Abstract
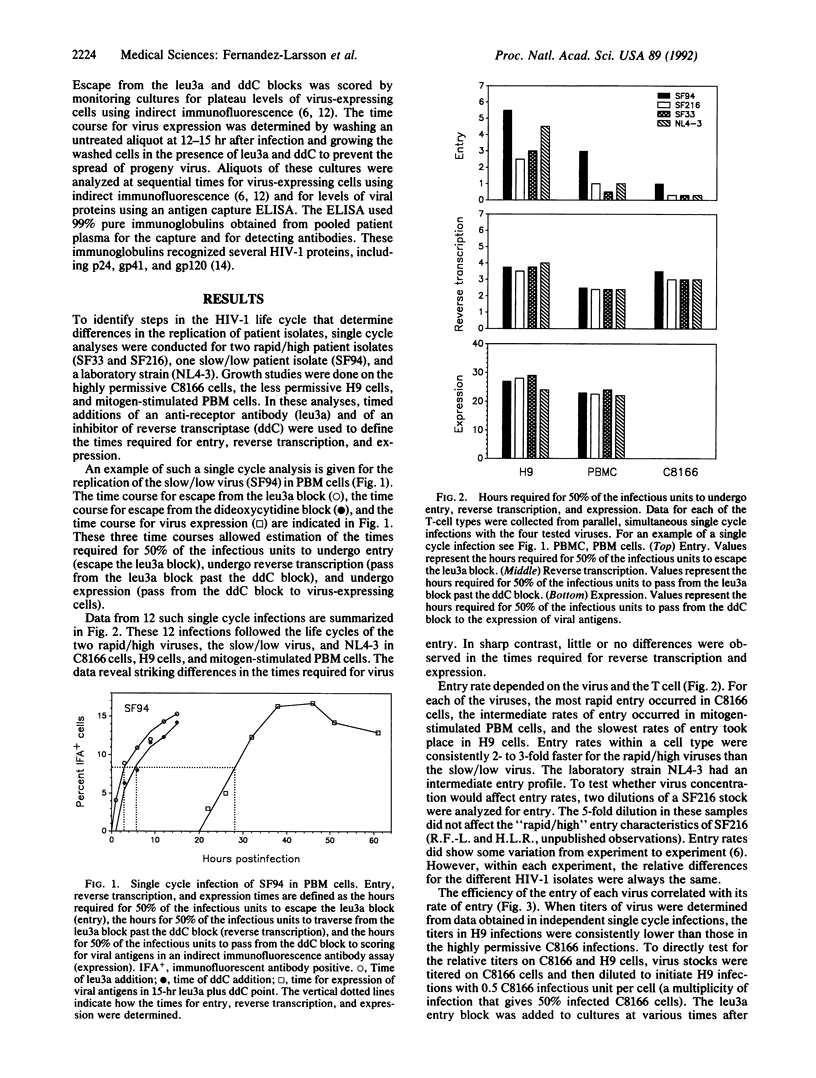
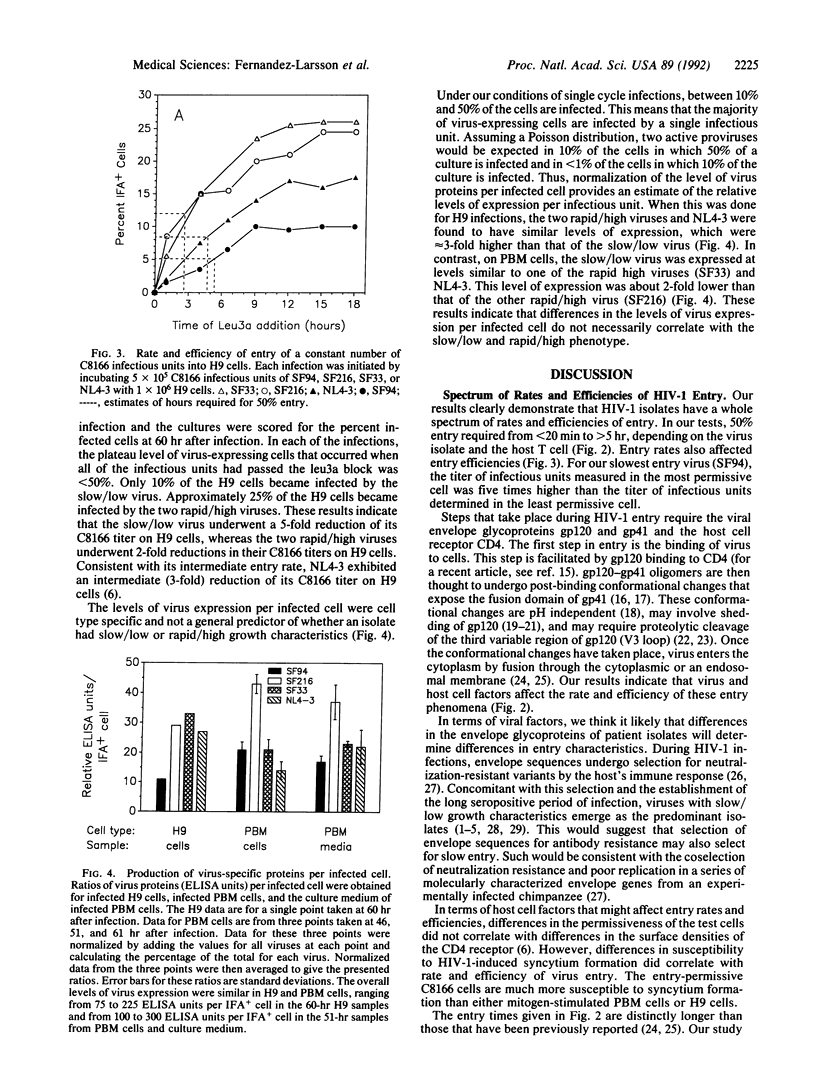
Isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) undergo many different rates of replication, with the time course of replication being determined by the host cell and the virus. Recently, we demonstrated that the permissiveness of four CD4+ T-cell lines for the laboratory strain NL4-3 correlated with the rate and efficiency of virus entry. In this study, we have analyzed the replication of a "slow/low" isolate from the pre-AIDS period of infection and two "rapid/high" isolates from the AIDS period of infection to determine which steps in the virus life cycle determine differences in the growth characteristics of patient isolates. Differences in the growth of the patient isolates correlated with differences in entry but not postentry steps of the virus life cycle. The two rapid/high patient isolates (SF33 and SF216) underwent 50% entry in less than or equal to 0.5 hr in C8166 cells, in less than or equal to 1 hr in mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and in greater than or equal to 2.5 hr in H9 cells. In contrast, a class 3 slow/low patient isolate required 1 hr for 50% entry into C8166 cells, 3 hr for 50% entry into peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and 5-6 hr for 50% entry into H9 cells. Entry efficiency correlated with entry rate, with the rapid/high viruses having a 2-fold higher titer and the slow/low virus having a 5-fold higher titer on C8166 than H9 cells. The laboratory strain NL4-3 displayed intermediate rates and efficiencies of entry. These data demonstrate that entry characteristics are major determinants of the pathogenic potential of patient isolates.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert J., Abrahamsson B., Nagy K., Aurelius E., Gaines H., Nyström G., Fenyö E. M. Rapid development of isolate-specific neutralizing antibodies after primary HIV-1 infection and consequent emergence of virus variants which resist neutralization by autologous sera. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):107–112. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199002000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asjö B., Morfeldt-Månson L., Albert J., Biberfeld G., Karlsson A., Lidman K., Fenyö E. M. Replicative capacity of human immunodeficiency virus from patients with varying severity of HIV infection. Lancet. 1986 Sep 20;2(8508):660–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Seto D., Tateno M., Levy J. A. Biologic features of HIV-1 that correlate with virulence in the host. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.2832945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Saag M. S., Decker W. D., Campbell-Hill S., Roberson J. L., Veldkamp P. J., Kappes J. C., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. High titers of cytopathic virus in plasma of patients with symptomatic primary HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):954–960. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. J., Price-Jones M. J., Stephens P. E., Sutton C., Schulz T. F., Clapham P. R., McKeating J. A., McClure M. O., Thomson S., Marsh M. The V3 loops of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 surface glycoproteins contain proteolytic cleavage sites: a possible function in viral fusion? AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Jan;7(1):3–16. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins L. M., Weinhold K. J., Matthews T. J., Langlois A. J., Perno C. F., Condie R. M., Allain J. P. Preparation and characterization of an intravenous solution of IgG from human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive donors. Blood. 1991 Mar 1;77(5):1111–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar E. S., Moudgil T., Meyer R. D., Ho D. D. Transient high levels of viremia in patients with primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):961–964. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenyö E. M., Morfeldt-Månson L., Chiodi F., Lind B., von Gegerfelt A., Albert J., Olausson E., Asjö B. Distinct replicative and cytopathic characteristics of human immunodeficiency virus isolates. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4414–4419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4414-4419.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallaher W. R. Detection of a fusion peptide sequence in the transmembrane protein of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):327–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90485-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewe C., Beck A., Gelderblom H. R. HIV: early virus-cell interactions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(10):965–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart T. K., Kirsh R., Ellens H., Sweet R. W., Lambert D. M., Petteway S. R., Jr, Leary J., Bugelski P. J. Binding of soluble CD4 proteins to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and infected cells induces release of envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2189–2193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Koito A., Takatsuki K., Kido H., Katunuma N. Involvement of tryptase-related cellular protease(s) in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):48–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. S., Boyle T. J., Lyerly H. K., Cullen B. R. Identification of the envelope V3 loop as the primary determinant of cell tropism in HIV-1. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1905842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsh R., Hart T. K., Ellens H., Miller J., Petteway S. A., Jr, Lambert D. M., Leary J., Bugelski P. J. Morphometric analysis of recombinant soluble CD4-mediated release of the envelope glycoprotein gp120 from HIV-1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Oct;6(10):1209–1212. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. Q., Wood C., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. The viral envelope gene is involved in macrophage tropism of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strain isolated from brain tissue. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6148–6153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6148-6153.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. O., Marsh M., Weiss R. A. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of CD4-bearing cells occurs by a pH-independent mechanism. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):513–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., McKnight A., Moore J. P. Differential loss of envelope glycoprotein gp120 from virions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates: effects on infectivity and neutralization. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):852–860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.852-860.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Broder S. Inhibition of the in vitro infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotrophic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus (HTLV-III/LAV) by 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1911–1915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Smit L., Dunlop N., Hatch W., Merges M., Waters D., Kelliher J., Gallo R. C., Fischinger P. J., Goudsmit J. Emergence of viruses resistant to neutralization by V3-specific antibodies in experimental human immunodeficiency virus type 1 IIIB infection of chimpanzees. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3779–3791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3779-3791.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien W. A., Koyanagi Y., Namazie A., Zhao J. Q., Diagne A., Idler K., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 tropism for mononuclear phagocytes can be determined by regions of gp120 outside the CD4-binding domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):69–73. doi: 10.1038/348069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D., Price T. M. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of T cells and monocytes proceeds via receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):959–968. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Zinkus D. M. Accumulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA in T cells: results of multiple infection events. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4836–4841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4836-4841.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. E., Kwong P. D., Truneh A., Porter T. G., Arthos J., Rosenberg M., Dai X. P., Xuong N. H., Axel R., Sweet R. W. Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):419–426. doi: 10.1038/348419a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Markham P. D., Wong-Staal F., Franchini G., Kalyanaraman V. S., Gallo R. C. Restricted expression of human T-cell leukemia--lymphoma virus (HTLV) in transformed human umbilical cord blood lymphocytes. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Dalgleish A. G., Weiss R. A., Beverley P. C. Epitopes of the CD4 antigen and HIV infection. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1120–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.2430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Macrophage and T cell-line tropisms of HIV-1 are determined by specific regions of the envelope gp120 gene. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):167–169. doi: 10.1038/349167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava K. K., Fernandez-Larsson R., Zinkus D. M., Robinson H. L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 NL4-3 replication in four T-cell lines: rate and efficiency of entry, a major determinant of permissiveness. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3900–3902. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3900-3902.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tersmette M., Gruters R. A., de Wolf F., de Goede R. E., Lange J. M., Schellekens P. T., Goudsmit J., Huisman H. G., Miedema F. Evidence for a role of virulent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) variants in the pathogenesis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: studies on sequential HIV isolates. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2118–2125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2118-2125.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt P., Gendelman H. E., Ratner L. Identification of a determinant within the human immunodeficiency virus 1 surface envelope glycoprotein critical for productive infection of primary monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3097–3101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York-Higgins D., Cheng-Mayer C., Bauer D., Levy J. A., Dina D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 cellular host range, replication, and cytopathicity are linked to the envelope region of the viral genome. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):4016–4020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.4016-4020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



