Abstract
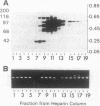
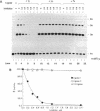
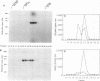
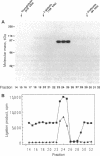
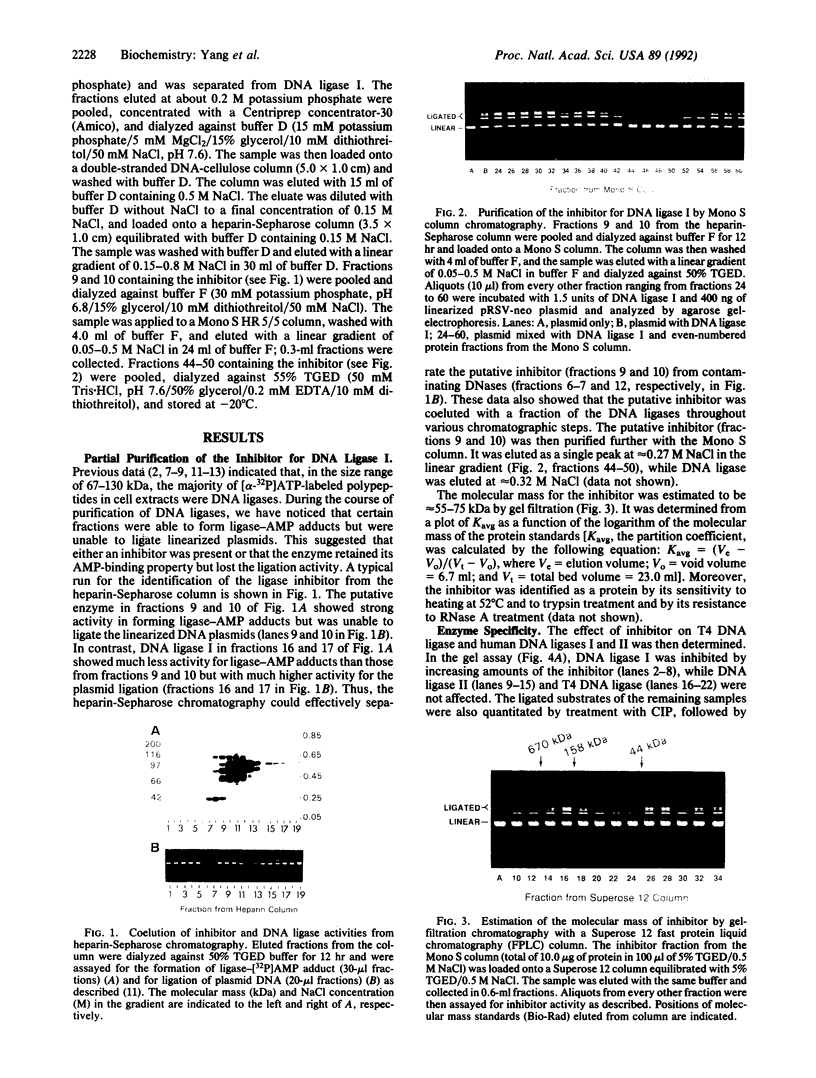
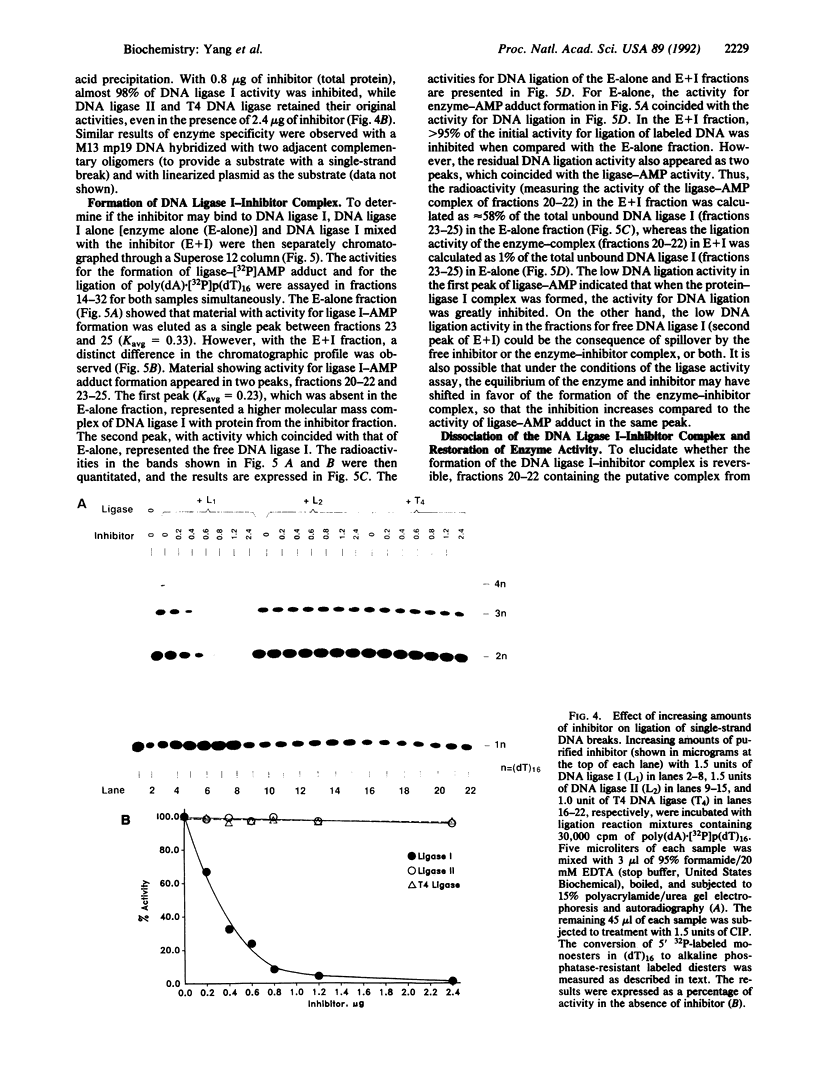
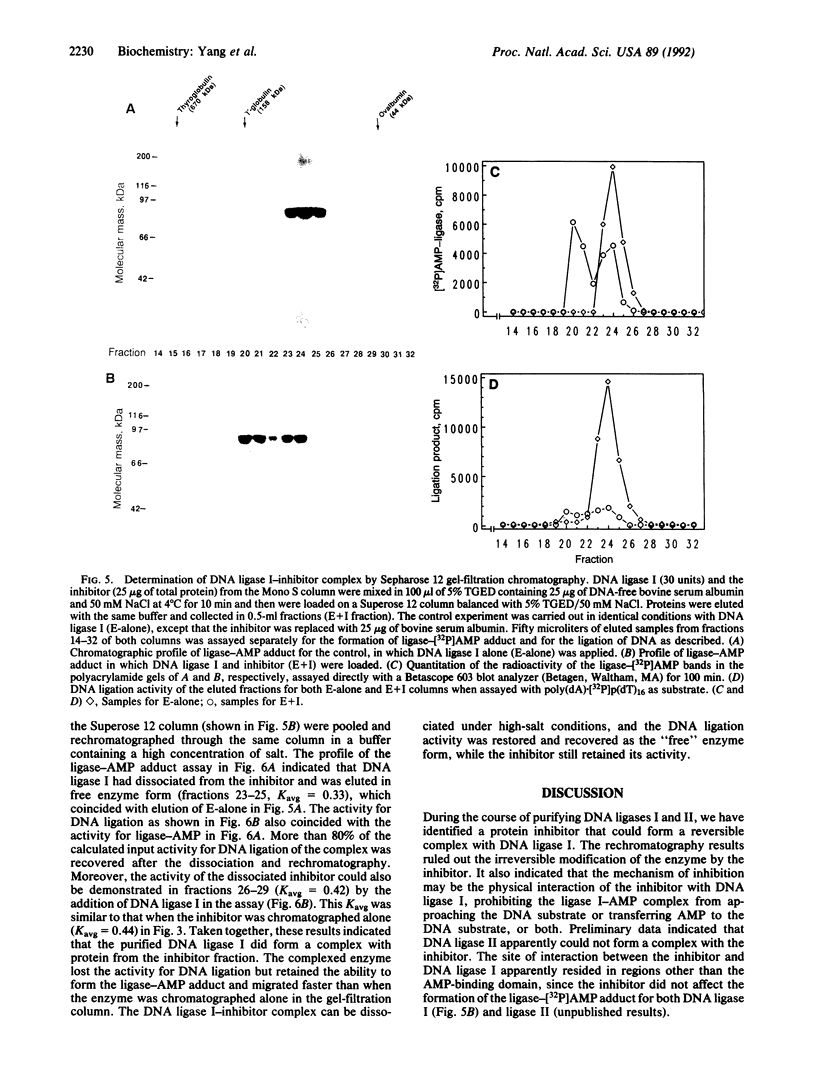
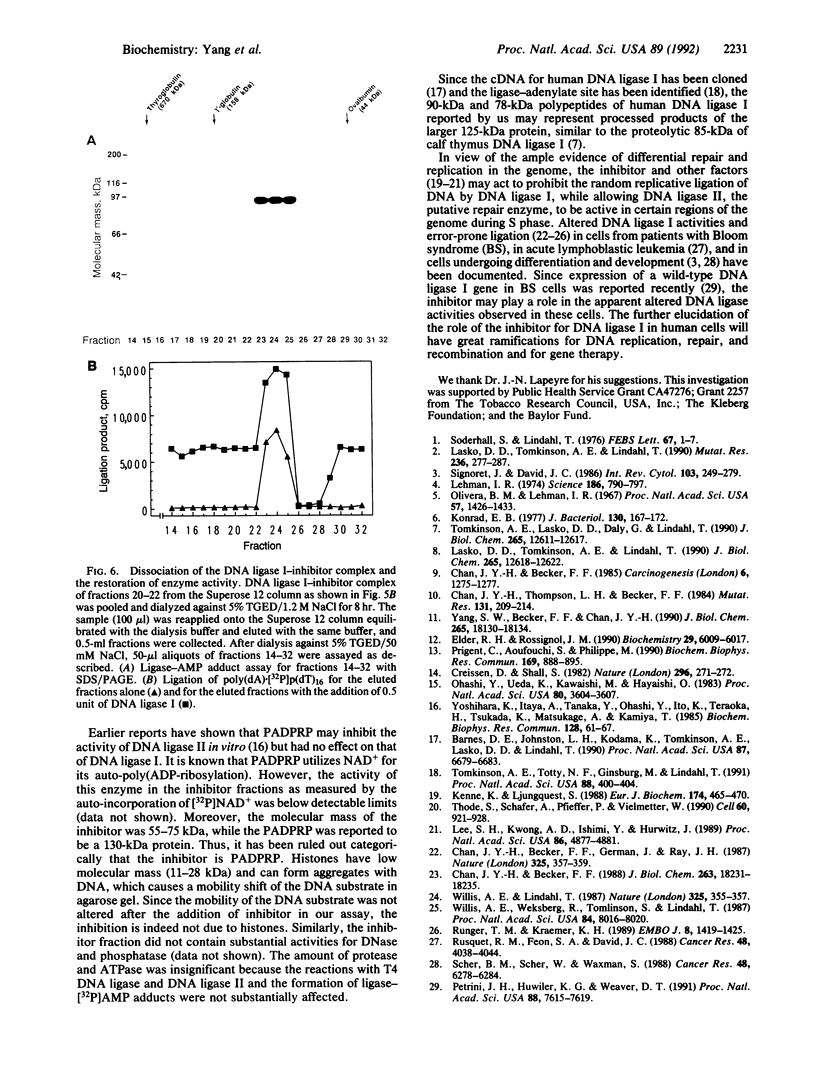
A protein inhibitor for human DNA ligase I has recently been identified. It was copurified with a fraction of the enzymes from HeLa cells through several steps of chromatography. The inhibitor was first identified by the absence of ligation activity of the associated enzyme, while it retained the ability to form the ligase-[32P]AMP adducts. The inhibitor was eluted as a single peak at approximately 0.25-0.30 M NaCl from a Mono S column. It inhibited the ligation of both double-stranded and single-stranded breaks by purified DNA ligase I but not by T4 DNA ligase and DNA ligase II. Subsequent gel-filtration chromatography indicated that this inhibitor, with a molecular mass of 55-75 kDa, could form a complex with DNA ligase I and inhibited the DNA ligation activity. Rechromatography of the ligase I-inhibitor complex in high-salt conditions resulted in the dissociation of the complex and the restoration of enzyme activity, indicating that the physical interaction of inhibitor with DNA ligase I is one of the mechanisms of inhibition. These data indicate that this protein inhibitor for DNA ligase I may play a specific role in regulating DNA ligation during replication, repair, or recombination.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. E., Johnston L. H., Kodama K., Tomkinson A. E., Lasko D. D., Lindahl T. Human DNA ligase I cDNA: cloning and functional expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6679–6683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Becker F. F. DNA ligase activities during hepatocarcinogenesis induced by N-2-acetylaminofluorene. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Sep;6(9):1275–1277. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.9.1275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Becker F. F. Defective DNA ligase I in Bloom's syndrome cells. Simultaneous analysis using immunoblotting and the ligase-[32P]AMP adduct assay. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18231–18235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Becker F. F., German J., Ray J. H. Altered DNA ligase I activity in Bloom's syndrome cells. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):357–359. doi: 10.1038/325357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J. Y., Thompson L. H., Becker F. F. DNA-ligase activities appear normal in the CHO mutant EM9. Mutat Res. 1984 May-Jun;131(5-6):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creissen D., Shall S. Regulation of DNA ligase activity by poly(ADP-ribose). Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):271–272. doi: 10.1038/296271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. H., Rossignol J. M. DNA ligases from rat liver. Purification and partial characterization of two molecular forms. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):6009–6017. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne K., Ljungquist S. Expression of a DNA-ligase-stimulatory factor in Bloom's syndrome cell line GM1492. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 15;174(3):465–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad E. B. Method for the isolation of Escherichia coli mutants with enhanced recombination between chromosomal duplications. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):167–172. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.167-172.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko D. D., Tomkinson A. E., Lindahl T. Eukaryotic DNA ligases. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90011-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasko D. D., Tomkinson A. E., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Biosynthesis and intracellular localization of DNA ligase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12618–12622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Kwong A. D., Ishimi Y., Hurwitz J. Studies on the DNA elongation inhibitor and its proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent control in simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4877–4881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman I. R. DNA ligase: structure, mechanism, and function. Science. 1974 Nov 29;186(4166):790–797. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4166.790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Ueda K., Kawaichi M., Hayaishi O. Activation of DNA ligase by poly(ADP-ribose) in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3604–3607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Lehman I. R. Linkage of polynucleotides through phosphodiester bonds by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1426–1433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini J. H., Huwiler K. G., Weaver D. T. A wild-type DNA ligase I gene is expressed in Bloom's syndrome cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7615–7619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prigent C., Aoufouchi S., Philippe M. Identification of DNA ligase I related polypeptides in three different human cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 29;169(3):888–895. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91976-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusquet R. M., Feon S. A., David J. C. Association of a possible DNA ligase deficiency with T-cell acute leukemia. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 15;48(14):4038–4044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rünger T. M., Kraemer K. H. Joining of linear plasmid DNA is reduced and error-prone in Bloom's syndrome cells. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1419–1425. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher B. M., Scher W., Waxman S. A possible effect of heme on the fate of DNA ligase activity extracted from differentiating mouse erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6278–6284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signoret J., David J. C. Control of the expression of genes for DNA ligase in eukaryotes. Int Rev Cytol. 1986;103:249–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60837-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderhäll S., Lindahl T. DNA ligases of eukaryotes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80858-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode S., Schäfer A., Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. A novel pathway of DNA end-to-end joining. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90340-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Lasko D. D., Daly G., Lindahl T. Mammalian DNA ligases. Catalytic domain and size of DNA ligase I. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12611–12617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkinson A. E., Totty N. F., Ginsburg M., Lindahl T. Location of the active site for enzyme-adenylate formation in DNA ligases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):400–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. E., Lindahl T. DNA ligase I deficiency in Bloom's syndrome. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):355–357. doi: 10.1038/325355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis A. E., Weksberg R., Tomlinson S., Lindahl T. Structural alterations of DNA ligase I in Bloom syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8016–8020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. W., Becker F. F., Chan J. Y. Fingerprinting of near-homogeneous DNA ligase I and II from human cells. Similarity of their AMP-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18130–18134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshihara K., Itaya A., Tanaka Y., Ohashi Y., Ito K., Teraoka H., Tsukada K., Matsukage A., Kamiya T. Inhibition of DNA polymerase alpha, DNA polymerase beta, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, and DNA ligase II by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reaction in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91644-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]