Abstract
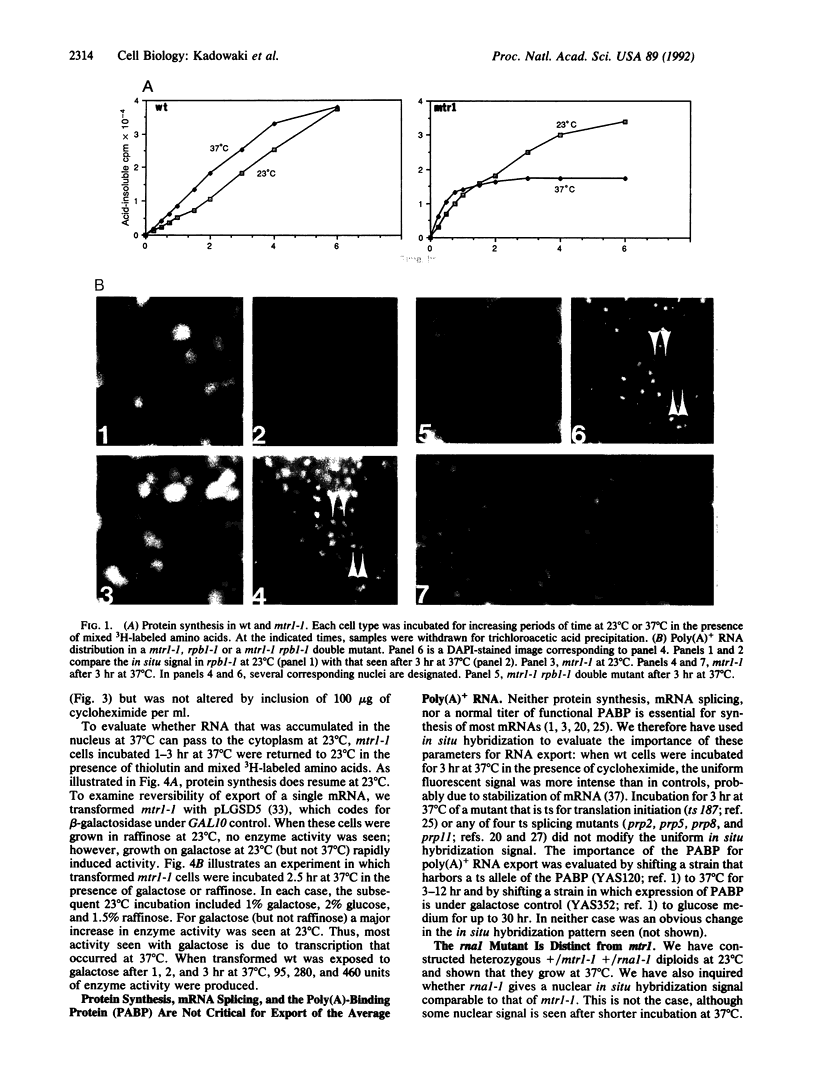
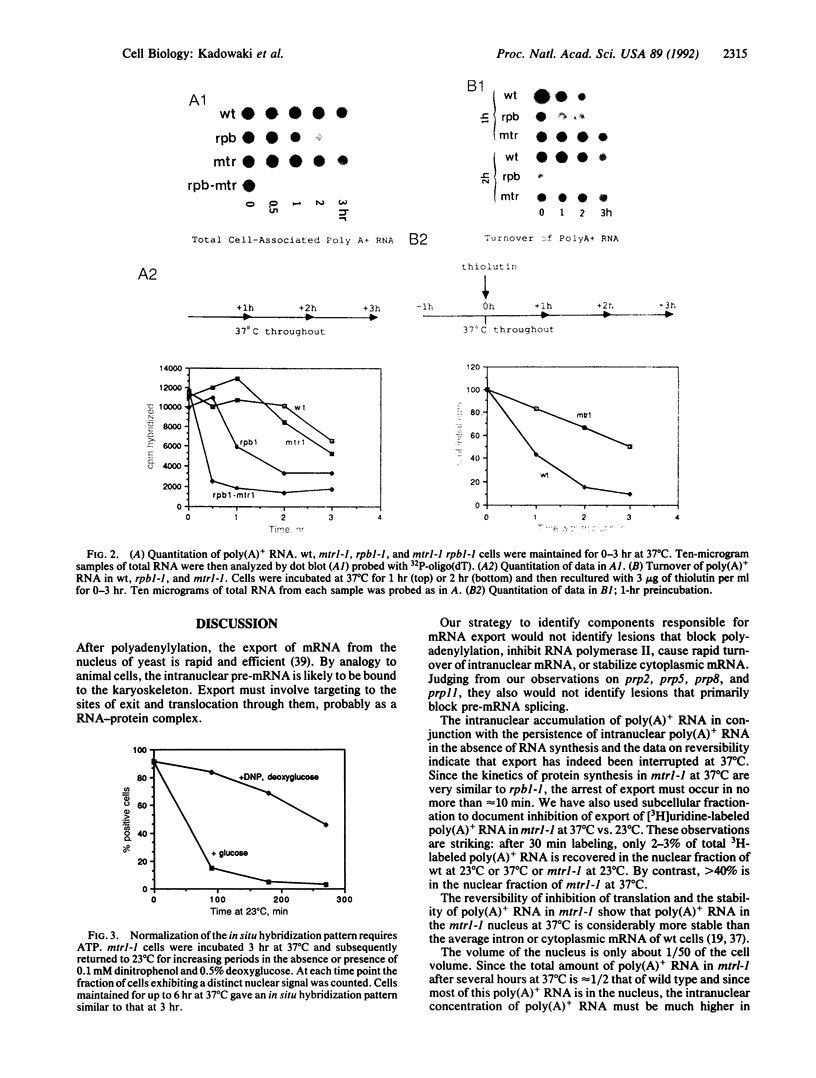
Transport of mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm is critical for eukaryotic gene expression; however, the mechanism of export is unknown. Selection and screening procedures have therefore been used to obtain a family of temperature-sensitive conditional mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that accumulate poly(A)+ RNA in the nucleus when incubated at 37 degrees C, as judged by in situ hybridization. In one such mRNA transport mutant, mtr1-1, RNA synthesis continues, the export of poly(A)+ RNA is inhibited, intranuclear poly(A)+ is remarkably stable, and protein synthesis gradually stops. Thus, there is no tight coupling between RNA synthesis and export. The export lesion is reversible. Although mRNA export is clearly not a default option, neither inhibition of protein synthesis, inhibition of mRNA splicing, nor inhibition of poly(A)-binding protein function blocks export of the average poly(A)+, as judged by in situ hybridization. Further analysis of the family of mtr mutants should help map the path of RNA transport.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. L., Douglas M. G. Organization of the nuclear pore complex in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1989 Aug;102(2):95–108. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(89)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bataillé N., Helser T., Fried H. M. Cytoplasmic transport of ribosomal subunits microinjected into the Xenopus laevis oocyte nucleus: a generalized, facilitated process. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1571–1582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer R. A., Lehner C. F., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. The Role of the poly(A) sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. C., Emerson C. P., Jr The role of cap methylation in the translational activation of stored maternal histone mRNA in sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):691–700. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clawson G. A., Feldherr C. M., Smuckler E. A. Nucleocytoplasmic RNA transport. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 Jul;67(2):87–99. doi: 10.1007/BF02370167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Fink G. R. The NUP1 gene encodes an essential component of the yeast nuclear pore complex. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):965–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworetzky S. I., Feldherr C. M. Translocation of RNA-coated gold particles through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):575–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Darby M. K., Gerace L. A monoclonal antibody against the nuclear pore complex inhibits nucleocytoplasmic transport of protein and RNA in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1289–1297. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner B., Phillips S. L. Polyadenylate metabolism in the nuclei and cytoplasm of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5640–5646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guddat U., Bakken A. H., Pieler T. Protein-mediated nuclear export of RNA: 5S rRNA containing small RNPs in xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90665-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Monomethylated cap structures facilitate RNA export from the nucleus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90292-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., McLaughlin C. S. A mutant of yeast apparently defective in the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):468–474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., McLaughlin C. S., Warner J. R. Identification of ten genes that control ribosome formation in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(1):42–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00334045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick D., Parker R., Jacobson A. Identification and comparison of stable and unstable mRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2269–2284. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Traglia H. M., Dunst R. W. The yeast RNA1 gene product necessary for RNA processing is located in the cytosol and apparently excluded from the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):309–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp G., Beckmann J. S., Johnson P. F., Fuhrman S. A., Abelson J. Transcription and processing of intervening sequences in yeast tRNA genes. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):221–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustig A. J., Lin R. J., Abelson J. The yeast RNA gene products are essential for mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):953–963. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90810-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehrbass U., Kern H., Mutvei A., Horstmann H., Marshallsay B., Hurt E. C. NSP1: a yeast nuclear envelope protein localized at the nuclear pores exerts its essential function by its carboxy-terminal domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90063-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Scafe C., Sexton J., Young R. Eucaryotic RNA polymerase conditional mutant that rapidly ceases mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1602–1611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Kataoka N., Shimura Y. A nuclear cap binding protein from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6989–6995. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piñol-Roma S., Adam S. A., Choi Y. D., Dreyfuss G. Ultraviolet-induced cross-linking of RNA to proteins in vivo. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:410–418. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Three forms of the 5.8-S ribosomal RNA species in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Brown T. A., Trumpower B. L. A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3091–3092. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Bachmann M., Diehl-Seifert B., Müller W. E. Transport of mRNA from nucleus to cytoplasm. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1987;34:89–142. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60494-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiokawa K., Pogo A. O. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in controlling the transport of nuclear messenger RNA and initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2658–2662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sripati C. E., Groner Y., Warner J. R. Methylated, blocked 5' termini of yeast mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):2898–2904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J. Inhibition of yeast ribonucleic acid polymerases by thiolutin. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):245–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.245-256.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobian J. A., Drinkard L., Zasloff M. tRNA nuclear transport: defining the critical regions of human tRNAimet by point mutagenesis. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., van Venrooij W., Ramaekers F. The nuclear matrix: structure and composition. J Cell Sci. 1988 May;90(Pt 1):11–36. doi: 10.1242/jcs.90.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan U., Company M., Abelson J. Isolation and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1206–1216. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Synthesis of ribosomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):256–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.256-271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr Nuclear pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Yeast. 1989 Nov-Dec;5(6):439–457. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]