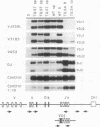
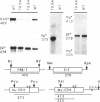
Abstract
Formation of a complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain transcription unit involves the ordered rearrangement of variable (V), diversity (D), and joining (J) region gene segments. In antibody-producing cells, this process is regulated such that only one of two antibody genes is expressed. Experiments with transgenic mice suggest that this mechanism, known as allelic exclusion, is mediated through the membrane-bound form of the immunoglobulin heavy chain. However, in all transgenic lines produced to date exclusion of the endogenous genes by the transgene is incomplete. To characterize the molecular basis for this escape from regulation, we have examined the rearrangements of endogenous immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. We find that a transgene that encodes the membrane-bound form of human IgM efficiently inhibits rearrangements of endogenous gene segments located at the 5' end of the heavy-chain locus. However, recombining elements found at the 3' end of the locus escape and continue to undergo recombination. A transgene that encodes the secreted form of the same immunoglobulin protein has no effect on recombination, regardless of position of the recombining segment in the chromosome. These results have important implications for our understanding of the control of allelic exclusion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Wood C., Thomas E., Boss M., Coffman R., Rosenberg N., Tonegawa S., Baltimore D. Ordered rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region segments. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1209–1219. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Alt F. W. Mechanism and developmental program of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in mammals. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:605–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.003133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenstein T., Krawinkel U. Immunoglobulin VH region genes of the mouse are organized in overlapping clusters. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1351–1357. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Osman G. E., Mackle J. J., Lalor T. M. The organization of the mouse Igh-V locus. Dispersion, interspersion, and the evolution of VH gene family clusters. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2261–2278. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Riblet R. The immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the mouse. I. One hundred Igh-V genes comprise seven families of homologous genes. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):922–930. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L. Surface antigen expression and immunoglobulin gene rearrangement during mouse pre-B cell development. Immunol Rev. 1982;69:5–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dildrop R., Krawinkel U., Winter E., Rajewsky K. VH-gene expression in murine lipopolysaccharide blasts distributes over the nine known VH-gene groups and may be random. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Nov;15(11):1154–1156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Krippl B., Blackwell T. K., Furley A. J., Suh H., Winoto A., Cook W. D., Hood L., Costantini F., Alt F. W. Separate elements control DJ and VDJ rearrangement in a transgenic recombination substrate. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):117–125. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstein R. M., Frankel W. N., Hsieh C. L., Durdik J. M., Rath S., Coffin J. M., Nisonoff A., Selsing E. Isotype switching of an immunoglobulin heavy chain transgene occurs by DNA recombination between different chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):537–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90450-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandien A., Coutinho A., Andersson J., Freitas A. A. Endogenous VH gene family expression in immunoglobulin-transgenic mice: evidence for selection of antibody repertoires. Int Immunol. 1991 Jan;3(1):67–73. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Marx M. Stable propagation of the active transcriptional state of an immunoglobulin mu gene requires continuous enhancer function. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):645–654. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90223-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacomini J., Yannoutsos N., Bandyopadhay S., Imanishi-Kari T. Endogenous immunoglobulin expression in mu transgenic mice. Int Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(2):185–196. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinfield R., Hardy R. R., Tarlinton D., Dangl J., Herzenberg L. A., Weigert M. Recombination between an expressed immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene and a germline variable gene segment in a Ly 1+ B-cell lymphoma. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):843–846. doi: 10.1038/322843a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manz J., Denis K., Witte O., Brinster R., Storb U. Feedback inhibition of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement by membrane mu, but not by secreted mu heavy chains. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1363–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Schmidt E. V., Shaw A. C., Sinn E., Campos-Torres J., Mathey-Prevot B., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. A human immunoglobulin gene reduces the incidence of lymphomas in c-Myc-bearing transgenic mice. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):446–450. doi: 10.1038/336446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Shaw A. C., Sinn E., Campos-Torres J., Leder P. Allelic exclusion in transgenic mice carrying mutant human IgM genes. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1969–1974. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenzweig M. C., Shaw A. C., Sinn E., Danner D. B., Holmes K. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Leder P. Allelic exclusion in transgenic mice that express the membrane form of immunoglobulin mu. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):816–819. doi: 10.1126/science.3107126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Schatz D. G., Gorka C., Baltimore D. RAG-1 and RAG-2, adjacent genes that synergistically activate V(D)J recombination. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1517–1523. doi: 10.1126/science.2360047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto M., Murakami M., Shimizu A., Ozaki S., Tsubata T., Kumagai S., Honjo T. A transgenic model of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):71–79. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmutter R. M., Kearney J. F., Chang S. P., Hood L. E. Developmentally controlled expression of immunoglobulin VH genes. Science. 1985 Mar 29;227(4694):1597–1601. doi: 10.1126/science.3975629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rath S., Durdik J., Gerstein R. M., Selsing E., Nisonoff A. Quantitative analysis of idiotypic mimicry and allelic exclusion in mice with a mu Ig transgene. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):2074–2080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathbun G. A., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Organization of the murine immunoglobulin VH complex in the inbred strains. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2931–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. G., Jackson S., Alt F. W. VHDJH formation and DJH replacement during pre-B differentiation: non-random usage of gene segments. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Köhler G. Transmission and expression of a specific pair of rearranged immunoglobulin mu and kappa genes in a transgenic mouse line. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):330–334. doi: 10.1038/314330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D. Virus-transformed pre-B cells show ordered activation but not inactivation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and transcription. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):711–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze D. H., Kelsoe G. Genotypic analysis of B cell colonies by in situ hybridization. Stoichiometric expression of three VH families in adult C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):163–172. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Nussenzweig M. C., Han H., Sanchez M., Honjo T. Trans-splicing as a possible molecular mechanism for the multiple isotype expression of the immunoglobulin gene. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1385–1393. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu A., Nussenzweig M. C., Mizuta T. R., Leder P., Honjo T. Immunoglobulin double-isotype expression by trans-mRNA in a human immunoglobulin transgenic mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8020–8023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stall A. M., Kroese F. G., Gadus F. T., Sieckmann D. G., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Rearrangement and expression of endogenous immunoglobulin genes occur in many murine B cells expressing transgenic membrane IgM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storb U. Transgenic mice with immunoglobulin genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:151–174. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D., Costantini F., Imanishi-Kari T., Baltimore D. A transgenic immunoglobulin mu gene prevents rearrangement of endogenous genes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):117–127. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. E., Paige C. J. VH gene family utilization in colonies derived from B and pre-B cells detected by the RNA colony blot assay. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3475–3481. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Desiderio S. V., Paskind M., Kearney J. F., Baltimore D., Alt F. W. Preferential utilization of the most JH-proximal VH gene segments in pre-B-cell lines. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):727–733. doi: 10.1038/311727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Malynn B. A., Alt F. W. Developmentally regulated and strain-specific expression of murine VH gene families. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):417–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]