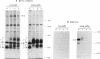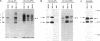Abstract
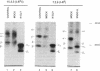
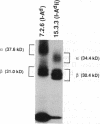
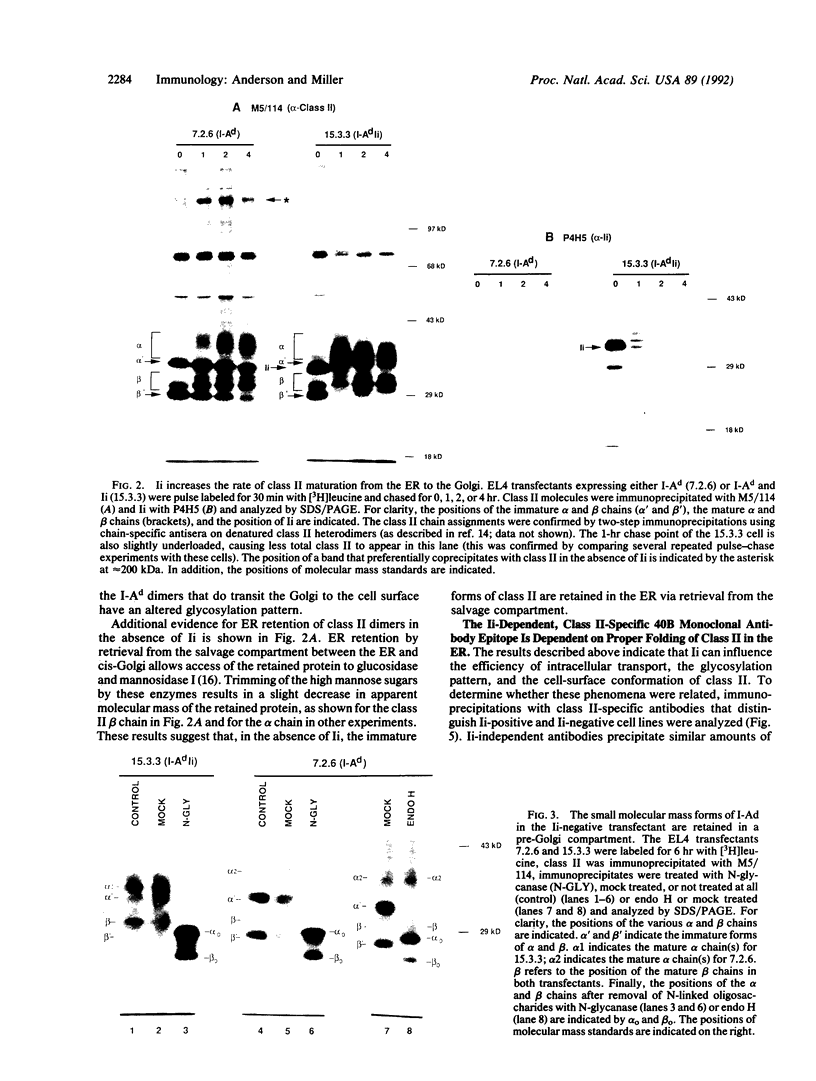
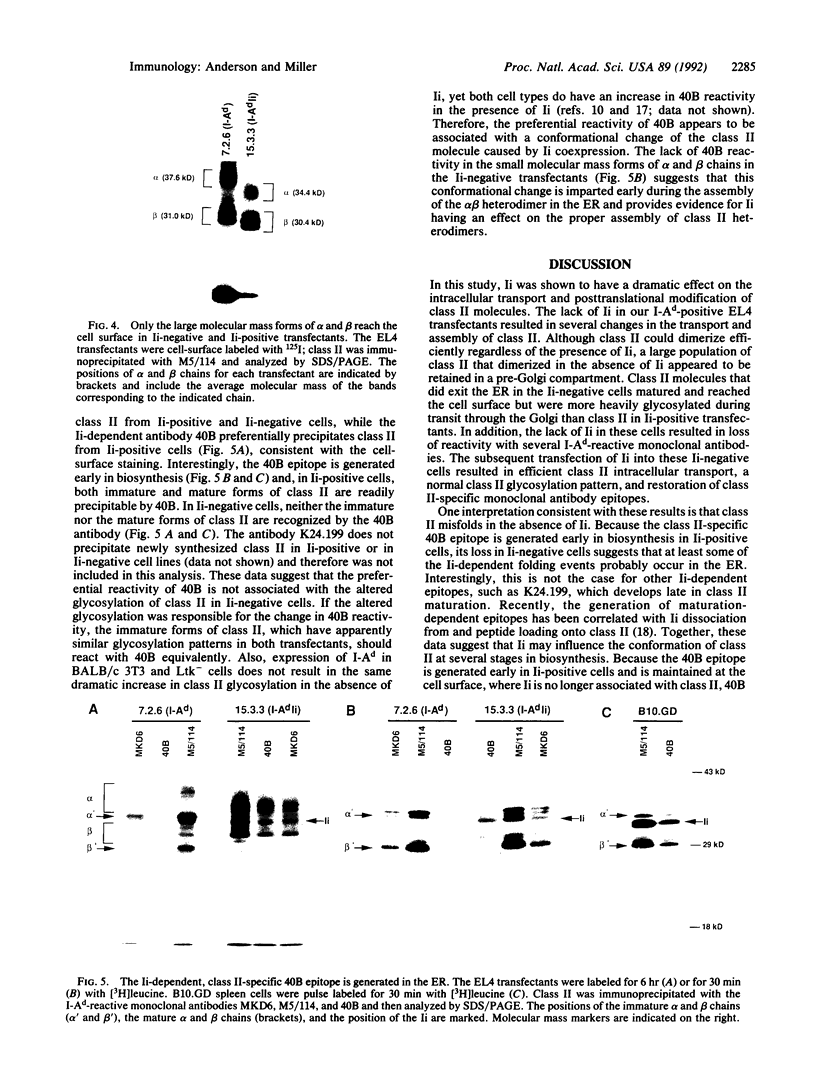
During biosynthesis, class II major histocompatibility complex molecules are intimately associated with invariant chain (Ii). The Ii-class II association has been shown to block peptide-class II binding and to affect the ultimate conformation of class II expressed on the cell surface. To assess the biochemical basis for the effects of Ii on class II, we have analyzed the biosynthesis of class II in EL4 cells transfected with I-Ad with and without Ii. In these studies, we found that Ii had a profound effect on the biosynthesis of I-Ad. In the absence of Ii, class II could form dimers efficiently, but these dimers appeared to be misfolded and this altered conformation resulted in the loss of some monoclonal antibody epitopes and inefficient transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. In addition, class II that was transported through the Golgi accumulated an abnormally increased molecular mass associated with N-linked glycosylation. Subsequent transfection of Ii into these cells resulted in recovery of normal class II conformation, causing a restoration of monoclonal antibody epitopes, efficient intracellular transport, and normal glycosylation. Together, these data indicate that Ii can have a profound effect on the folding, transport, and modification of class II molecules and suggest that one function of Ii may be to act as a class II-specific chaperone.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accolla R. S., Carra G., Buchegger F., Carrel S., Mach J. P. The human Ia-associated invariant chain is synthesized in Ia-negative B cell variants and is not expressed on the cell surface of both Ia-negative and Ia-positive parental cells. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3265–3271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakke O., Dobberstein B. MHC class II-associated invariant chain contains a sorting signal for endosomal compartments. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. S., Cresswell P. Role for intracellular proteases in the processing and transport of class II HLA antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3975–3979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. Proteins as molecular chaperones. 1987 Jul 30-Aug 5Nature. 328(6129):378–379. doi: 10.1038/328378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Hendrix L. R. MHC class II structure, occupancy and surface expression determined by post-endoplasmic reticulum antigen binding. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):134–139. doi: 10.1038/353134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guagliardi L. E., Koppelman B., Blum J. S., Marks M. S., Cresswell P., Brodsky F. M. Co-localization of molecules involved in antigen processing and presentation in an early endocytic compartment. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):133–139. doi: 10.1038/343133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Bränden C. I. Crystal structure of chaperone protein PapD reveals an immunoglobulin fold. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):248–251. doi: 10.1038/342248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt G. D., Swiedler S. J., Freed J. H., Hart G. W. Murine Ia-associated invariant chain's processing to complex oligosaccharide forms and its dissociation from the I-Ak complex. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):399–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman J. F., Auffray C., Korman A. J., Shackelford D. A., Strominger J. The class II molecules of the human and murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski S., Takeshita T., Boehncke W. H., Takahashi H., Boyd L. F., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A., Margulies D. H. Excess beta 2 microglobulin promoting functional peptide association with purified soluble class I MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):74–77. doi: 10.1038/349074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layet C., Germain R. N. Invariant chain promotes egress of poorly expressed, haplotype-mismatched class II major histocompatibility complex A alpha A beta dimers from the endoplasmic reticulum/cis-Golgi compartment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2346–2350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotteau V., Teyton L., Peleraux A., Nilsson T., Karlsson L., Schmid S. L., Quaranta V., Peterson P. A. Intracellular transport of class II MHC molecules directed by invariant chain. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):600–605. doi: 10.1038/348600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehringer J. H., Harris M. R., Kindle C. S., McCourt D. W., Cullen S. E. Characterization of fragments of the murine Ia-associated invariant chain. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):920–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Germain R. N. Efficient cell surface expression of class II MHC molecules in the absence of associated invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1478–1489. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Hatch J. A., Simonis S., Cullen S. E. Identification of the glycosaminoglycan-attachment site of mouse invariant-chain proteoglycan core protein by site-directed mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1359–1363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. A., Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Fan D. P., Braciale T. J. Differences in antigen presentation to MHC class I-and class II-restricted influenza virus-specific cytolytic T lymphocyte clones. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):903–921. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Stollorz V., Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Ploegh H. L. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Heat shock and the sorting of luminal ER proteins. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3171–3176. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M., Miller J. Invariant chain influences the immunological recognition of MHC class II molecules. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):172–174. doi: 10.1038/345172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Cresswell P. Invariant chain association with HLA-DR molecules inhibits immunogenic peptide binding. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):615–618. doi: 10.1038/345615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sant A. J., Hendrix L. R., Coligan J. E., Maloy W. L., Germain R. N. Defective intracellular transport as a common mechanism limiting expression of inappropriately paired class II major histocompatibility complex alpha/beta chains. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):799–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonis S., Miller J., Cullen S. E. The role of the Ia-invariant chain complex in the posttranslational processing and transport of Ia and invariant chain glycoproteins. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3619–3625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyton L., O'Sullivan D., Dickson P. W., Lotteau V., Sette A., Fink P., Peterson P. A. Invariant chain distinguishes between the exogenous and endogenous antigen presentation pathways. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):39–44. doi: 10.1038/348039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Elliott T., Cerundolo V., Foster L., Barber B., Tse A. Assembly of MHC class I molecules analyzed in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):285–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90366-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Ohlén C., Bastin J., Ljunggren H. G., Foster L., Kärre K. Association of class I major histocompatibility heavy and light chains induced by viral peptides. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):443–448. doi: 10.1038/340443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R. The binary logic of antigen processing and presentation to T cells. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):203–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90356-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]