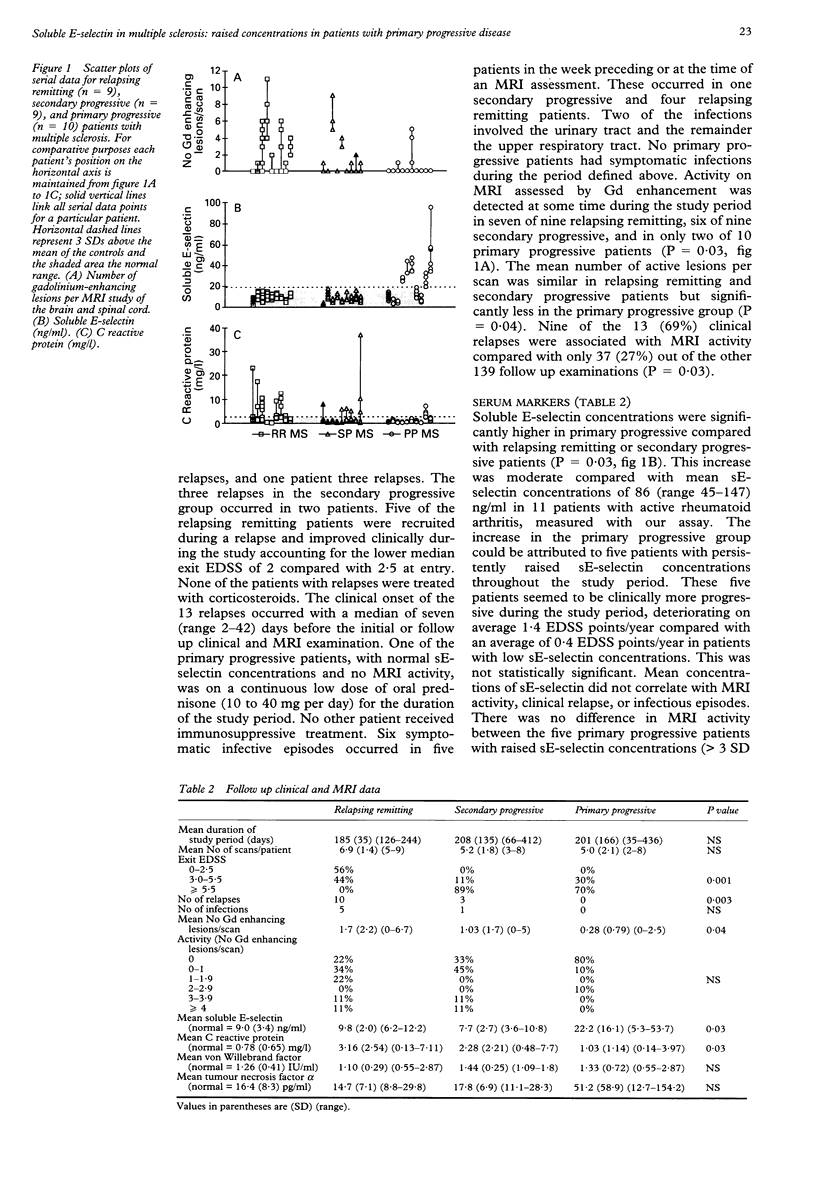
Abstract
OBJECTIVE--To determine whether concentrations of soluble E-selectin (sE-selectin), an immunological marker of endothelial activation, were correlated with gadolinium-DPTA enhancement on MRI in patients with multiple sclerosis. METHODS--Serial sE-selectin concentrations were measured in 28 patients with multiple sclerosis undergoing monthly gadolinium (Gd) enhanced MRI of the brain and spinal cord, and in 10 control subjects. C reactive protein (CRP), von Willebrand factor (vWF), and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) were also determined. RESULTS--Primary progressive patients had significantly increased sE-selectin concentrations compared with the relapsing remitting and secondary progressive patients who had normal sE-selectin concentrations (22.2 (SD1 6.1) ng/ml v 9.8 (SD2.1) ng/ml and 7.7 (SD2.7) ng/ml, respectively, P = 0.03). This difference was attributable to five of the 10 primary progressive patients who had persistently raised sE-selectin concentrations, with relatively inactive MRI studies. No correlation could be found between sE-selectin concentrations and Gd enhancement on MRI, but a close correlation existed between mean concentrations of sE-selectin and TNF alpha (r = 0.71, P < 0.001). Despite raised sE-selectin and TNF alpha concentrations, primary progressive patients had normal CRP concentrations (1.03 (SD1.14) mg/l), which were significantly lower than the relapsing remitting (3.16 (SD2.54) mg/l) and secondary progressive patients (2.28 (SD2.1) mg/l, P = 0.03). Raised CRP concentrations did correlate with infectious episodes, clinical relapse, and Gd enhancement, and were significantly raised when no MRI activity was found. Concentrations of vWF were normal in all patient groups. CONCLUSIONS--The results further high-light the differences between patients with primary progressive and those with relapsing remitting/secondary progressive multiple sclerosis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antel J. P., Owens T. The attraction of adhesion molecules. Ann Neurol. 1993 Aug;34(2):123–124. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P. Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:767–804. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.004003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserr H. F., Knopf P. M. Cervical lymphatics, the blood-brain barrier and the immunoreactivity of the brain: a new view. Immunol Today. 1992 Dec;13(12):507–512. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dore-Duffy P., Newman W., Balabanov R., Lisak R. P., Mainolfi E., Rothlein R., Peterson M. Circulating, soluble adhesion proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with multiple sclerosis: correlation with clinical activity. Ann Neurol. 1995 Jan;37(1):55–62. doi: 10.1002/ana.410370111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling P. C., Cook S. D. Disease markers in acute multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 1976 Oct;33(10):668–667. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500100002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Khew-Goodall Y., Vadas M. A. Transforming growth factor-beta inhibits E-selectin expression on human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1993 May 15;150(10):4494–4503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Reiners K., Michels M., Hughes R. A., Heidenreich F., Zielasek J., Enders U., Toyka K. V. Serum levels of soluble E-selectin (ELAM-1) in immune-mediated neuropathies. Neurology. 1994 Jun;44(6):1153–1158. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.6.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser S. L., Bhan A. K., Gilles F., Kemp M., Kerr C., Weiner H. L. Immunohistochemical analysis of the cellular infiltrate in multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):578–587. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins C. P., Munro P. M., MacKenzie F., Kesselring J., Tofts P. S., du Boulay E. P., Landon D. N., McDonald W. I. Duration and selectivity of blood-brain barrier breakdown in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis studied by gadolinium-DTPA and protein markers. Brain. 1990 Apr;113(Pt 2):365–378. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.2.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillert J., Grönning M., Nyland H., Link H., Olerup O. An immunogenetic heterogeneity in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Oct;55(10):887–890. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.10.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Imura A., Tanaka K., Shirane H., Okuma M., Uchiyama T. E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 mediate adult T-cell leukemia cell adhesion to endothelial cells. Blood. 1993 Sep 1;82(5):1590–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D., Taubenberger J. K., Cannella B., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S., McFarland H. F. Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging findings and lesion development in chronic, active multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1993 Nov;34(5):661–669. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermode A. G., Thompson A. J., Tofts P., MacManus D. G., Kendall B. E., Kingsley D. P., Moseley I. F., Rudge P., McDonald W. I. Breakdown of the blood-brain barrier precedes symptoms and other MRI signs of new lesions in multiple sclerosis. Pathogenetic and clinical implications. Brain. 1990 Oct;113(Pt 5):1477–1489. doi: 10.1093/brain/113.5.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D. S., Lee K. Y. Serum soluble E-selectin levels in Kawasaki disease. Scand J Rheumatol. 1994;23(5):283–286. doi: 10.3109/03009749409103730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1444–1452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuruvilla A. P., Shah R., Hochwald G. M., Liggitt H. D., Palladino M. A., Thorbecke G. J. Protective effect of transforming growth factor beta 1 on experimental autoimmune diseases in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2918–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. P., Kvaale G., Riise T., Nyland H., Aarli J. A. Multiple sclerosis--more than one disease? Acta Neurol Scand. 1985 Aug;72(2):145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1985.tb00856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeuwenberg J. F., Smeets E. F., Neefjes J. J., Shaffer M. A., Cinek T., Jeunhomme T. M., Ahern T. J., Buurman W. A. E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 are released by activated human endothelial cells in vitro. Immunology. 1992 Dec;77(4):543–549. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link J., Söderström M., Ljungdahl A., Höjeberg B., Olsson T., Xu Z., Fredrikson S., Wang Z. Y., Link H. Organ-specific autoantigens induce interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 mRNA expression in mononuclear cells in multiple sclerosis and myasthenia gravis. Neurology. 1994 Apr;44(4):728–734. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.4.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Chi-Rosso G., Leone D. R., Rosa M. D., Bixler S., Newman B. M., Luhowskyj S., Benjamin C. D., Dougas I. G., Goelz S. E. Expression and functional characterization of a soluble form of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):124–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigand M., Oger J. J., Fauchet R., Sabouraud O., Genetet B. HLA profiles in multiple sclerosis suggest two forms of disease and the existence of protective haplotypes. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Mar;53(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. H., Barkhof F., Berry I., Kappos L., Scotti G., Thompson A. J. Magnetic resonance imaging in monitoring the treatment of multiple sclerosis: concerted action guidelines. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1991 Aug;54(8):683–688. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.54.8.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusinow S. R., Federici A. B., Zimmerman T. S., Curd J. G. Increased von Willebrand factor antigen in the plasma of patients with vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Dec;27(12):1405–1410. doi: 10.1002/art.1780271211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka N., Akiguchi I., Kawasaki T., Ohnishi K., Kimura J. Elevated serum levels of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecules in Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol. 1994 May;35(5):621–624. doi: 10.1002/ana.410350518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olerup O., Hillert J., Fredrikson S., Olsson T., Kam-Hansen S., Möller E., Carlsson B., Wallin J. Primarily chronic progressive and relapsing/remitting multiple sclerosis: two immunogenetically distinct disease entities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7113–7117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paleolog E. M., Carew M. A., Pearson J. D. Effects of tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1 on von Willebrand factor secretion from human vascular endothelial cells. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Jul-Aug;60(1-2):279–285. doi: 10.1080/09553009114552011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porta M., Townsend C., Clover G. M., Nanson M., Alderson A. R., McCraw A., Kohner E. M. Evidence for functional endothelial cell damage in early diabetic retinopathy. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):597–601. doi: 10.1007/BF00257426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser C. M., Paty D. W., Scheinberg L., McDonald W. I., Davis F. A., Ebers G. C., Johnson K. P., Sibley W. A., Silberberg D. H., Tourtellotte W. W. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):227–231. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poser S., Raun N. E., Poser W. Age at onset, initial symptomatology and the course of multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand. 1982 Sep;66(3):355–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1982.tb06856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racke M. K., Sriram S., Carlino J., Cannella B., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E. Long-term treatment of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by transforming growth factor-beta 2. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jul;46(1-2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90247-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revesz T., Kidd D., Thompson A. J., Barnard R. O., McDonald W. I. A comparison of the pathology of primary and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain. 1994 Aug;117(Pt 4):759–765. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.4.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riches P., Gooding R., Millar B. C., Rowbottom A. W. Influence of collection and separation of blood samples on plasma IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-alpha concentrations. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Aug 30;153(1-2):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90314-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieckmann P., Martin S., Weichselbraun I., Albrecht M., Kitze B., Weber T., Tumani H., Broocks A., Lüer W., Helwig A. Serial analysis of circulating adhesion molecules and TNF receptor in serum from patients with multiple sclerosis: cICAM-1 is an indicator for relapse. Neurology. 1994 Dec;44(12):2367–2372. doi: 10.1212/wnl.44.12.2367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez M., Scheithauer B. W., Forbes G., Kelly P. J. Oligodendrocyte injury is an early event in lesions of multiple sclerosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993 Jul;68(7):627–636. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60597-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuller E., Allinquant B. Determination of C-reactive protein by electroimmunodiffusion in blood and CSF of neurological patients. Eur Neurol. 1973;9(4):216–223. doi: 10.1159/000114227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Hentges R. Association between tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease progression in patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 15;325(7):467–472. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108153250704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. J., Kermode A. G., Wicks D., MacManus D. G., Kendall B. E., Kingsley D. P., McDonald W. I. Major differences in the dynamics of primary and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1991 Jan;29(1):53–62. doi: 10.1002/ana.410290111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lambalgen R., Sanders E. A., D'Amaro J. Sex distribution, age of onset and HLA profiles in two types of multiple sclerosis. A role for sex hormones and microbial infections in the development of autoimmunity? J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;76(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(86)90138-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



