Abstract
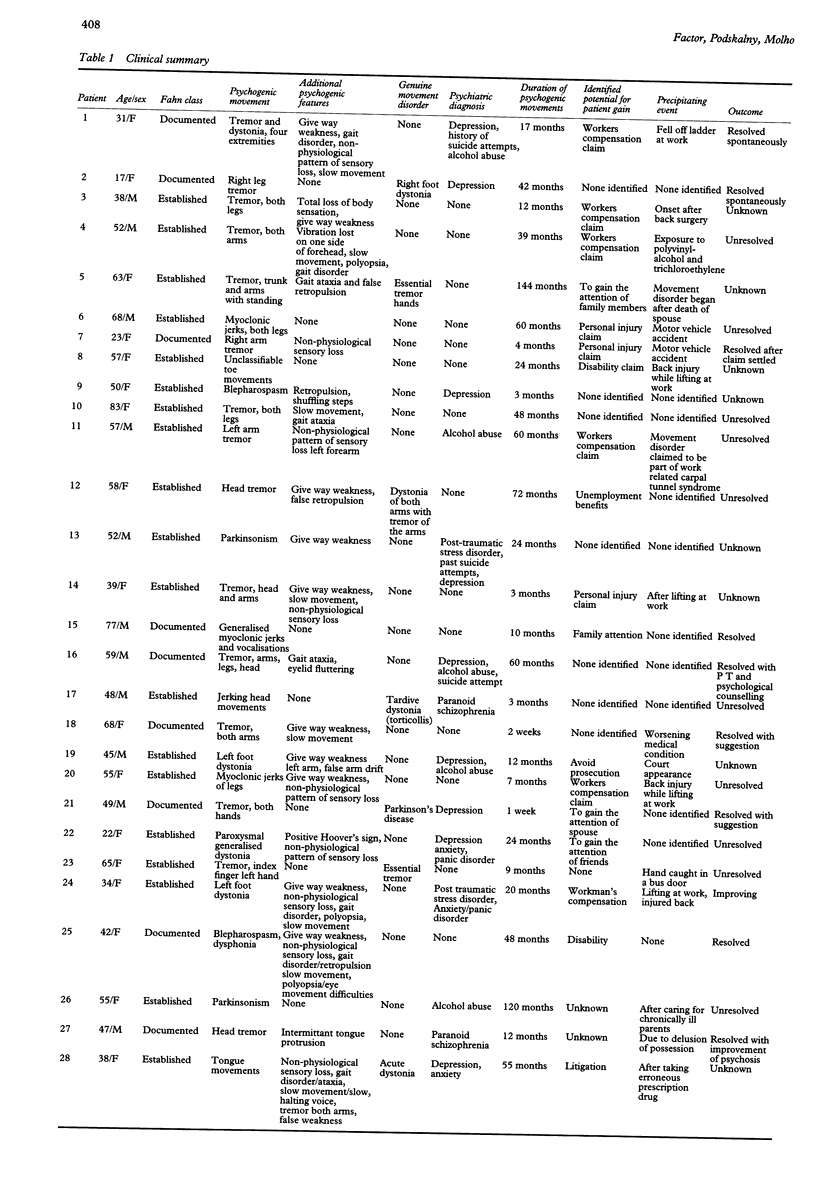
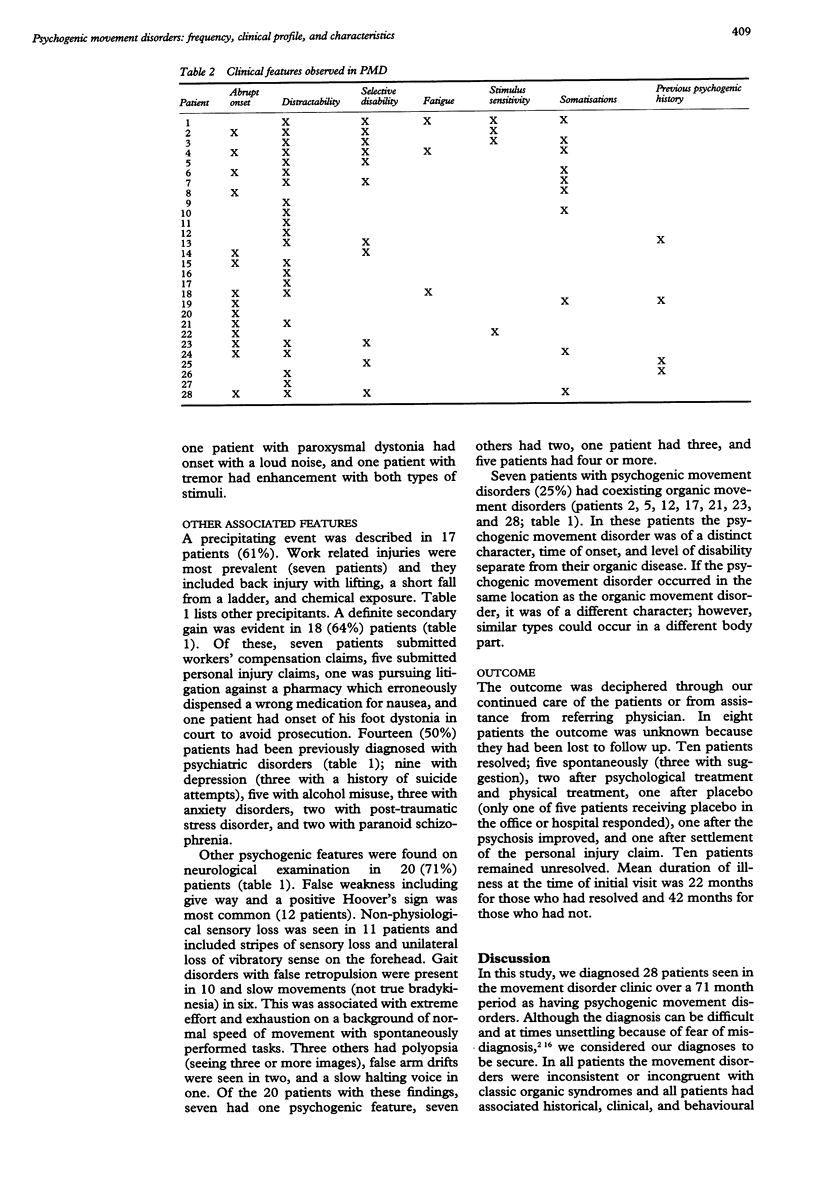
Of 842 consecutive patients with movement disorders seen over a 71 month period, 28 (3.3%) were diagnosed as having a documented or clinically established psychogenic movement disorder. Tremor was most common (50%) followed by dystonia, myoclonus, and parkinsonism. Clinical descriptions of various types are reviewed. Clinical characteristics common in these patients included distractability (86%), abrupt onset (54%), and selective disabilities (39%). Distractability seems to be most important in tremor and least important in dystonia. Other diagnostic clues included entrainment of tremor to the frequency of repetitive movements of another limb, fatigue of tremor, stimulus sensitivity, and previous history of psychogenic illness. On examination, 71% had other psychogenic features. Over 60% had a clear history of a precipitating event and secondary gain and 50% had a psychiatric diagnosis (usually depression). Twenty five per cent of patients presented with combined psychogenic movement disorder and organic movement disorder; 35% resolved and this subgroup had a shorter duration of disease than those who are unresolved. Psychogenic movement disorder represents an uncommon diagnosis among patients with movement disorders. The ability to make a diagnosis rests on the presence of a multitude of clinical clues and therapeutic action should be taken as early as possible.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assael M. Hysterical blepharospasm. Dis Nerv Syst. 1967 Apr;28(4):256–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batshaw M. L., Wachtel R. C., Deckel A. W., Whitehouse P. J., Moses H., 3rd, Fochtman L. J., Eldridge R. Munchausen's syndrome simulating torsion dystonia. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 30;312(22):1437–1439. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505303122207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooley J. M., Stokes A., Gordon K. E. Pseudo-tics in Tourette syndrome. J Child Neurol. 1994 Jan;9(1):50–51. doi: 10.1177/088307389400900112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahn S., Williams D. T. Psychogenic dystonia. Adv Neurol. 1988;50:431–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankovic J., Ford J. Blepharospasm and orofacial-cervical dystonia: clinical and pharmacological findings in 100 patients. Ann Neurol. 1983 Apr;13(4):402–411. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller W., Lang A., Vetere-Overfield B., Findley L., Cleeves L., Factor S., Singer C., Weiner W. Psychogenic tremors. Neurology. 1989 Aug;39(8):1094–1099. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.8.1094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. E. Psychogenic dystonia: a review of 18 cases. Can J Neurol Sci. 1995 May;22(2):136–143. doi: 10.1017/s031716710004021x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lempert T., Dieterich M., Huppert D., Brandt T. Psychogenic disorders in neurology: frequency and clinical spectrum. Acta Neurol Scand. 1990 Nov;82(5):335–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1990.tb03312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D. Hysteria--a neurologist's view. Psychol Med. 1986 May;16(2):277–288. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700009090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monday K., Jankovic J. Psychogenic myoclonus. Neurology. 1993 Feb;43(2):349–352. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramani V. Intensive monitoring of psychogenic seizures, aggression, and dyscontrol syndromes. Adv Neurol. 1987;46:203–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranawaya R., Riley D., Lang A. Psychogenic dyskinesias in patients with organic movement disorders. Mov Disord. 1990;5(2):127–133. doi: 10.1002/mds.870050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomone G. A complex case of hysterical blepharospasm. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 1983 Dec;5(6):468–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters A. S., Boudwin J., Wright D., Jones K. Three hysterical movement disorders. Psychol Rep. 1988 Jun;62(3):979–985. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1988.62.3.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters A. S., Hening W. A. Noise-induced psychogenic tremor associated with post-traumatic stress disorder. Mov Disord. 1992 Oct;7(4):333–338. doi: 10.1002/mds.870070406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolsey R. M. Hysteria: 1875 to 1975. Dis Nerv Syst. 1976 Jul;37(7):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



