Abstract
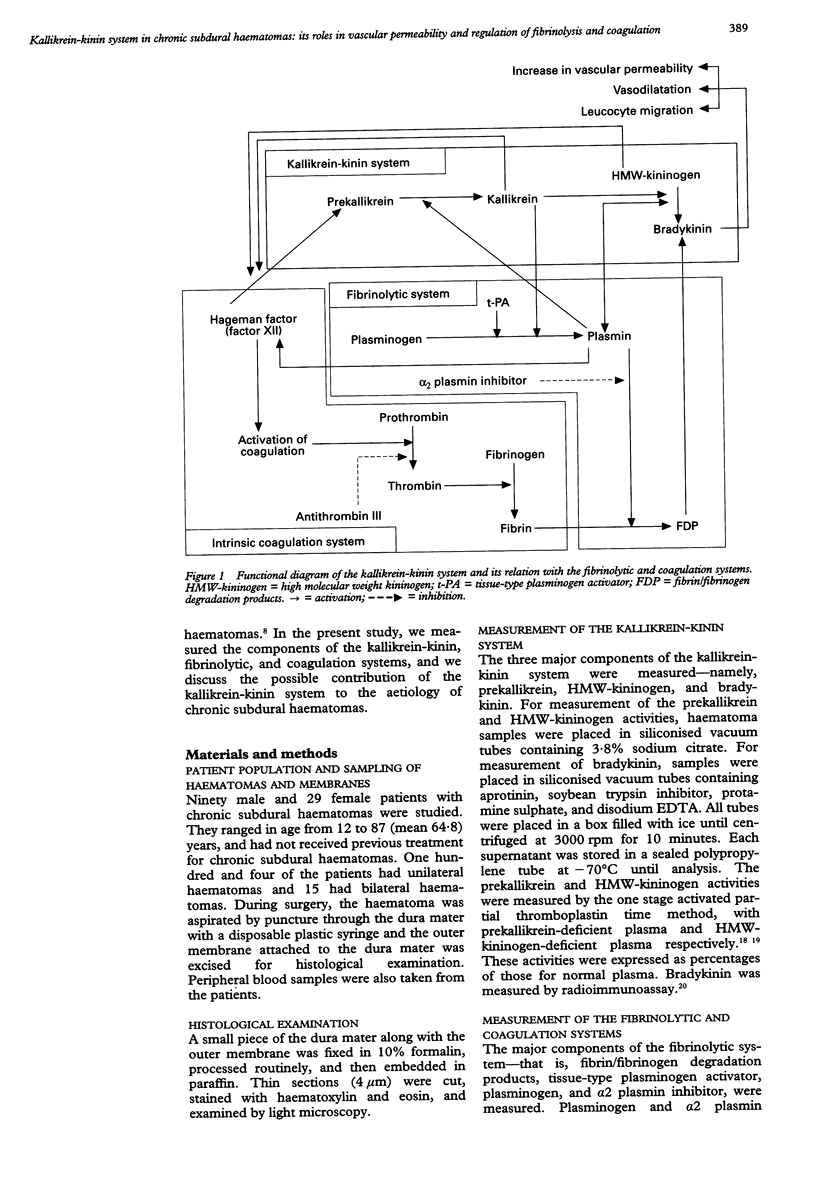
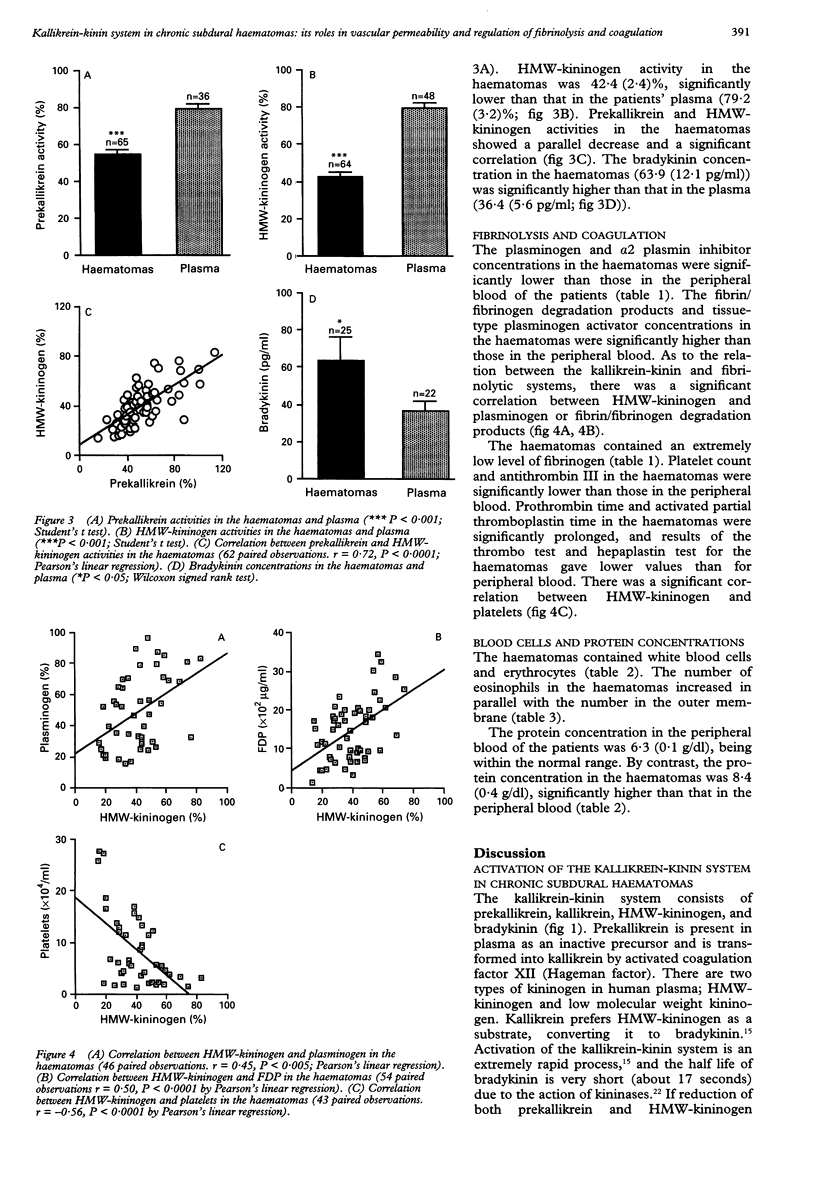
The kallikrein-kinin system is closely related to both fibrinolysis and coagulation, and bradykinin--the end product of this system--is a powerful mediator which increases vascular permeability. In the present study, to test the hypothesis that the kallikrein-kinin system plays a part in the aetiology of chronic subdural haematomas, components of this system (prekallikrein, high molecular weight kininogen (HMW-kininogen), and bradykinin), and those of the fibrinolytic and coagulation systems were measured at 134 haematoma sites in 119 patients. The activities of prekallikrein and HMW-kininogen in the haematomas were significantly lower than those in the plasma of the patients, and showed a parallel decrease. The bradykinin concentration in the haematomas was significantly higher than that in the plasma. These results indicate activation of the kallikrein-kinin system in chronic subdural haematomas. The activation of both fibrinolysis and coagulation was also shown, and there was a significant correlation between HMW-kininogen and plasminogen, fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products, or platelets in the haematomas. This suggests regulation of fibrinolysis and coagulation by the kallikrein-kinin system or mutual stimulation of these systems. In the outer membrane, perivascular haemorrhage, interstitial oedema, and leucocyte migration were evident microscopically, indicating an increase in vascular permeability. The protein concentration in the haematomas was significantly higher than that in the peripheral blood, indicating plasma exudation from the capillaries in the outer membrane. The activation of the kallikrein-kinin system, by increasing vascular permeability, may cause blood extravasation and plasma exudation from the capillaries into both the outer membrane and the haematoma cavity, resulting in enlargement of the haematoma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACK N., STEGER R. ACTIVATION OF BOVINE BRADYKININOGEN BY HUMAN PLASMIN. Life Sci. 1965 Jan;4:153–157. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsdorf N., Nilsson T., Wallén P. An enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for determination of tissue plasminogen activator applied to patients with thromboembolic disease. Thromb Haemost. 1983 Oct 31;50(3):740–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buluk K., Malofiejew M. The pharmacological properties of fibrinogen degradation products. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jan;35(1):79–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friede R. L., Schachenmayr W. The origin ofsubdural neomembranes. II. Fine structural of neomembranes. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jul;92(1):69–84. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa H., Ito H., Saito K., Ikeda K., Nitta H., Yamashita J. Immunohistochemical localization of tissue-type plasminogen activator in the lining wall of chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 1991 Jun;35(6):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(91)90177-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa M., Yamashima T., Yamashita J., Suzuki M., Shimada S. Traumatic subdural hygroma: pathology and meningeal enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosurgery. 1992 Sep;31(3):580–585. doi: 10.1227/00006123-199209000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway W. E., Belhasen L. P., Hathaway H. S. Evidence for a new plasma thromboplastin factor. I. Case report, coagulation studies and physicochemical properties. Blood. 1965 Nov;26(5):521–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoda K., Tamaki N., Masumura M., Matsumoto S., Maeda F. Magnetic resonance images of chronic subdural hematomas. J Neurosurg. 1987 Nov;67(5):677–683. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.67.5.0677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Tanaka K., Katori M. Potentiation of bradykinin-induced vascular permeability increase by prostaglandin E2 and arachidonic acid in rabbit skin. Prostaglandins. 1975 Nov;10(5):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Komai T., Yamamoto S. Fibrin and fibrinogen degradation products in chronic subdural hematoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1975;15 Pt 1:51–55. doi: 10.2176/nmc.15pt1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Saito K., Yamamoto S., Hasegawa T. Tissue-type plasminogen activator in the chronic subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 1988 Sep;30(3):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0090-3019(88)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Yamamoto S., Komai T., Mizukoshi H. Role of local hyperfibrinolysis in the etiology of chronic subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1976 Jul;45(1):26–31. doi: 10.3171/jns.1976.45.1.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Yamamoto S., Saito K., Ikeda K., Hisada K. Quantitative estimation of hemorrhage in chronic subdural hematoma using the 51Cr erythrocyte labeling method. J Neurosurg. 1987 Jun;66(6):862–864. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.66.6.0862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasawa H., Tomita S., Suzuki S. Chronic subdural hematomas. Time-density curve and iodine concentration in enhanced CT. Neuroradiology. 1987;29(1):36–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00341034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami Y., Chikama M., Tamiya T., Shimamura Y. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurgery. 1989 Jul;25(1):25–29. doi: 10.1097/00006123-198907000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS G. P. Formation of plasma kinins by plasmin. J Physiol. 1958 Feb 17;140(2):285–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau F., Lussier A., Regoli D., Giroud J. P. Pharmacology of kinins: their relevance to tissue injury and inflammation. Gen Pharmacol. 1983;14(2):209–229. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(83)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmon K. L., Webster M. E., Goldfinger S. E., Seegmiller J. E. The presence of a kinin in inflammatory synovial effusion from arthritides of varying etiologies. Arthritis Rheum. 1967 Feb;10(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/art.1780100103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Ohmori H., Kanazawa Y., Munekata K., Fukushima H., Kamata K. [The pathogenesis of chronic subdural hematoma--sequential study with computerized tomography (author's transl)]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1980 Aug;20(8):875–881. doi: 10.2176/nmc.20.875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naganuma H., Fukamachi A., Kawakami M., Misumi S., Nakajima H., Wakao T. Spontaneous resolution of chronic subdural hematomas. Neurosurgery. 1986 Nov;19(5):794–798. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198611000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh-ishi S., Katori M., Nam Han Y., Iwanaga S., Kato H. Possible physiological role of new peptide fragments released from bovine high molecular weight kininogen by plasma kallikrein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jan 15;26(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Suzuki R., Masaoka H., Matsushima Y., Inaba Y., Monma S. Role of traumatic subdural fluid collection in developing process of chronic subdural hematoma. Bull Tokyo Med Dent Univ. 1986 Sep;33(3):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYAN J. W., MOFFAT J. G., THOMPSON A. G. ROLE OF BRADYKININ IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF ACUTE PANCREATITIS. Nature. 1964 Dec 19;204:1212–1213. doi: 10.1038/2041212a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnoff O. D. Mediators of inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1976 Sep;58(3):438–446. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(76)90125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Goldsmith G., Waldmann R. Fitzgerald factor (high molecular weight kininogen) clotting activity in human plasma in health and disease in various animal plasmas. Blood. 1976 Dec;48(6):941–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Poon M. C., Vicic W., Goldsmith G. H., Jr, Menitove J. E. Human plasma prekallikrein (Fletcher factor) clotting activity and antigen in health and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jul;92(1):84–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Suzuki J. Ultrastructural observations of the capsule of chronic subdural hematoma in various clinical stages. J Neurosurg. 1975 Nov;43(5):569–578. doi: 10.3171/jns.1975.43.5.0569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John J. N., Dila C. Traumatic subdural hygroma in adults. Neurosurgery. 1981 Dec;9(6):621–626. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198112000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. L., Lang R. G., Sugar O., Moody R. A. Traumatic subdural hygroma. Neurosurgery. 1981 May;8(5):542–550. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198105000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Mikami J., Ueda M., Ito K., Sato H., Matsuoka H., Takeda S., Ohkawara S. [Analysis of chronic subdural hematoma based on CT (Part III). Clinical stage classification based on CT findings]. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 1984 Aug;24(8):607–614. doi: 10.2176/nmc.24.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The release and fate of vaso-active hormones in the circulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;35(2):209–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir B., Gordon P. Factors affecting coagulation: fibrinolysis in chronic subdural fluid collections. J Neurosurg. 1983 Feb;58(2):242–245. doi: 10.3171/jns.1983.58.2.0242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashima T., Yamamoto S., Friede R. L. The role of endothelial gap junctions in the enlargement of chronic subdural hematomas. J Neurosurg. 1983 Aug;59(2):298–303. doi: 10.3171/jns.1983.59.2.0298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasu N., Tamura A., Wakai S., Yoshimoto S. [Evolution from acute subdural hemorrhage to chronic subdural hematoma --observation of subdural hematoma by computerized tomography (author's transl)]. No Shinkei Geka. 1981 Aug;9(9):1025–1031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



