Abstract
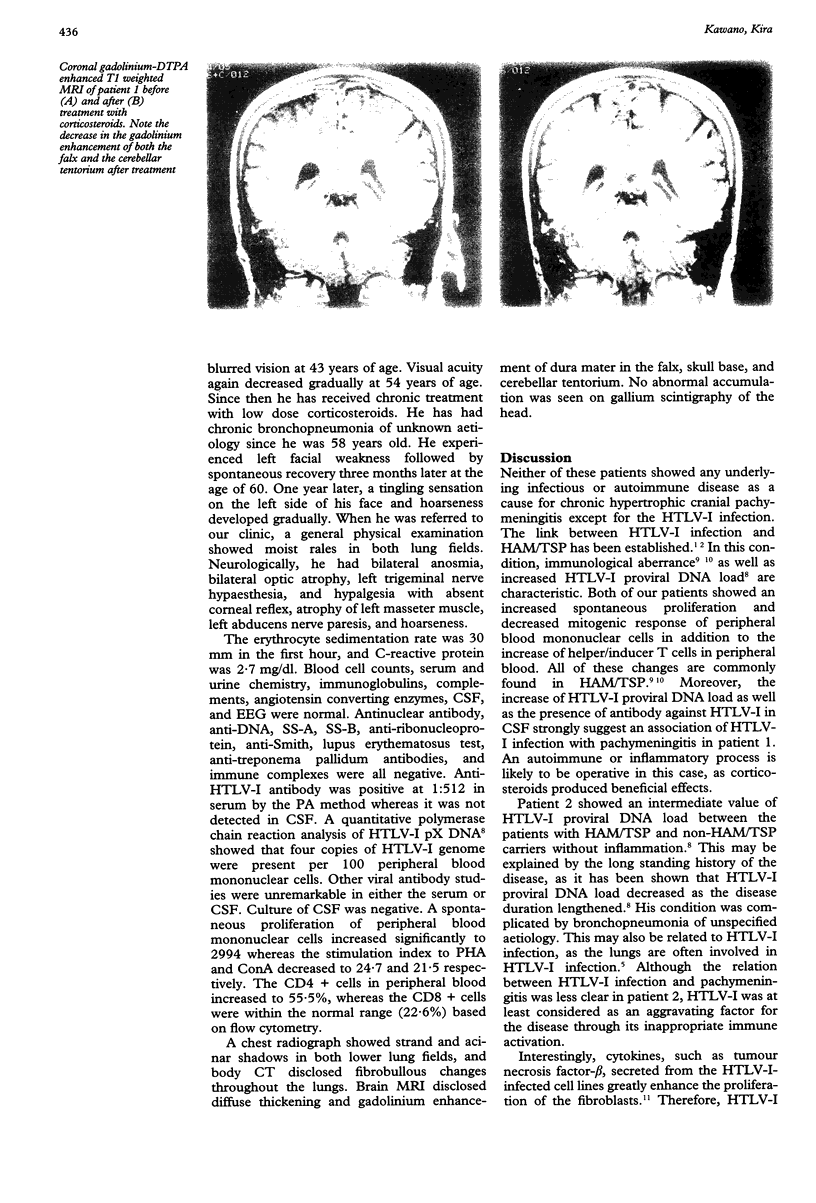
Two patients presenting with recurrent multiple cranial neuropathy showed diffuse thickening and gadolinium enhancement of the dura mater on brain MRI. Both had anti-HTLV-I antibodies in serum. A quantitative polymerase chain reaction study of the peripheral blood disclosed that the HTLV-I proviral DNA loads increased considerably in one case and moderately in the other. Both showed a spontaneous proliferation of peripheral blood lymphocytes as well as an increase in helper/inducer T cells. Neither had any other underlying infections or autoimmune diseases. Thus it is possible that hypertrophic pachymeningitis developed as a result of multiorgan involvement of HTLV-I infection in these patients.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gessain A., Barin F., Vernant J. C., Gout O., Maurs L., Calender A., de Thé G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985 Aug 24;2(8452):407–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92734-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Kira J., Fujii N., Goto I., Yamamoto N. Increases in helper inducer T cells and activated T cells in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol. 1989 Aug;26(2):257–262. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Minato S., Kira J., Goto I., Sato H., Okochi K., Yamamoto N. Spontaneous proliferation of peripheral blood lymphocytes increased in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Neurology. 1988 Aug;38(8):1302–1307. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.8.1302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y. Pathology of chronic myelopathy associated with HTLV-I infection (HAM/TSP). J Neurol Sci. 1990 Apr;96(1):103–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90060-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kira J., Koyanagi Y., Yamada T., Itoyama Y., Goto I., Yamamoto N., Sasaki H., Sakaki Y. Increased HTLV-I proviral DNA in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: a quantitative polymerase chain reaction study. Ann Neurol. 1991 Feb;29(2):194–201. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki M., Watanabe T., Yamaguchi K., Takatsuki K., Yoshimura K., Shirao M., Nakashima S., Mori S., Araki S., Miyata N. HTLV-I uveitis: a distinct clinical entity caused by HTLV-I. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1992 Mar;83(3):236–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1992.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka K., Maruyama I., Sato K., Kitajima I., Nakajima Y., Osame M. Chronic inflammatory arthropathy associated with HTLV-I. Lancet. 1989 Feb 25;1(8635):441–441. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfisterer M., Burkart F., Jockers G., Meyer B., Regenass S., Burckhardt D., Schmitt H. E., Müller-Brand J., Skarvan K., Stulz P. Trial of low-dose aspirin plus dipyridamole versus anticoagulants for prevention of aortocoronary vein graft occlusion. Lancet. 1989 Jul 1;2(8653):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto M., Nakashima H., Watanabe S., Uyama E., Tanaka F., Ando M., Araki S., Kawasaki S. T-lymphocyte alveolitis in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Lancet. 1987 Nov 21;2(8569):1220–1220. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91362-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F., Itoyama Y., Kira J., Fujihara K., Kobayashi T., Kitamoto T., Suzumura A., Yamamoto N., Nakajima Y., Goto I. TNF-beta produced by human T lymphotropic virus type I-infected cells influences the proliferation of human endothelial cells and fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5930–5938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




