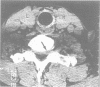
Abstract
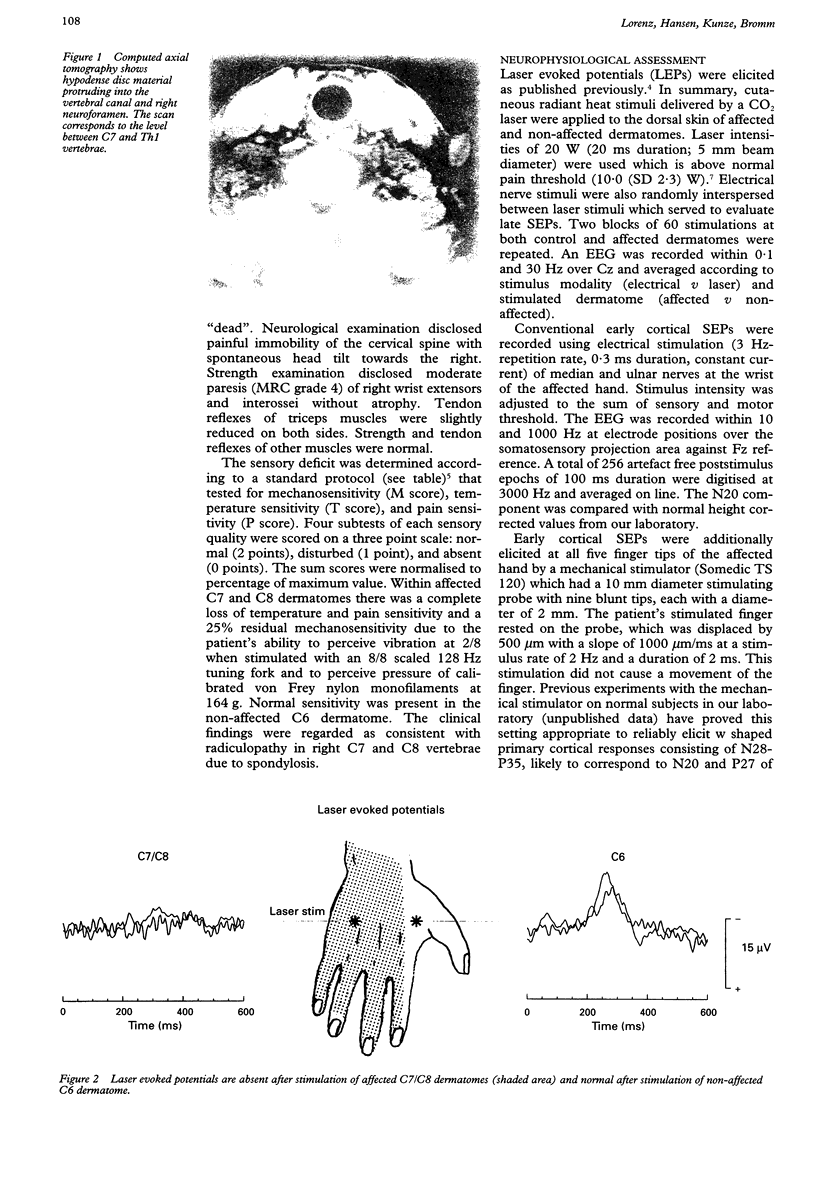
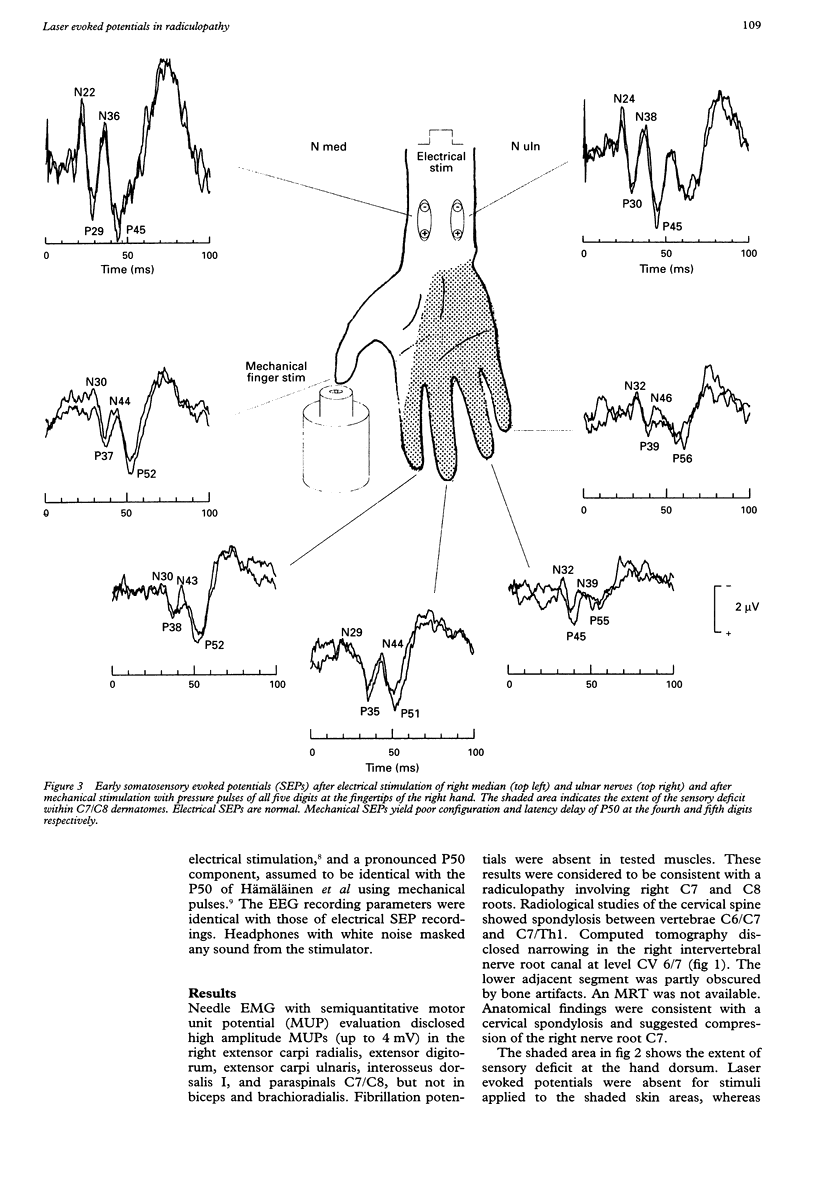
Somatosensory evoked potentials (SEPs) in response to painful laser stimuli were measured in a patient with a unilateral sensory deficit due to radiculopathy at cervical levels C7 and C8. Laser evoked potentials (LEPs) were compared with SEPs using standard electrical stimulation of median and ulnar nerves at the wrist and mechanical stimulation of the fingertips by means of a mechanical stimulator. Early and late ulnar and median nerve SEPs were normal. Mechanical stimulation resulted in w shaped early SEPs from all five fingertips with some degree of abnormality at the fourth and fifth digits of the affected hand. Late LEPs were completely absent for stimulations at affected dermatomes and normal in the unaffected control dermatomes. The border between skin areas with normal or absent LEPs was very sharp and fitted the dermatomes of intact C6 and damaged C7 and C8 nerve roots. It is suggested that pain dermatomes are narrower than tactile dermatomes because thin fibres of the nociceptive system, activated by laser stimuli, probably do not overlap between adjacent spinal segments to the same extent as thick fibres of the mechanoreceptive system, activated by standard electrical or mechanical stimulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aminoff M. J., Goodin D. S., Barbaro N. M., Weinstein P. R., Rosenblum M. L. Dermatomal somatosensory evoked potentials in unilateral lumbosacral radiculopathy. Ann Neurol. 1985 Feb;17(2):171–176. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aminoff M. J., Goodin D. S., Parry G. J., Barbaro N. M., Weinstein P. R., Rosenblum M. L. Electrophysiologic evaluation of lumbosacral radiculopathies: electromyography, late responses, and somatosensory evoked potentials. Neurology. 1985 Oct;35(10):1514–1518. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.10.1514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromm B., Frieling A., Lankers J. Laser-evoked brain potentials in patients with dissociated loss of pain and temperature sensibility. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991 Jul-Aug;80(4):284–291. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(91)90111-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Huy N. T., Bourguet M. The cognitive P40, N60 and P100 components of somatosensory evoked potentials and the earliest electrical signs of sensory processing in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1983 Oct;56(4):272–282. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(83)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinsod M., Blau D., Findler G., Hadani M., Beller A. J. Somatosensory evoked potential to peroneal nerve stimulation in patients with herniated lumbar discs. Neurosurgery. 1982 Oct;11(4):506–511. doi: 10.1227/00006123-198210000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen H., Kekoni J., Sams M., Reinikainen K., Nätänen R. Human somatosensory evoked potentials to mechanical pulses and vibration: contributions of SI and SII somatosensory cortices to P50 and P100 components. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1990 Feb;75(2):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(90)90148-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye Y., Buchthal F. Segmental sensory innervation determined by potentials recorded from cervical spinal nerves. Brain. 1977 Dec;100(4):731–748. doi: 10.1093/brain/100.4.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treede R. D., Lankers J., Frieling A., Zangemeister W. H., Kunze K., Bromm B. Cerebral potentials evoked by painful, laser stimuli in patients with syringomyelia. Brain. 1991 Aug;114(Pt 4):1595–1607. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.4.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walk D., Fisher M. A., Doundoulakis S. H., Hemmati M. Somatosensory evoked potentials in the evaluation of lumbosacral radiculopathy. Neurology. 1992 Jun;42(6):1197–1202. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.6.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]