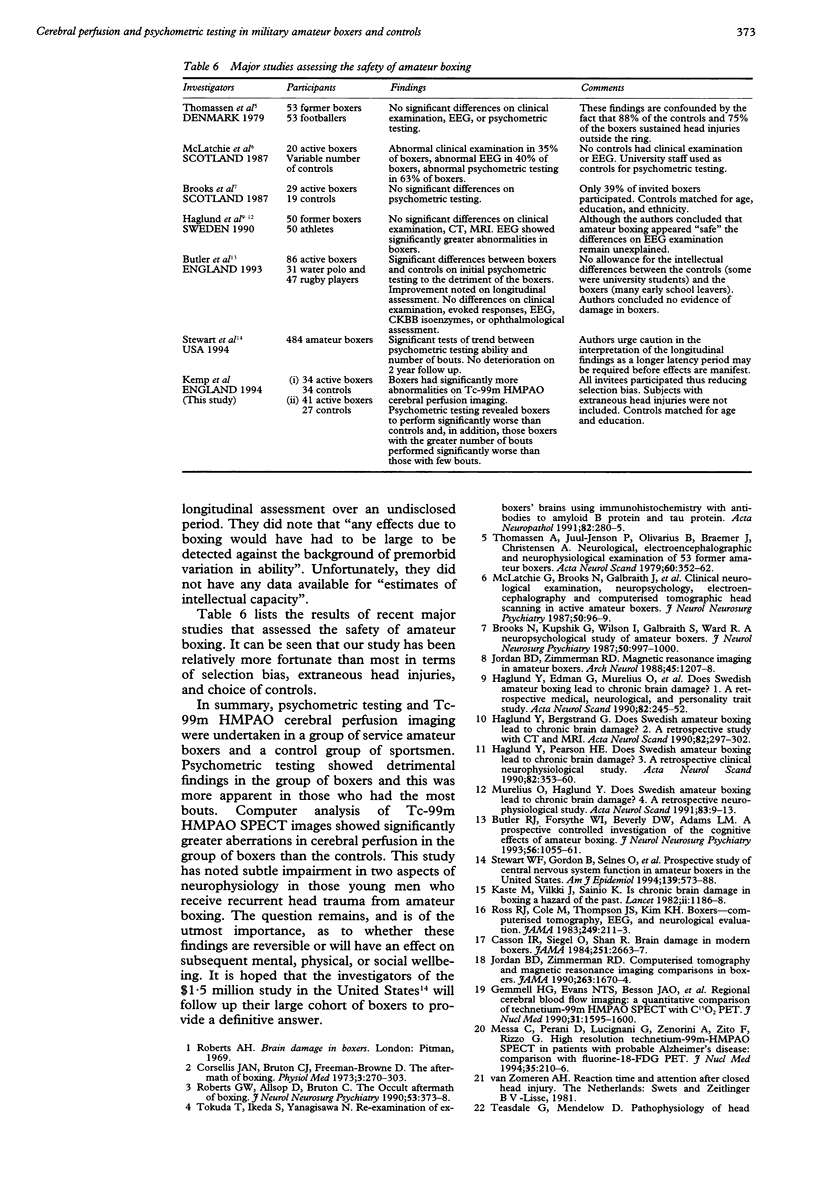
Abstract
The objective was to compare two neurophysiological variables in active amateur boxers with non-boxing sportsmen. 41 boxers and 27 controls were given psychometric tests: 34 boxers and 34 controls underwent technetium-99m hexamethylpropyleneamineoxime single photon emission computerised tomography (Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT) cerebral perfusion scans. The controls performed better at most aspects of the psychometric tests. Boxers who had fought fewer bouts had a tendency to perform better at psychometric tests than those boxers who had fought more bouts. Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT cerebral perfusion scanning showed that controls had less aberrations in cerebral perfusion than the boxers. In conclusion, significant differences were shown in two neurophysiological variables between young amateur sportsmen who box and those who do not. The long term effects of these findings remain unknown.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashall F., Bramwell M. E., Harris H. A new marker for human cancer cells. 1 The Ca antigen and the Ca1 antibody. Lancet. 1982 Jul 3;2(8288):1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azari N. P., Pettigrew K. D., Schapiro M. B., Haxby J. V., Grady C. L., Pietrini P., Salerno J. A., Heston L. L., Rapoport S. I., Horwitz B. Early detection of Alzheimer's disease: a statistical approach using positron emission tomographic data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993 May;13(3):438–447. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1993.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber D. C. Registration of low resolution medical images. Phys Med Biol. 1992 Jul;37(7):1485–1498. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/37/7/002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks N., Kupshik G., Wilson L., Galbraith S., Ward R. A neuropsychological study of active amateur boxers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Aug;50(8):997–1000. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.8.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler R. J., Forsythe W. I., Beverly D. W., Adams L. M. A prospective controlled investigation of the cognitive effects of amateur boxing. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1993 Oct;56(10):1055–1061. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.56.10.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buée L., Hof P. R., Bouras C., Delacourte A., Perl D. P., Morrison J. H., Fillit H. M. Pathological alterations of the cerebral microvasculature in Alzheimer's disease and related dementing disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 1994;87(5):469–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00294173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casson I. R., Siegel O., Sham R., Campbell E. A., Tarlau M., DiDomenico A. Brain damage in modern boxers. JAMA. 1984 May 25;251(20):2663–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C. M., Ammann W., Martin W. R., Ty P., Hayden M. R. The FDG/PET methodology for early detection of disease onset: a statistical model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Mar;11(2):A96–102. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C., Carson R., Kessler R., Margolin R., Buchsbaum M., DeLisi L., King C., Cohen R. Alternative statistical models for the examination of clinical positron emission tomography/fluorodeoxyglucose data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Mar;5(1):142–150. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsellis J. A., Bruton C. J., Freeman-Browne D. The aftermath of boxing. Psychol Med. 1973 Aug;3(3):270–303. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700049588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas F., Alavi A., Chawluk J. B., Zimmerman R. A., Hackney D., Bilaniuk L., Rosen M., Alves W. M., Hurtig H. I., Jamieson D. G. Comparison of CT, MR, and PET in Alzheimer's dementia and normal aging. J Nucl Med. 1989 Oct;30(10):1607–1615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell H. G., Evans N. T., Besson J. A., Roeda D., Davidson J., Dodd M. G., Sharp P. F., Smith F. W., Crawford J. R., Newton R. H. Regional cerebral blood flow imaging: a quantitative comparison of technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT with C15O2 PET. J Nucl Med. 1990 Oct;31(10):1595–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentleman S. M., Graham D. I., Roberts G. W. Molecular pathology of head trauma: altered beta APP metabolism and the aetiology of Alzheimer's disease. Prog Brain Res. 1993;96:237–246. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63270-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronwall D., Wrightson P. Cumulative effect of concussion. Lancet. 1975 Nov 22;2(7943):995–997. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund Y., Bergstrand G. Does Swedish amateur boxing lead to chronic brain damage? 2. A retrospective study with CT and MRI. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990 Nov;82(5):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1990.tb03307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund Y., Edman G., Murelius O., Oreland L., Sachs C. Does Swedish amateur boxing lead to chronic brain damage? 1. A retrospective medical, neurological and personality trait study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990 Oct;82(4):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1990.tb01614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haglund Y., Persson H. E. Does Swedish amateur boxing lead to chronic brain damage? 3. A retrospective clinical neurophysiological study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990 Dec;82(6):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1990.tb03316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston A. S., Kemp P. M., Macleod M. A. A method for assessing the significance of abnormalities in HMPO brain SPECT images. J Nucl Med. 1994 Feb;35(2):239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. D., Zimmerman R. D. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging comparisons in boxers. JAMA. 1990 Mar 23;263(12):1670–1674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan B. D., Zimmerman R. D. Magnetic resonance imaging in amateur boxers. Arch Neurol. 1988 Nov;45(11):1207–1208. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520350045014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin H. S., Amparo E., Eisenberg H. M., Williams D. H., High W. M., Jr, McArdle C. B., Weiner R. L. Magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography in relation to the neurobehavioral sequelae of mild and moderate head injuries. J Neurosurg. 1987 May;66(5):706–713. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.66.5.0706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeith I. G., Bartholomew P. H., Irvine E. M., Cook J., Adams R., Simpson A. E. Single photon emission computerised tomography in elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease and multi-infarct dementia. Regional uptake of technetium-labelled HMPAO related to clinical measurements. Br J Psychiatry. 1993 Nov;163:597–603. doi: 10.1192/bjp.163.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLatchie G., Brooks N., Galbraith S., Hutchison J. S., Wilson L., Melville I., Teasdale E. Clinical neurological examination, neuropsychology, electroencephalography and computed tomographic head scanning in active amateur boxers. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Jan;50(1):96–99. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.1.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messa C., Perani D., Lucignani G., Zenorini A., Zito F., Rizzo G., Grassi F., Del Sole A., Franceschi M., Gilardi M. C. High-resolution technetium-99m-HMPAO SPECT in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease: comparison with fluorine-18-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 1994 Feb;35(2):210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaldi D., Brooks D. N., McColl J. H., Wyper D., Patterson J., Barron E., McCulloch J. Measurements of regional cerebral blood flow and cognitive performance in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 Jan;53(1):33–38. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murelius O., Haglund Y. Does Swedish amateur boxing lead to chronic brain damage? 4. A retrospective neuropsychological study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991 Jan;83(1):9–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1991.tb03952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton M. R., Greenwood R. J., Britton K. E., Charlesworth M., Nimmon C. C., Carroll M. J., Dolke G. A study comparing SPECT with CT and MRI after closed head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Feb;55(2):92–94. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer D. R. Microscopic lesions in the brain following head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):299–306. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W., Allsop D., Bruton C. The occult aftermath of boxing. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 May;53(5):373–378. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.5.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. J., Cole M., Thompson J. S., Kim K. H. Boxers--computed tomography, EEG, and neurological evaluation. JAMA. 1983 Jan 14;249(2):211–213. doi: 10.1001/jama.249.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. F., Gordon B., Selnes O., Bandeen-Roche K., Zeger S., Tusa R. J., Celentano D. D., Shechter A., Liberman J., Hall C. Prospective study of central nervous system function in amateur boxers in the United States. Am J Epidemiol. 1994 Mar 15;139(6):573–588. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a117047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomassen A., Juul-Jensen P., de Fine Olivarius B., Braemer J., Christensen A. L. Neurological, electroencephalographic and neuropsychological examination of 53 former amateur boxers. Acta Neurol Scand. 1979 Dec;60(6):352–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1979.tb07661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda T., Ikeda S., Yanagisawa N., Ihara Y., Glenner G. G. Re-examination of ex-boxers' brains using immunohistochemistry with antibodies to amyloid beta-protein and tau protein. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82(4):280–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00308813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnage J. J., Kennedy R. S., Smith M. G., Baltzley D. R., Lane N. E. Development of microcomputer-based mental acuity tests. Ergonomics. 1992 Oct;35(10):1271–1295. doi: 10.1080/00140139208967393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



