To the Editor: Sleeping sickness, or human African trypanosomiasis, is a neglected tropical parasitic infection transmitted by the tsetse fly bite. In central and western Africa, trypanosomiasis is caused by the Trypanosoma brucei subspecies gambiense. Chronic symptoms of the disease include neurologic impairment and sleep disorders (1). Infected children and adults can exhibit other nonspecific symptoms (1,2) attributable to biologic inflammatory syndrome, usually accompanied by an increase of IgM. Sleeping sickness can be fatal if left untreated (3). Although the efforts of the World Health Organization (WHO), national control programs, and nongovernmental organizations such as Médecins Sans Frontières have substantially reduced the global burden of human African trypanosomiasis, its current annual incidence is still estimated to be ≈10,000 new cases (1,4). Most cases occur during long stays in trypanosomiasis-endemic areas. Rare alternative routes of transmission are possible in nonendemic areas (e.g., through blood transfusion or organ transplantation) (5). We report the case of a 14-month-old boy infected with Tr. brucei through the transplacental route.
The child was referred to a pediatric care unit because of psychomotor retardation and axial hypotonia. His mother was from the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and had arrived in France 3 years earlier. The pregnancy, which had been initiated and monitored in France, was normal through delivery. Nonetheless, the newborn was placed with a foster family because his mother had vigilance disorders, aphasia, fluctuating hemiparesia and tetraparesia, convulsions associated with choreiform movements, anxiety, and severe depression. The foster family reported that the child did not smile and had been unable to grasp objects in the last 8 months.
Clinical examination showed z-scores of −2.25 SD and −1.38 SD for height and weight, respectively; multiple lymph node enlargement; and absence of tendon reflexes. Intermittent fever and dystonic movements were reported later during a subsequent hospitalization. The results from blood tests were compatible with chronic inflammatory syndrome (albumin 28 g/L; hypergammaglobulinemia with IgM 7.38 g/L and IgG 31.3 g/L; leukocytes 20.9 g/L; hemoglobin concentration 98 g/L). Cranial magnetic resonance imaging showed several lesions of the white matter, mostly in the left frontotemporal lobe. The boy’s cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) contained glucose at 2.5 mmol/L, protein at 0.88 g/L, and 125 leukocytes/μL (100% lymph cells). Microscopic observation of CSF and blood smear highlighted Tr. brucei trypomastigotes (Figure, panels A and B; Video).
Figure.
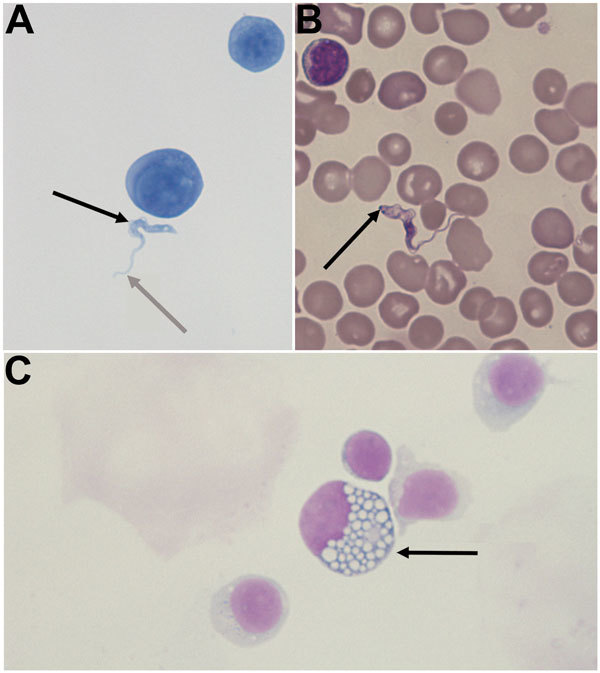
A) Cytological slide prepared from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from a child with congenital trypanosomiasis who was born in France to an African mother (Gram staining, original magnification ×1,000). B) Blood smear from the child (May-Grunewald Giemsa [MGG] staining, original magnification ×1,000). C) Mott cell in the mother’s CSF (MGG staining, original magnification ×1,000). Trypomastigote forms of Trypanosoma brucei are extracellular structures, 2 × 25 μm, with a terminal flagellum (gray arrow, panel A), which is prolonged by an undulating membrane (black arrow, panel A). A central nucleus, which was difficult to visualize by Gram staining, shows that the microorganism is eukaryote. The kinetoplast (arrow, panel B) is more visible by MGG staining. It is a small organelle at the end of the cell that permits the synchronous movement of the flagellum and the undulating membrane. The kinetoplast contains circular mitochondrial DNA (1). The numerous mononuclear cells in CSF and blood are activated lymphocytes. The Mott cell (arrow, panel C) is a plasma cell that has spherical inclusions packed into its cytoplasm. It is often found in human trypanosomiasis (3). Diagnosis was subsequently confirmed by PCR.
Video.
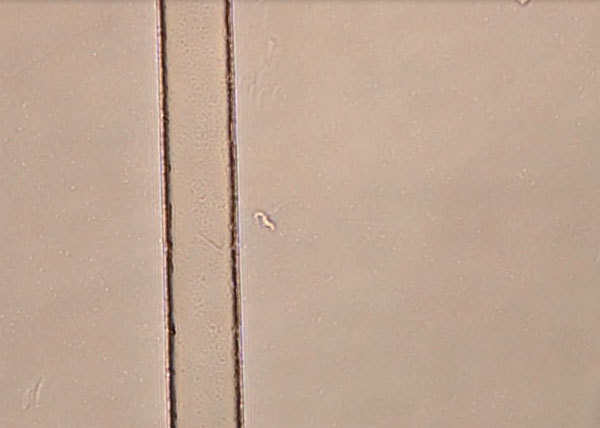
(video link forthcoming) Direct observation of the cerebrospinal fluid from a child with congenital trypanosomiasis who was born in France to an African mother (fresh mount in a Malassez counting cell, original magnification ×400). A mobile form (≈15–25 μm long) is visible along the edge of the Malassez counting chamber.
All the clinical and biologic findings were compatible with a diagnosis of autochthonous congenital trypanosomiasis in the meningo-encephalitic second stage. In addition to diffuse bilateral lesions of her white matter and biologic inflammatory syndrome, the mother also exhibited the same neurologic symptoms as the boy, at least since her last stay in DRC, a trypanosomiasis-endemic country that currently harbors ≈90% of new cases of African trypanosomiasis worldwide (6). She previously lived in Kinshasa and also reported a short visit into the bush in Angola. Until trypomastigotes were observed in her son’s CSF, the mother had not received a definitive diagnosis. She was thereafter invited for clinical and laboratory examination. Lumbar puncture and blood tests were then performed: Mott cells were present in her CSF, but no parasite was detected (Figure, panel C). Diagnosis of trypanosomiasis was subsequently supported by positive serologic test results (7).
The 2 patients were administered 400 mg/kg eflornithine monotherapy (difluoromethylornithine) daily for 2 weeks (8,9). The clinical outcome was globally satisfactory for the mother. Her serologic tests remained positive 8 months after treatment, which is long but not unusual, and confirms that serologic testing is unreliable for posttherapeutic follow up (4,7). Magnetic resonance imaging showed a substantial decrease of her brain lesions. Her son still exhibited serious neurologic sequelae, although trypomastigotes quickly disappeared from his CSF after treatment. He still had a restricted grip, axial hypotonia, and peripheral hypertonus 2 years later. To date, he has limited contact with his environment and is not able to stand up or eat alone.
Altogether, this case is exceptional for 2 reasons: 1) the diagnosis of human African trypanosomiasis in adults and children is very unusual in countries where the disease is not endemic (<100 cases are estimated to have occurred over a 10-year period) (10); and 2) congenital transmission seems to be extremely rare, even in Africa (2). To our knowledge, 17 probable cases of congenital trypanosomiasis have been reported to date, but only 14 were sufficiently described to confirm mother-to-fetus transmission (13 were attributed to Tr. brucei gambiense, and 1 was attributed to Tr. brucei rhodesiense, the eastern African subspecies) (2). Because not all official guidelines mention this route of transmission, the incidence of congenital trypanosomiasis is thought to be underestimated (4).
The diagnosis of human trypanosomiasis should always be considered for persons who have neurologic and sleep disorders and have spent time in sub-Saharan Africa as soon as infection is suspected. Congenital trypanosomiasis is rarely studied, and incidence data are limited; however, because this is another possible route of infection, even when infection of the fetus occurs long after infection of the mother, we believe congenital transmission occurs more often than suspected.
Acknowledgment
We thank Alex Edelman & Associates for scientific editing and translation of this article.
Footnotes
Suggested citation for this article: Lestrade-Carluer De Kyvon M-A, Maakaroun-Vermesse Z, Lanotte P, Priotto G, Perez-Simarro P, Guennoc A-M, et al. Congenital trypanosomiasis in child born in France to African mother [letter]. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016 May [date cited]. http://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid2205.160133
References
- 1.Kennedy PG. Clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness). Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:186–94. 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70296-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lindner AK, Priotto G. The unknown risk of vertical transmission in sleeping sickness—a literature review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4:e783. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000783 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Greenwood BM, Whittle HC. Cerebrospinal-fluid IgM in patients with sleeping-sickness. Lancet. 1973;2:525–7. 10.1016/S0140-6736(73)92348-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.World Health Organization. Control and surveillance of human African trypanosomiasis. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 2013;984:1–237 . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Herwaldt BL. Laboratory-acquired parasitic infections from accidental exposures. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001;14:659–88. 10.1128/CMR.14.3.659-688.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Simarro PP, Diarra A, Ruiz Postigo JA, Franco JR, Jannin JG. The human African trypanosomiasis control and surveillance programme of the World Health Organization 2000–2009: the way forward. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2011;5:e1007. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Noireau F, Lemesre JL, Nzoukoudi MY, Louembet MT, Gouteux JP, Frezil JL. Serodiagnosis of sleeping sickness in the Republic of the Congo: comparison of indirect immunofluorescent antibody test and card agglutination test. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82:237–40. 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90430-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lutje V, Seixas J, Kennedy A. Chemotherapy for second-stage human African trypanosomiasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;6:CD006201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Alirol E, Schrumpf D, Amici Heradi J, Riedel A, de Patoul C, Quere M, et al. Nifurtimox-eflornithine combination therapy for second-stage gambiense human African trypanosomiasis: Médecins Sans Frontières experience in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56:195–203. 10.1093/cid/cis886 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Simarro PP, Franco JR, Cecchi G, Paone M, Diarra A, Ruiz Postigo JA, et al. Human African trypanosomiasis in non-endemic countries (2000–2010). J Travel Med. 2012;19:44–53. 10.1111/j.1708-8305.2011.00576.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


