Abstract
Although rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most common autoimmune disease, affecting approximately 1% of the population worldwide, its pathogenic mechanisms are poorly understood. Tobacco smoke, an environmental risk factor for RA, contains several ligands of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr), also known as dioxin receptor. Ahr plays critical roles in the immune system. We previously demonstrated that Ahr in helper T-cells contributes to development of collagen-induced arthritis, a mouse model of RA. Other studies have shown that cigarette smoke condensate and pure Ahr ligands exacerbate RA by altering bone metabolism and inducing proinflammatory responses in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Consistent with these findings, several Ahr antagonists such as α-naphthoflavone, resveratrol, and GNF351 reverse the effect of Ahr ligands in RA pathogenesis. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of Ahr function in the immune system and the potential clinical benefits of Ahr antagonism in treating RA.
Keywords: dioxin receptor, antagonists, autoimmunity
The roles of Ahr in RA
RA pathogenesis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic and chronic inflammatory disease characterized by synovial inflammation and subsequent joint destruction. Bone damage and cartilage loss triggered by osteoclasts and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) are also observed in RA patients. Accordingly, the immune system, particularly T-cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and B-cells as well as proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, is implicated in RA pathogenesis.1–8 In particular, IL-17A-producing CD4+ T-cells (so-called Th17 cells) have attracted attention in this context because accumulating evidence indicates that this T helper (Th) subset plays critical roles in several autoimmune diseases, including RA.9–11 Furthermore, neutralizing antibodies against IL-6 and TNF-α are promising therapies for RA.12–18
RA is thought to be induced by interactions between environmental and genetic risk factors. Environmental risk factors for this disease include smoking and infection, and the best-known genetic risk factors are HLA-DRB1 alleles that encode a shared epitope (SE).19–22 Several groups have reported a link between SE and cigarette smoking in relation to RA risk,23–25 illustrating that disease pathogenesis involves both environmental and genetic factors. Although cigarette smoke contains several aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr) ligands, such as 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), 3-methyl cholanthrene (3-MC), and benzo[a]pyrene (BaP), the precise mechanisms by which these molecules contribute to RA development are not yet understood. In this review, we summarize our current knowledge about the roles of Ahr in immune cells, including in Th17 cells, during RA pathogenesis, thereby providing further possibility of its use as a target.
Ahr pathway
Ahr is a ligand-activated transcription factor of the bHLH/PAS family.26–28 It is expressed abundantly in liver and such barrier tissues as skin, lung, gut, placenta, and mucosal epithelia, but at low levels or not at all in muscle, testis, kidney, and brain, indicating that immune cells express high levels of Ahr.29 Under steady-state conditions, Ahr localizes in cytoplasm and forms complexes with various proteins including HSP90, AIP, and p23.30–32 Upon binding to its ligands, Ahr translocates into the nucleus, where it binds Ahr nuclear translocator; the resultant complex activates xenobiotic-responsive elements in the promoters of target genes, such as those encoding cytochrome p450 enzymes.26,33–35 In addition, Ahr controls degradation of specific targets such as estrogen via its ligand-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase activity.36,37 Activated Ahr is itself degraded by the 26S proteasome pathway after being exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.38–40 In addition to the canonical Ahr signaling pathway, as described, Ahr also participates in other signaling pathways, resulting in noncanonical Ahr activities.41 For instance, TCDD-induced association of Ahr with the NF-κB subunit RelB upregulates inflammatory genes such as IL-8 via the RelB/Ahr responsive element in macrophages and breast cancer cells.42,43 However, Ahr-deficient mice exhibit more severe inflammatory symptoms following exposure to lipopolysaccharide or cigarette smoke extract due to destabilization of the RelB protein,44,45 suggesting that Ahr can function as either a pro- or anti-inflammatory regulator in different situations (eg, in response to different stimuli or in different cell types and diseases). Therefore, further study is necessary to elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which Ahr-binding partners and target genes are determined.
Ahr in RA
Because Ahr acts as an important mediator of xenobiotic metabolism by inducing cytochrome p450 enzymes such as CYP1A1, over the past 3 decades it was primarily studied in the field of toxicology and pharmacology. However, two different groups reported that Ahr controls generation of Th17, a recently identified Th cell subset,46,47 leading many immunologists to study Ahr in the immune system. Th17 cells, which are induced by IL-6 and TGF-β via RORγt transcription, are believed to play a key role in the progression of several autoimmune diseases, including RA and multiple sclerosis (MS).9–11,48 One of the two groups demonstrated ligand-specific Ahr action in T-cells: the endogenous ligand FICZ exacerbates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a mouse model of MS, by promoting generation of Th17 cells, whereas the exogenous ligand TCDD suppresses disease progression by inducing production of regulatory T (Treg) cells.47 It remains unclear how Ahr causes opposite outcomes when activated by FICZ or TCDD; however, several studies have demonstrated mechanisms by which Ahr contributes to Th17 differentiation through various intracellular signaling pathways (eg, inhibition of STAT1/STAT5, Aiolos-mediated transcription, and direct interaction with the IL-17 promoter).49–52 In addition, several microRNAs (miRNAs) are regulated by Ahr under pathological conditions such as immune disorders and cancers. miRNAs are short (20–22 nucleotide) noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate gene expression by base-pairing with binding sites in the 3′-UTR regions of target mRNAs.53–56 miR-132/212 is induced in an Ahr-dependent manner under Th17-polarizing conditions, and enhances the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis.57,58 Several miRNAs form positive or negative feedback loops. For instance, although miR-132/212 expression in neurons is controlled by CREB, CREB itself can be upregulated by miR-132.59,60 Therefore, identification of Ahr-regulated miRNAs and their targets may contribute to understanding of the Ahr signaling network.61
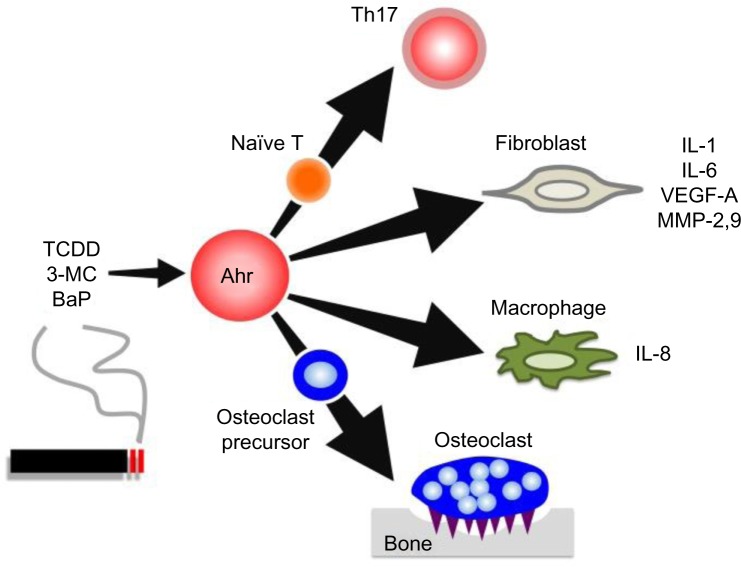
As already mentioned, tobacco smoke is a major environmental risk factor of RA and contains several kinds of Ahr ligands such as TCDD, 3-MC, and BaP. In addition, Ahr expression in synovial tissue is significantly higher in RA patients than in osteoarthritis patients.62 Several studies have reported that when FLS cell lines or synoviocytes from RA patients are stimulated by Ahr ligands or cigarette smoke condensate, they upregulate proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β.63–66 Moreover, Ahr-knockout (KO) mice exhibited significantly reduced severity of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA), the most widely used mouse model of RA.67 More importantly, the same study also demonstrated that Ahr deletion in T-cells inhibits CIA development as efficiently as Ahr-KO, with reduced numbers of Th17 cells in draining lymph nodes. In another context, Ahr may contribute to pathogenesis of RA via its effects on bone metabolism. For instance, osteoblasts isolated from CIA-treated mice express high levels of Ahr, and TCDD negatively regulates osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via activation of the ERK-signaling pathway.68 Moreover, Ahr ligand promotes osteoclast formation in vitro and bone resorption in vivo.69 These findings raise the possibility that Ahr in other cell types may affect disease progression. Indeed, several lines of evidence have shown that Ahr plays various roles in immune cells including macrophages, dendritic cells, and B-cells, as well as in T-cells.70–72 Taken together, these findings indicate that Ahr expression is important for RA pathogenesis in several ways: by inducing proinflammatory cytokine production in FLSs, by influencing bone metabolism via modulating the balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts, and by regulating Th17 generation. The roles of Ahr in RA pathogenesis are summarized in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Ahr roles in RA pathogenesis.
Notes: Cigarette smoke contains several Ahr ligands such as TCDD, 3-MC, and BaP. Ahr activation contributes several aspects of RA pathogenesis: differentiation into Th17 cells from naïve T-cells; inflammation, angiogenesis, and cartilage destruction by producing IL-1, IL-6, VEGF, and MMPs in fibroblasts; production of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-8 in macrophages; and osteoclastogenesis.
Abbreviations: Ahr, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; 3-MC, 3-methylcholanthrene; BaP, benzo[a]pyrene; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; IL, interleukin.
Treatment of RA via antagonizing Ahr signaling
Ahr activation by ligands such as TCDD can induce the production of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β and IL-6, in human FLS cell lines and RA synoviocytes.62,63 Researchers have used both Ahr-KO mice and Ahr antagonists to investigate the functions of Ahr in RA development.62,66,67 In Ahr-KO mice, serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-6 are reduced in the CIA model.67 Interestingly, T-cell-specific deficiency of Ahr suppresses CIA development by inhibiting production of IL-1β and IL-6 and generation of Th17 cells.67 The functions of several Ahr antagonists in RA are discussed further.
α-naphthoflavone
α-naphthoflavone inhibits TCDD-induced upregulation of IL-1β in FLS via the NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways.62 In addition, in the synovial fibroblast cell line MH7A, isolated from RA patients, α-naphthoflavone inhibits the induction of IL-1β and CYP1A1 by cigarette smoke, which contains such Ahr ligands as TCDD.66 IL-1, and in particular IL-1β, is a key mediator of the pathogenesis of RA, and blocking of IL-1/IL-1 receptor alleviates RA symptoms in both animal models and clinical studies.73–79 In the CIA model, IL-1-KO mice develop less arthritis than controls.80 Moreover, IL-1 can promote Th17 cell development, thereby increasing the level of IL-17 during the onset of spontaneous arthritis in IL-1 antagonist KO mice.81 Together, these results raise the possibility that α-naphthoflavone can suppress IL-1β production and subsequent Th17 cell generation induced by cigarette smoke or Ahr ligands such as TCDD in patients with RA.
Resveratrol (3,5,49-trihydroxystilbene)
Resveratrol, a molecule found in red wine, blocks TCDD-mediated effects such as induction of CYP1A1 and IL-1β in the cancer cell lines T-47D and RL95-2, respectively.82 In rats, resveratrol treatment inhibits induction of CYP1A1 by pure Ahr ligands such as BaP and 7,12-dimethylbenz[a] anthracene, compounds found in cigarette smoke, in cells of many organs including lung, kidney, liver, spleen, bone, and testis.82 Recent work showed that resveratrol inhibits CIA development by decreasing the IL-6 level in serum and reducing the frequency of Th17 in draining lymph nodes.83 Importantly, resveratrol decreases TCDD-mediated induction of IL-17 under Th17-polarizing conditions in vitro.83 Therefore, resveratrol may suppress Th17 generation. Another study showed that resveratrol induces apoptosis via sirtuin-1-mediated mitochondrial corruption in MH7A human RA synovial cells.84 Consistent with these results, resveratrol induces apoptosis via activation of caspase-8 in RA-derived FLS,85 or caspase-3/-9 in MH7A human RA synovial cells.86 Collectively, these findings suggest that resveratrol inhibits Ahr signaling to reduce the induction of CYP1A1, suppresses the function of Th17 cells, and induces apoptosis in RA synovial cells, contributing to control Ahr-mediated inflammatory diseases such as autoimmune arthritis.
GNF351 (N-(2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl)-9-isopropyl-2-(5-methylpyridin-3-yl)-9H-purin-6-amine)
GNF351 is a high-affinity Ahr antagonist.65,87–90 In human FLS isolated from RA patients, IL-1β production is suppressed by GNF351, and this suppression is rendered by pretreatment of human FLS with the Ahr antagonist CH223191 or by small interfering RNA targeting Ahr.65 Furthermore, GNF351 reduces IL-1β-induced production of growth factors such as vascular endothelia growth factor A (VEGF-A) in FLS of RA patients via an Ahr-dependent mechanism.88 Growth factors such as VEGF play important roles in FLS activation, leading to hyperplasia and increased angiogenesis, thereby promoting RA development.91 In addition, GNF351 reduces IL-1β-induced mRNA expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and -9 in FLS of RA patients.65 MMPs are elevated in FLS of RA patients, resulting in cartilage loss and are therefore considered to be promising targets for treatment of RA.92–96 In summary, GNF351 inhibits RA development by targeting IL-1β and IL-1β-induced VEGF and MMPs. Moreover, GNF351 can bind with high affinity to the ligand-binding pocket of AhR and is a more potent Ahr antagonist than compounds such as α-naphthoflavone and resveratrol.87
Potentially antagonistic plant-derived compounds
Previous studies have reported that plants contain secondary compounds such as β-carboline alkaloids that may exert various pharmacological activities.97–102 Several kinds of plant-derived alkaloids have antagonistic effects on dioxin-mediated CYP1A1 induction in mouse and human cell lines.98,99 Recently, our group showed that 7-methoxy-(9H-β-carbolin-1-il)-(E)-2-propenoic acid, a novel β-carboline alkaloid isolated from hairy-root cultures of the Vietnamese plant Eurycoma longifolia, has anti-inflammatory activity.103 Consistent with this, extract of E. longifolia is used in Vietnam and requires further study to establish its effectiveness to treat rheumatic disorders.104 This alkaloid is currently being investigated as a novel Ahr antagonist to treat inflammatory diseases including RA. The functions of several Ahr antagonists in RA are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1.
The functions of several Ahr antagonists in RA
| No | Compound | Main functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | α-naphthoflavone | Inhibits IL-1β production | Kobayashi et al62 |
| Inhibits induction of IL-1β and CYP1A1 | Adachi et al66 | ||
| 2 | Resveratrol | Inhibits IL-1β and CYP1A1 | Casper et al82 |
| Suppresses Th17 generation | Xuzhu et al83 | ||
| Activates caspase-8 | Byun et al85 | ||
| Activates caspase-3/-9 | Nakayama et al86 | ||
| 3 | GNF351 | Suppresses IL-1β production | Lahoti et al65 |
| Decreases IL-1β-induced production of VEGF-A | Lahoti et al88 | ||
| Reduces IL-1β-induced MMP-2 and MMP-9 | Lahoti et al65 | ||
| 4 | Plant-derived alkaloids | Inhibits dioxin-mediated CYP1A1 induction | El Gendy and El-Kadi98 |
| El Gendy et al99 |
Abbreviations: Ahr, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; CYP1A1, cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases.
Conclusion and future work
Research on the function of Ahr in RA pathogenesis has made significant progress. However, further study will be necessary to elucidate the precise molecular mechanisms by which deficiency of Ahr or Ahr antagonists such as α-naphthoflavone, resveratrol, and GNF351 suppress CIA development in mice and attenuate cells isolated from RA patients. Recently, we found that dioxin-exposed patients suffer from various inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid disorders (our unpublished data). Furthermore, expression of Ahr, CYP1A1, and inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β and IL-6 was highly upregulated in peripheral blood of these patients (our unpublished data). In future work, we will seek to characterize novel potential Ahr antagonists with strong anti-inflammatory properties, with the goal of alleviating the signs and symptoms of RA in dioxin-exposed patients.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Kishimoto Foundation, the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science Research Fellowship for Young Scientists (for Taisuke Nakahama), and Project VAST02.01/15-16 (for Nam Trung Nguyen) from the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology.
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Janossy G, Panayi G, Duke O, Bofill M, Poulter LW, Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Harris ED., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322(18):1277–1289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brennan F, Foey A. Cytokine regulation in RA synovial tissue: role of T cell/macrophage contact-dependent interactions. Arthritis Res. 2002;4(Suppl 3):S177–S182. doi: 10.1186/ar556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T. Interleukin 6: from bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2(11):619–626. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(6):429–442. doi: 10.1038/nri2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205–2219. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1004965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Astry B, Harberts E, Moudgil KD. A cytokine-centric view of the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune arthritis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31(12):927–940. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wing K, Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(1):7–13. doi: 10.1038/ni.1818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Murphy CA, Langrish CL, Chen Y, et al. Divergent pro- and antiinflam-matory roles for IL-23 and IL-12 in joint autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2003;198(12):1951–1957. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM, et al. IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2005;201(2):233–240. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, et al. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441(7090):235–238. doi: 10.1038/nature04753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maini R, St Clair EW, Breedveld F, et al. Infliximab (chimeric anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving concomitant methotrexate: a randomised phase III trial. ATTRACT Study Group. Lancet. 1999;354(9194):1932–1939. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)05246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Weinblatt ME, Keystone EC, Furst DE, et al. Adalimumab, a fully human anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody, for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in patients taking concomitant methotrexate: the ARMADA trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(1):35–45. doi: 10.1002/art.10697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, et al. A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(4):253–259. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199901283400401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Graninger W, Smolen J. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by TNF-blocking agents. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2002;127(1):10–14. doi: 10.1159/000048164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yokota S, Imagawa T, Mori M, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, withdrawal phase III trial. Lancet. 2008;371(9617):998–1006. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60454-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yokota S, Imagawa T, Mori M, et al. Long-term treatment of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis with tocilizumab: results of an open-label extension study in Japan. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(4):627–628. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yokota S, Miyamae T, Imagawa T, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of humanized recombinant anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody in children with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(3):818–825. doi: 10.1002/art.20944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gregersen PK, Silver J, Winchester RJ. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987;30(11):1205–1213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Turesson C, Schaid DJ, Weyand CM, et al. The impact of HLA-DRB1 genes on extra-articular disease manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(6):R1386–R1393. doi: 10.1186/ar1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Moreno I, Valenzuela A, García A, Yélamos J, Sánchez B, Hernánz W. Association of the shared epitope with radiological severity of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996;23(1):6–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gonzalez-Gay MA, Garcia-Porrua C, Hajeer AH. Influence of human leukocyte antigen-DRB1 on the susceptibility and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002;31(6):355–360. doi: 10.1053/sarh.2002.32552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Padyukov L, Silva C, Stolt P, Alfredsson L, Klareskog L. A gene-environment interaction between smoking and shared epitope genes in HLA-DR provides a high risk of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(10):3085–3092. doi: 10.1002/art.20553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pedersen M, Jacobsen S, Garred P, et al. Strong combined gene-environment effects in anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-positive rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide case-control study in Denmark. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(5):1446–1453. doi: 10.1002/art.22597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Karlson EW, Chang SC, Cui J, et al. Gene-environment interaction between HLA-DRB1 shared epitope and heavy cigarette smoking in predicting incident rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(1):54–60. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.102962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Burbach KM, Poland A, Bradfield CA. Cloning of the Ah-receptor cDNA reveals a distinctive ligand-activated transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(17):8185–8189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ema M, Sogawa K, Watanabe N, et al. cDNA cloning and structure of mouse putative Ah receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;184(1):246–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91185-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Ema M, Mimura J, Sogawa K. Ah receptor: a novel ligand-activated transcription factor. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1994;11(2–3):65–74. doi: 10.1159/000424195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Esser C, Rannug A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology, and toxicology. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67(2):259–279. doi: 10.1124/pr.114.009001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Perdew GH. Association of the Ah receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(27):13802–13805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kazlauskas A, Poellinger L, Pongratz I. Evidence that the co-chaperone p23 regulates ligand responsiveness of the dioxin (Aryl hydrocarbon) receptor. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(19):13519–13524. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.13519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ma Q, Whitlock JP., Jr A novel cytoplasmic protein that interacts with the Ah receptor, contains tetratricopeptide repeat motifs, and augments the transcriptional response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(14):8878–8884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sogawa K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Ah receptor, a novel ligand-activated transcription factor. J Biochem. 1997;122(6):1075–1079. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schrenk D. Impact of dioxin-type induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes on the metabolism of endo- and xenobiotics. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55(8):1155–1162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(97)00591-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tomita S, Jiang HB, Ueno T, et al. T cell-specific disruption of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt) gene causes resistance to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced thymic involution. J Immunol. 2003;171(8):4113–4120. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.8.4113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ohtake F, Baba A, Takada I, et al. Dioxin receptor is a ligand-dependent E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nature. 2007;446(7135):562–566. doi: 10.1038/nature05683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ohtake F, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Kato S. AhR acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to modulate steroid receptor functions. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77(4):474–484. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.08.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Davarinos NA, Pollenz RS. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor imported into the nucleus following ligand binding is rapidly degraded via the cytosplasmic proteasome following nuclear export. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(40):28708–28715. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.40.28708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ma Q, Baldwin KT. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced degradation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Role of the transcription activaton and DNA binding of AhR. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(12):8432–8438. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.12.8432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pollenz RS, Barbour ER. Analysis of the complex relationship between nuclear export and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(16):6095–6104. doi: 10.1128/mcb.20.16.6095-6104.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Denison MS, Soshilov AA, He G, DeGroot DE, Zhao B. Exactly the same but different: promiscuity and diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor. Toxicol Sci. 2011;124(1):1–22. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vogel CF, Li W, Wu D, et al. Interaction of aryl hydrocarbon receptor and NF-κB subunit RelB in breast cancer is associated with interleukin-8 overexpression. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2011;512(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.05.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vogel CF, Sciullo E, Li W, Wong P, Lazennec G, Matsumura F. RelB, a new partner of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated transcription. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(12):2941–2955. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Thatcher TH, Maggirwar SB, Baglole CJ, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice develop heightened inflammatory responses to cigarette smoke and endotoxin associated with rapid loss of the nuclear factor-kappaB component RelB. Am J Pathol. 2007;170(3):855–864. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Baglole CJ, Maggirwar SB, Gasiewicz TA, Thatcher TH, Phipps RP, Sime PJ. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor attenuates tobacco smoke-induced cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin production in lung fibroblasts through regulation of the NF-kappaB family member RelB. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(43):28944–28957. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800685200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Veldhoen M, Hirota K, Westendorf AM, et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor links TH17-cell-mediated autoimmunity to environmental toxins. Nature. 2008;453(7191):106–109. doi: 10.1038/nature06881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Quintana FJ, Basso AS, Iglesias AH, et al. Control of T(reg) and T(H)17 cell differentiation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 2008;453(7191):65–71. doi: 10.1038/nature06880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chen Z, Laurence A, O’Shea JJ. Signal transduction pathways and transcriptional regulation in the control of Th17 differentiation. Semin Immunol. 2007;19(6):400–408. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.10.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kimura A, Naka T, Nohara K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Kishimoto T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates Stat1 activation and participates in the development of Th17 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(28):9721–9726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804231105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Veldhoen M, Hirota K, Christensen J, O’Garra A, Stockinger B. Natural agonists for aryl hydrocarbon receptor in culture medium are essential for optimal differentiation of Th17 T cells. J Exp Med. 2009;206(1):43–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Quintana FJ, Jin H, Burns EJ, et al. Aiolos promotes TH17 differentiation by directly silencing Il2 expression. Nat Immunol. 2012;13(8):770–777. doi: 10.1038/ni.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cui G, Qin X, Wu L, et al. Liver X receptor (LXR) mediates negative regulation of mouse and human Th17 differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2011;121(2):658–670. doi: 10.1172/JCI42974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5(7):522–531. doi: 10.1038/nrg1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(8):839–845. doi: 10.1038/ni.f.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215–233. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, Baltimore D. Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(2):111–122. doi: 10.1038/nri2708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Nakahama T, Hanieh H, Nguyen NT, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated induction of the microRNA-132/212 cluster promotes interleukin-17-producing T-helper cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(29):11964–11969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311087110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chinen I, Nakahama T, Kimura A, et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor/microRNA-212/132 axis in T cells regulates IL-10 production to maintain intestinal homeostasis. Int Immunol. 2015;27(8):405–415. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxv015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wayman GA, Davare M, Ando H, et al. An activity-regulated microRNA controls dendritic plasticity by down-regulating p250GAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(26):9093–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803072105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hollander JA, Im HI, Amelio AL, et al. Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB signalling. Nature. 2010;466(7303):197–202. doi: 10.1038/nature09202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Nguyen NT, Nakahama T, Le DH, Van Son L, Chu HH, Kishimoto T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and kynurenine: recent advances in autoimmune disease research. Front Immunol. 2014;5:551. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kobayashi S, Okamoto H, Iwamoto T, et al. A role for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and the dioxin TCDD in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47(9):1317–1322. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Tamaki A, Hayashi H, Nakajima H, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon increases mRNA level for interleukin 1 beta in human fibroblast-like synoviocyte line via aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27(3):407–410. doi: 10.1248/bpb.27.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Shizu M, Itoh Y, Sunahara R, et al. Cigarette smoke condensate upregulates the gene and protein expression of proinflammatory cytokines in human fibroblast-like synoviocyte line. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2008;28(8):509–521. doi: 10.1089/jir.2007.0081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lahoti TS, John K, Hughes JM, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonism mitigates cytokine-mediated inflammatory signalling in primary human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(10):1708–1716. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Adachi M, Okamoto S, Chujyo S, et al. Cigarette smoke condensate extracts induce IL-1-beta production from rheumatoid arthritis patient-derived synoviocytes, but not osteoarthritis patient-derived synoviocytes, through aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent NF-kappa-B activation and novel NF-kappa-B sites. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013;33(6):297–307. doi: 10.1089/jir.2012.0107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Nakahama T, Kimura A, Nguyen NT, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor deficiency in T cells suppresses the development of collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(34):14222–14227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111786108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Yu H, Du Y, Zhang X, et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor suppresses osteoblast proliferation and differentiation through the activation of the ERK signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;280(3):502–510. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.08.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Iqbal J, Sun L, Cao J, et al. Smoke carcinogens cause bone loss through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and induction of Cyp1 enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(27):11115–11120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220919110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nguyen NT, Hanieh H, Nakahama T, Kishimoto T. The roles of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in immune responses. Int Immunol. 2013;25(6):335–343. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxt011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Nguyen NT, Kimura A, Nakahama T, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates dendritic cell immunogenicity via a kynurenine-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(46):19961–19966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014465107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Nguyen NT, Nakahama T, Kishimoto T. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and experimental autoimmune arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2013;35(6):637–644. doi: 10.1007/s00281-013-0392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gabay C, Arend WP. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with IL-1 inhibitors. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1998;20(1–2):229–246. doi: 10.1007/BF00832009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Joosten LA, Helsen MM, Saxne T, van De Loo FA, Heinegard D, van Den Berg WB. IL-1 alpha beta blockade prevents cartilage and bone destruction in murine type II collagen-induced arthritis, whereas TNF-alpha blockade only ameliorates joint inflammation. J Immunol. 1999;163(9):5049–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Schiff MH. Role of interleukin 1 and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the mediation of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(Suppl 1):i103–i108. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kay J, Calabrese L. The role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004;43(Suppl 3):iii2–iii9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lamacchia C, Palmer G, Seemayer CA, Talabot-Ayer D, Gabay C. Enhanced Th1 and Th17 responses and arthritis severity in mice with a deficiency of myeloid cell-specific interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(2):452–462. doi: 10.1002/art.27235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Alten R, Gram H, Joosten LA, et al. The human anti-IL-1 beta monoclonal antibody ACZ885 is effective in joint inflammation models in mice and in a proof-of-concept study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(3):R67. doi: 10.1186/ar2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Dinarello CA. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:519–550. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Saijo S, Asano M, Horai R, Yamamoto H, Iwakura Y. Suppression of autoimmune arthritis in interleukin-1-deficient mice in which T cell activation is impaired due to low levels of CD40 ligand and OX40 expression on T cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(2):533–544. doi: 10.1002/art.10172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Koenders MI, Devesa I, Marijnissen RJ, et al. Interleukin-1 drives pathogenic Th17 cells during spontaneous arthritis in interleukin-1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(11):3461–3470. doi: 10.1002/art.23957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Casper RF, Quesne M, Rogers IM, et al. Resveratrol has antagonist activity on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor: implications for prevention of dioxin toxicity. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;56(4):784–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Xuzhu G, Komai-Koma M, Leung BP, et al. Resveratrol modulates murine collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting Th17 and B-cell function. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(1):129–135. doi: 10.1136/ard.2011.149831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Nishizaki T, Kanno T. Resveratrol: a candidate drug for treating rheumatoid arthritis. In: Lemmey A, editor. Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatment. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech; 2012. [Accessed October 7, 2015]. Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/rheumatoid-arthritis-treatment/resveratrol-a-candidate-drugfor-treating-rheumatoid-arthritis. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Byun HS, Song JK, Kim YR. Caspase-8 has an essential role in resveratrol-induced apoptosis of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47(3):301–308. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Nakayama H, Yaguchi T, Yoshiya S, Nishizaki T. Resveratrol induces apoptosis MH7A human rheumatoid arthritis synovial cells in a sirtuin 1-dependent manner. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(1):151–157. doi: 10.1007/s00296-010-1598-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Smith KJ, Murray IA, Tanos R, et al. Identification of a high-affinity ligand that exhibits complete aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;338(1):318–327. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.178392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Lahoti TS, Hughes JM, Kusnadi A, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor antagonism attenuates growth factor expression, proliferation, and migration in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014;348(2):236–245. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.209726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Vogel C, Donat S, Döhr O, et al. Effect of subchronic 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure on immune system and target gene responses in mice: calculation of benchmark doses for CYP1A1 and CYPIA2 related enzyme activities. Arch Toxicol. 1997;71(6):372–382. doi: 10.1007/s002040050401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Chabaud M, Fossiez F, Taupin JL, Miossec P. Enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1-induced IL-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes and its regulation by Th2 cytokines. J Immunol. 1998;161(1):409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Koch AE. The role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: recent developments. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(Suppl 1):i65–i71. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.García-Vicuña R, Gómez-Gaviro MV, Domínguez-Luis MJ, et al. CC and CXC chemokine receptors mediate migration, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinase production by fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(12):3866–3877. doi: 10.1002/art.20615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Giannelli G, Erriquez R, Iannone F, Marinosci F, Lapadula G, Antonaci S. MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22(3):335–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010;233(1):233–255. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Xue M, McKelvey K, Shen K, et al. Endogenous MMP-9 and not MMP-2 promotes rheumatoid synovial fibroblast survival, inflammation and cartilage degradation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2014;53(12):2270–2279. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ahn JK, Huang B, Bae EK, et al. The role of α-defensin-1 and related signal transduction mechanisms in the production of IL-6, IL-8 and MMPs in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2013;52(8):1368–1376. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ket147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Cao R, Peng W, Wang Z, Xu A. beta-Carboline alkaloids: biochemical and pharmacological functions. Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(4):479–500. doi: 10.2174/092986707779940998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.El Gendy MA, El-Kadi AO. Harmine and harmaline downregulate TCDD-induced Cyp1a1 in the livers and lungs of C57BL/6 mice. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:258095. doi: 10.1155/2013/258095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.El Gendy MA, Soshilov AA, Denison MS, El-Kadi AO. Transcriptional and posttranslational inhibition of dioxin-mediated induction of CYP1A1 by harmine and harmol. Toxicol Lett. 2012;208(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.09.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Park S, Nhiem NX, Kiem PV, et al. Five new quassinoids and cytotoxic constituents from the roots of Eurycoma longifolia. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24(16):3835–3840. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.06.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Kuo PC, Shi LS, Damu AG, et al. Cytotoxic and antimalarial beta-carboline alkaloids from the roots of Eurycoma longifolia. J Nat Prod. 2003;66(10):1324–1327. doi: 10.1021/np030277n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Tran TV, Malainer C, Schwaiger S, et al. NF-kappaB inhibitors from Eurycoma longifolia. J Nat Prod. 2014;77(3):483–488. doi: 10.1021/np400701k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Pham BN, Pham TB, Nguyen HD, et al. A new anti-inflammatory β-carboline alkaloid from the hairy-root cultures of Eurycoma longifolia. Nat Prod Res. 2015:1–6. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2015.1056187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Do HB, Dang QC, Bui XC, editors. The Medicinal Plants and Animals in Vietnam. 1st ed. Hanoi, Vietnam: Science and Technology Publishing House; 2004. pp. 116–118. [Google Scholar]