Abstract
In recent years, there has been an increase in the prevalence of hyperuricemia, and the latter has attracted attention as an adult lifestyle-associated disease, together with hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Although hyperuricemia is known to be an independent risk factor for hypertension, whether it is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease remains controversial. Recently, some small-scale interventional studies on antihyperuricemic medications showed that the latter improved angina symptoms and prevented cardiovascular disease. Here, we will mainly explain the cause of hyperuricemia and the associations between hyperuricemia, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease based on the latest published evidence.
Key Words: Cardiovascular disease, Hypertension, Risk factor, Uric acid, Uric acid transporter
Introduction
The increasing frequency of hyperuricemia and gout are most likely caused by westernized lifestyle and environment [1]. Although the physiological solubility of uric acid occurs at 6.4 mg/dl, the presence of uric acid-binding proteins increases this solubility to 7.0 mg/dl before reaching a supersaturated state. For this reason, hyperuricemia occurs when the serum level of uric acid exceeds 7.0 mg/dl, at which point it starts to crystalize within the human body. However, an increase in the serum uric acid level is considered to accompany the increased risk of disease associated with adult lifestyle habits (lifestyle diseases) even when the serum level of uric acid is ≤7.0 mg/dl. In women, especially, the disease risk increases at even lower serum uric acid levels compared to men and requires more attention.
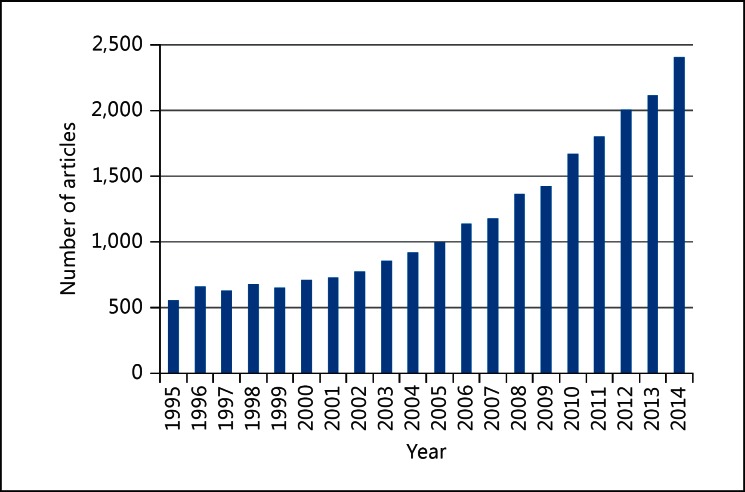
Hyperuricemia often accompanies metabolic syndrome, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, chronic renal disease, and obesity, and the serum uric acid level is known to vary significantly depending on meals, lifestyle, gender, and previous use of diuretics [2]. Based on these facts, it is believed that the uric acid level only partly reflects the lifestyle origins of the disease, and it merely serves as a marker of cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, since female hormones lower the serum uric acid levels, they tend to increase after menopause, and the evaluation of uric acid becomes more difficult. The number of confounding factors involved in evaluating serum uric acid levels complicates the sole analysis of uric acid; indeed, intervention tests that focused only on uric acid are rare. However, due to the advanced research methods and the discovery of new antihyperuricemic drugs such as febuxostat, uric acid studies have been attracting attention (fig. 1). Based on previous clinical studies, we will determine whether hyperuricemia can be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
Fig. 1.
The number of PubMed articles that were published in the last two decades. PubMed was searched for the term ‘hyperuricemia’ or ‘uric acid’ or ‘urate’ or ‘gout’.
Physiological Mechanisms of the Production and Excretion of Uric Acid
When we consider the possibility of hyperuricemia being a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, it is important to be aware of the mechanisms involved in the production of uric acid. The facts, including the circumstances that lead to the production of uric acid and the processes involved, may reveal the relationship between uric acid and lifestyle diseases as well as cardiovascular disease.
Uric acid is a final metabolite of purine metabolism in humans. Although many mammals such as rats have uricase, an enzyme that degrades uric acid into allantoin, humans lost uricase during the course of evolution. As a result, uric acid tends to accumulate. Constituting the base components of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA), adenine and guanine are the purines with purine skeletons. Although there are two routes by which purine enters the human body, through oral intake or biosynthesis, a significantly higher amount of purines is biosynthesized than taken orally.
As for oral intake, given that a unit of nucleic acid exists per cell, foods such as liver are rich in purines as they contain more cells. In contrast, although a chicken egg is relatively large, it only contains single cells and extremely low amounts of purines. Purines that entered the body by ingestion are absorbed in the digestive tract and metabolized to uric acid, the final product. However, the amount is relatively low in comparison to the amount biosynthesized within the human body.
The major energy source in humans, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) structure, centers on adenine, which is converted into hypoxanthine, xanthine, and eventually uric acid during ATP metabolism, and is subsequently excreted from the cell and into the blood. During this process, hypoxanthine is converted into xanthine and later, uric acid, with the activation of xanthine oxygenase (XO) and the production of reactive oxygen during metabolism. This reactive oxygen binds to nitric oxide (NO), a vasodilator substance, and inhibits its function, which is supposedly one of the factors involved in the development of arteriosclerosis. During the metabolism of fructose in soft drinks and alcohol, a large amount of ATP is consumed resulting in the increased amount of uric acid, its final metabolite. Recent increases in the rates of obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease are mainly caused by the elevated intake of sugars including fructose [3]. In pathological conditions such as congenital heart failure and serious heart failure, aggravated anaerobic metabolism in tissues due to oxygen shortage tends to increase the levels of serum lactic acid. The increased lactic acid levels then intensify the reabsorption of uric acid in the kidney, which leads to increased serum uric acid levels [4]. Additionally, the production of uric acid rises during intense exercise. Although the serum uric acid levels are also influenced by excretion from the kidney and digestive tract, increased serum uric acid levels due to the aggravated production of uric acid may be a marker of systemic circulatory failure. Medications such as XO inhibitors (i.e., allopurinol and febuxostat) are effective for the treatment of hyperuricemia due to aggravated uric acid production.
In terms of the excretion of uric acid, approximately two thirds and one third supposedly occur in the kidney and digestive tract, respectively. In the kidney, reabsorption by urate transporter 1 (URAT1) located at the proximal renal tubules plays the biggest role [5]. Nevertheless, other uric acid transporters have also been reported (URATv1/GLUT9, ABCG2, NPT1, NPT4, OAT1, OAT3). Moreover, ABCG2, a uric acid transporter located in the digestive tract, has recently been shown to be involved in the extrarenal excretion of uric acid [6]. The use of URAT1 inhibitors such as benzbromarone and probenecid, are effective for the treatment of the extrarenal urate underexcretion type hyperuricemia. Medications such as angiotensin receptor blockers (e.g., losartan) and the antidyslipidemia drug fenofibrate also inhibit URAT1 and facilitate uric acid excretion in the kidney. In contrast, diuretics such as thiazide and furosemide elevate serum uric acid levels.
Various factors are involved in the processes of uric acid production and secretion. Since medications also have an enormous impact, these factors complicate the process of identification of the reasons for the fluctuation of serum uric acid levels. In order to determine whether the cause of hyperuricemia is overproduction or underexcretion, uric acid or creatinine clearances are utilized for the diagnosis of the underlying disease.
The J-Curve Phenomenon
Since hyperuricemia is closely related to the onset of gout and lifestyle diseases, the negative effects are apparent. In humans, uric acid exerts a strong reducing effect together with bilirubin and ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and acts as an antioxidant. When uric acid levels are too low, the reducing effect also decreases. As a result, reactive oxygen produced within the body cannot be neutralized. According to the PIUMA study [7], when the serum uric acid level decreases to <4.5 and 3.2 mg/dl in male and female hypertensive patients, respectively, the J-curve phenomenon occurs, along with significant increases in rates of cardiovascular disease or even cardiovascular disease-related deaths. The J-curve phenomenon was also reported in the Euro study [8]. In hypertensive patients, hypouricemia needs to be addressed in addition to hyperuricemia. Among several hypouricemia cases, the deletion of URAT1 (SLC22A12) resulted in decreased vascular endothelial function during flow-mediated dilation measurement [9]. Uric acid transporters may also be involved in the J-curve phenomenon. Since excess uric acid not only has an adverse effect, but also acts preferably as a reducing substance, this dual nature needs to be considered.
Hyperuricemia and Hypertension
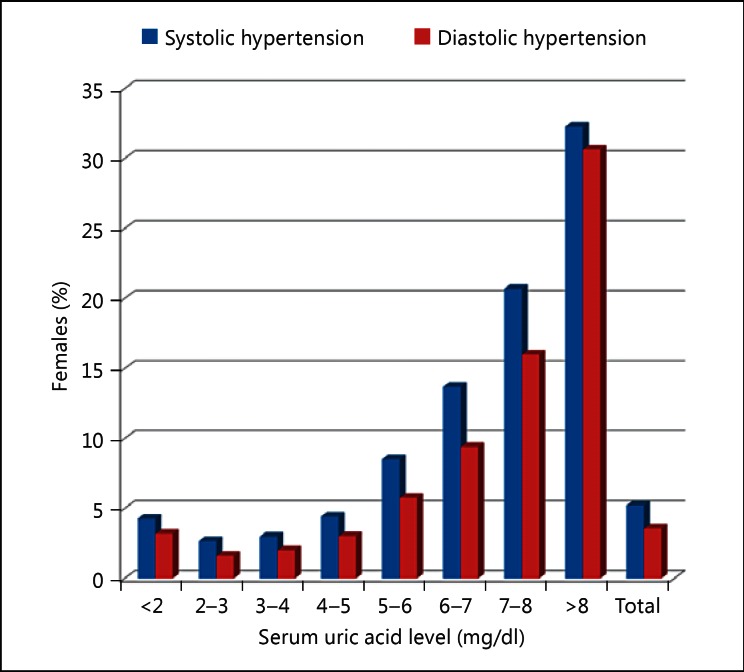
Recent cross-sectional, cohort, and interventional studies have identified hyperuricemia as an independent risk factor for hypertension [10,11,12,13,14,15]. Although several studies have reported the relationship between serum uric acid level and hypertension, the high serum uric acid level group also included many patients with obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Furthermore, drugs easily affect serum uric acid levels. Due to the presence of many confounding factors, the effect of uric acid was considered difficult to interpret. Recent reports on uric acid and hypertension attempted to exclude such confounding factors as much as possible, and double-blind interventional tests were also conducted using drugs in order to demonstrate the relationship between uric acid and hypertension. Our cross-sectional study, which targeted more than 90,000 subjects who visited St. Luke's International Hospital for a health checkup, revealed that even when patients taking antihypertensive and antihyperuricemic medications were excluded and the analysis was adjusted according to age, BMI, dyslipidemia, diabetes, smoking, and estimated glomerular filtration rate, an increase in serum uric levels by 1 mg/dl increased the prevalence of hypertension by 1.2-fold. Furthermore, the quartile examination of serum uric acid levels showed that the group with the highest serum uric acid levels had 1.7- and 3.4-fold prevalence of hypertension in male and female patients, respectively, compared to the group with the lowest serum uric acid levels [10]. The relationship between the serum uric acid level and the prevalence of hypertension was elucidated in this research (fig. 2, 3, 4, 5) [11]. According to a cohort study that targeted 12- to 17-year-olds in the US, even when the high serum uric acid levels during youth were adjusted by other factors, these were independently involved in future increases in blood pressure [12]. Moreover, a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, interventional study, which targeted young obese patients with prehypertension, demonstrated that an inhibitor of uric acid production (allopurinol) and an accelerator of uric acid excretion (probenecid) both lead to decreased blood pressure [13,14]. The previous meta-analysis with allopurinol also showed the lowering effect of blood pressure, which accompanied the decrease in uric acid [15].
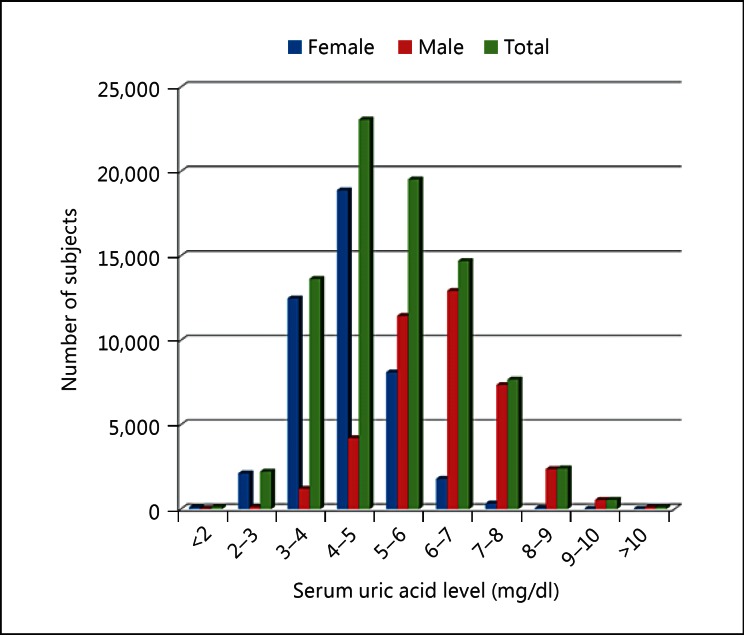
Fig. 2.
The number of subjects enrolled for each serum uric acid level. The average serum uric acid levels were 4.35 ± 0.92 and 6.19 ± 1.21 mg/dl in female and male patients, respectively, and 5.22 ± 1.41 mg/dl in all patients.
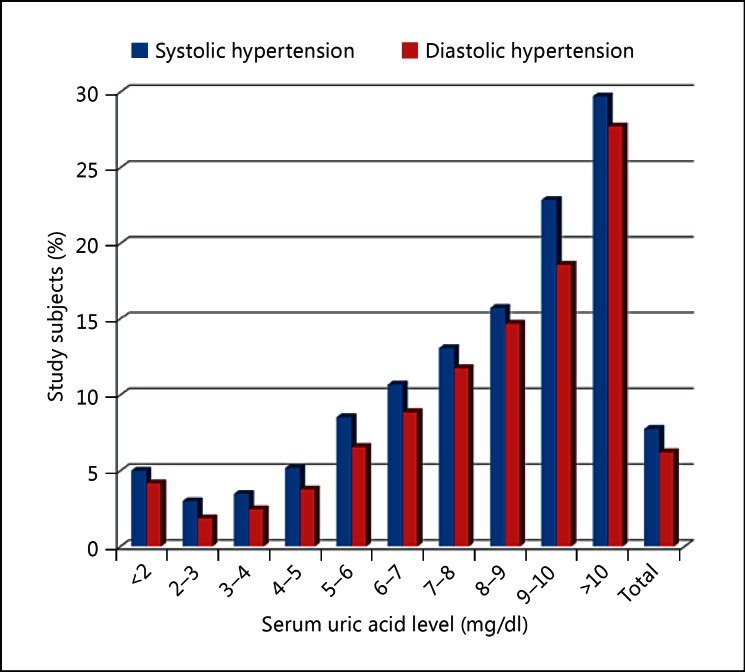
Fig. 3.
The relationship between the prevalence of hypertension and serum uric acid levels in the study subjects. Subjects with serum uric acid levels >5 mg/dl had a higher prevalence of systolic and diastolic hypertension compared to those with levels <5 mg/dl. Subjects with 2-3 mg/dl of serum uric acid were considered optimal due to the associated lowest prevalence of hypertension. Subjects with >10 mg/dl of serum uric acid had more than 10 times higher prevalence of hypertension compared to those with 2-3 mg/dl of serum uric acid.
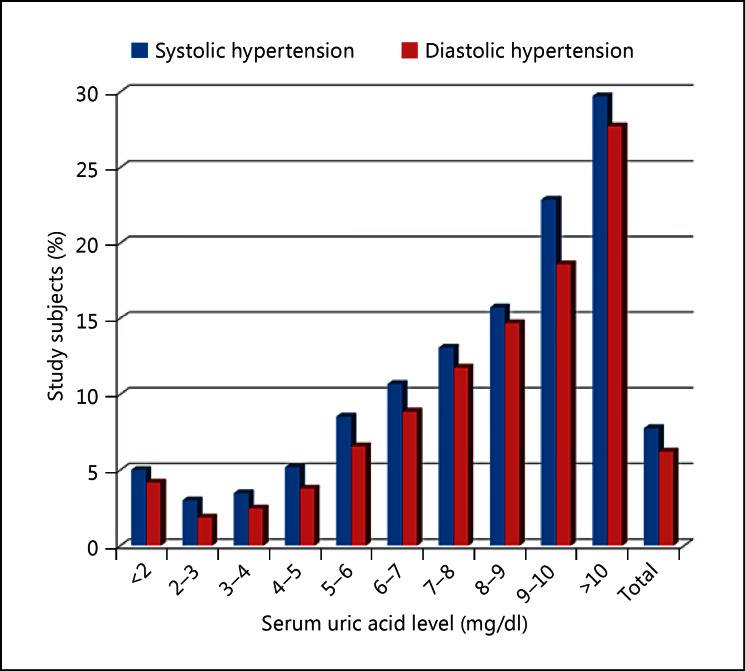
Fig. 4.
The relationship between the prevalence of hypertension and serum uric acid levels in the male study subjects.
Fig. 5.
The relationship between the prevalence of hypertension and serum uric acid levels in the female study subjects. Thirteen female subjects had serum uric acid levels >9 mg/dl, and the group with serum uric acid levels >8 mg/dl included these 13 subjects.
Based on the results of basic science research, the mechanisms by which uric acid triggers arteriosclerosis involve the effects of oxidative stress during uric acid production, urate transporter disorders, and vascular disorders from hyperuricemia (facilitation of arteriosclerosis by monosodium urate crystals) [16]. Clinical research has also shown that correlations between the higher serum uric acid levels and calcification of the coronary artery [17], the decreased flow-mediated dilation, which indicates the vascular endothelial function [18] and higher pulse wave velocity [19], suggest that hyperuricemia is associated with arteriosclerosis. It is almost certain that hyperuricemia induces arteriosclerosis and hypertension. In terms of preventing hypertension, hyperuricemia at a young age needs to be addressed.
Hyperuricemia and Cardiovascular Disease
Many observational studies have been reported on the relationship between hyperuricemia and cardiovascular disease. According to the Rotterdam [20] and NHANES I studies [21] that targeted the general population, the association between high levels of uric acid and myocardial and cerebral infarctions, and cardiovascular death persisted even after adjustment for related factors. In contrast, the Framingham Heart Study [22] and NIPPON DATA 80 [23] indicated that hyperuricemia is not an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease or death, but is only a marker of pathological conditions. Therefore, whether or not hyperuricemia is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease is still under debate. Currently, no conclusion has been reached as to whether a healthy individual manifesting with only hyperuricemia should be treated for hyperuricemia or not. A prospective study reported that treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia without risk for cardiovascular disease prevented urarthritis. However, no prospective study has been conducted with the aim of preventing cardiovascular disease, and a future large-scale prospective study is required.
In contrast, hyperuricemia complicated by hypertension has been reported as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. According to the worksite study that targeted patients with hypertension, when the serum uric acid level exceeds 7.5 and 6.2 mg/dl in male and female patients, respectively, the risk for cardiovascular disease is significantly elevated [24]. In a substudy, an increase in the serum uric acid level by 1 mg/dl resulted in an equivalent risk of 20 mg/dl increase in serum cholesterol as well as 10 mm Hg elevation of systolic blood pressure [25]. Similar results were also reported by the PIUMA study, where a significant increase in the onset of cardiovascular disease was seen when the serum uric acid level exceeded 6.2 and 4.6 mg/dl in male and female patients, respectively [7]. Also, the NHANES III study reported that the onset of cerebral and cardiovascular disease significantly increased when the serum uric acid level exceeded 6.0 mg/dl in both male and female patients [26]. Additionally, in patients with hypertension, a decrease in serum uric acid levels after blood pressure control resulted in the decreased risk for cardiovascular disease. The LIFE study, which compared the serum uric acid levels with the onset of cardiovascular disease among patients receiving losartan and atenolol, showed that the lowering effect of losartan on serum uric acid levels contributed to 29% of the improvement in prognosis in females [27]. In the worksite study mentioned above, patients who received diuretics with antihyperuricemics to normalize their serum uric acid levels had a significant decrease in the risk for cardiovascular disease-related death by 23% [24]. Also, in the SHEP study that targeted senior patients with hypertension, the serum uric acid levels after the blood pressure control were 6.7 and 5.7 mg/dl or higher in male and female patients, respectively, indicating a significant increase in the risk for cardiovascular disease [28]. In the Syst-China study, an increase in serum uric acid levels by 0.86 mg/dl increased the occurrence of death from cerebral or cardiovascular disease significantly [29]. Similar results are also available for patients at risk for cardiovascular disease other than hypertension. In the J-CAD study, a 3-year tracking cohort test, Japanese patients with coronary artery disease were targeted. In this study, a group with serum uric acid levels of 6.8 mg/dl or above showed a significant increase in the onset of cerebral and cardiovascular events including total death [30]. In other studies, an increase in the serum uric acid was shown to be associated with the prognosis of patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease [31]. This mechanism is difficult to explain, but a study showed the independent positive correlation between uric acid and the intensity of arterial wave reflection in the hypertensive but not normotensive subjects [32]. Comprehensively judging based on these results, it is desirable to actively treat hyperuricemia in patients with a high risk of cardiovascular disease, including hypertension, from the viewpoint of preventing cardiovascular disease.
Prospective Interventional Study
Despite being a small-scale study, an interventional study using antihyperuricemic drugs reported on their preventive effects on cardiovascular disease. In the absence of the oral administration of allopurinol, a uric acid production inhibitor, a group of patients with serum uric acid levels of 6 mg/dl (n = 57) was compared to a group with levels at ≥7 mg/dl (n = 56). After the follow-up (mean, 23.4 months), the onset of cardiovascular disease was significantly lower in the group receiving allopurinol [33]. As for angina, high oral doses of allopurinol (600 mg/day) resulted in the significant extension of time until the onset of chest pain (p = 0.001), time required for ST segment decrease (p = 0.002), and total time of exercise (p = 0.003) by a treadmill load test [34]. Although there are only a few prospective clinical tests available and they are all small scale, they support the results of observational studies and prospective clinical studies, and are considered to be very important. No large-scale prospective clinical intervention study targeting the onset of cardiovascular disease with the treatment of uric acid levels as a primary endpoint has been conducted. Thus, the issue of whether the interventions for hyperuricemia directly prevent cardiovascular disease remains controversial.
With regard to heart failure, hyperuricemia has been shown to result in poor prognoses in patients without the complications of chronic kidney disease [35]. In this study, hyperuricemia did not show any association with heart failure in patients with chronic kidney disease. For this reason, extrarenal urate underexcretion type hyperuricemia was considered to have no effect on heart failure, and the excessive uric acid producing hyperuricemia with high XO activity most likely had an adverse effect on heart failure. In contrast, the introduction of XO inhibitors reportedly failed to result in improvements in patients with advanced heart failure complicated by hyperuricemia. The EXACT-HF study targeted 253 patients with advanced heart failure and serum uric acid levels of ≥9.5 mg/dl and compared the oral administration of allopurinol with a placebo control. At 24 weeks, no changes in the clinical status, exercise capacity, quality of life, or left ventricular ejection fraction were reported [36]. Currently, the efficacy of an XO inhibitor on heart failure complicated by hyperuricemia remains uncertain.
Mechanisms of Angiopathy Caused by Hyperuricemia
The three main factors that affect the mechanism of angiopathy due to hyperuricemia include the effects of oxidative stress during uric acid production, the urate transporter disorders, and hyperuricemia-induced vascular disorders (i.e., facilitation of arteriosclerosis by deposition of monosodium urate crystals).
Effects of Oxidative Stress during Uric Acid Production
Uric acid, one of the final metabolites of proteins in humans, is produced by an enzyme, xanthine oxidase/dehydrogenase, via hypoxanthine and xanthine. ATP, which is required when humans consume energy, also produces uric acid as a final product. When human organs are in an ischemic state, anaerobic metabolism progresses and ATP consumption intensifies, which facilitates uric acid production. In addition, since ATP is also used during the degradation of fructose and alcohol, the excess intake of fructose and alcohol also leads to higher levels of uric acid. Furthermore, under an ischemic state, the enzyme takes the form of xanthine oxidase, which leads to an increase in uric acid production. When converted from hypoxanthine to uric acid via xanthine, reactive oxygen is produced. A reactive oxygen species, superoxide radical, has a proliferative stimulus effect on the vascular wall and is involved in arteriosclerosis. As a result, chronic xanthine oxidase activity causes vascular remodeling and is involved in arteriosclerosis. As the reactive oxygen generated during the course of uric acid production binds to NO, a vasodilator substance, and suppresses the function of NO, this effect is also considered as one of the factors for arteriosclerosis.
Disorder via Urate Transporter
Human vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells contain the urate transporters URAT1 (SLC22A12) and URATv1/GLUT9 (SLC2A9). Uric acid enters the cells via these transporters, activates COX-2 via redox reaction, increases the MCP-1, involved in the inflammation of blood vessels and cellular proliferation, and triggers arteriosclerosis. Drugs with URAT1 inhibitory activity, such as benzbromarone, probenecid, fenofibrate (antidyslipidemia drug), losartan, and irbesartan (angiotensin receptor blockers/antihypertensive drugs) are well known. According to the HEAAL study [37], the oral administration of high doses of losartan (high dose, 150 mg) in patients with heart failure lowered the death rates by heart failure or the frequency of hospitalization, compared to low doses (50 mg). The decreased level of uric acid is considered as one of the factors [38].
Hyperuricemia-Induced Vascular Disorders (Facilitation of Arteriosclerosis by Monosodium Urate Crystals)
When the serum uric acid level exceeds 7.0 mg/dl, uric acid that does not stay dissolved in the blood vessel precipitates as monosodium urate crystals. The monosodium urate crystals are deposited on the vascular wall and affect blood coagulation, which likely leads to arteriosclerosis. In blood vessels, the monosodium urate crystal easily precipitates as a result of mechanical stimuli caused by blood pressure. This is the main reason why hyperuricemia is defined as serum uric acid levels that exceed 7.0 mg/dl in the treatment guidelines for hyperuricemia and gout [1]. Monosodium urate crystals bind to plasma IgG, are recognized by the Fc receptors on blood platelets, and stimulate the platelets to induce coagulation; cytokines and thrombi that are produced during this process are involved in the progression of arteriosclerosis. Monosodium urate crystals also activate polynuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes, and generate a variety of inflammatory substances. When polymorphonuclear leukocytes engulf the monosodium urate crystals, this results in the release of superoxides, LDL oxidation, and disorders of endothelial cells and blood platelets - all of which facilitate arteriosclerosis.
Conclusion
Although hyperuricemia in a healthy individual without the risk of cardiovascular disease is considered as an independent risk factor for hypertension, whether it is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease is still controversial. However, hyperuricemia in patients with cardiovascular risks such as hypertension is considered as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and an appropriate intervention is likely necessary at an early stage. The serum uric acid levels need to be monitored, especially in patients at high risk of cardiovascular diseases. Although several small-scale interventional studies that focused on uric acid and cardiovascular diseases have been recently reported, future large-scale, placebo-controlled, double-blind, interventional studies are expected.
Disclosure Statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Prof. Ichiro Hisatome, my director of the postgraduate course at the Institute of Regenerative Medicine and Biofunction, Division of Regenerative Medicine and Therapeutics, Tottori University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Yonago, Tottori, Japan, and Koichiro Niwa, my director in the Department of Cardiology, St. Luke's International Hospital, Tokyo, Japan. I also thank Tsuguya Fukui and all the staff in the Center for Preventive Medicine, St. Luke's International Hospital, for permission to use data and assistance with data collection.
References
- 1.Guideline Revision Committee, JSNM . ed 2. Tokyo: Medical Review; 2010. Guideline for the Management of Hyperuricemia and Gout. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gavin AR, Struthers AD. Hyperuricemia and adverse outcomes in cardiovascular disease: potential for therapeutic intervention. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2003;3:309–314. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200303050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Johnson RJ, Segal MS, Sautin Y, et al. Potential role of sugar (fructose) in the epidemic of hypertension, obesity and the metabolic syndrome, diabetes, kidney disease, and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:899–906. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/86.4.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ross EA, Perloff JK, Danovitch GM, Child JS, Canobbio MM. Renal function and urate metabolism in late survivors with cyanotic congenital heart disease. Circulation. 1986;73:396–400. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Enomoto A, Kimura H, Chairoungdua A, et al. Molecular identification of a renal urate anion exchanger that regulates blood urate levels. Nature. 2002;417:447–452. doi: 10.1038/nature742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ichida K, Matsuo H, Takada T, et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia. Nat Commun. 2012;3:764. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Verdecchia P, Schillaci G, Reboldi G, Santeusanio F, Porcellati C, Brunetti P. Relation between serum uric acid and risk of cardiovascular disease in essential hypertension. The PIUMA study. Hypertension. 2000;36:1072–1078. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.36.6.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.De Leeuw PW, Thijs L, Birkenhager WH, et al. Prognostic significance of renal function in elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension: results from the Syst-Eur trial. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2213–2222. doi: 10.1097/01.asn.0000027871.86296.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sugihara S, Hisatome I, Kuwabara M, et al. Depletion of uric acid due to SLC22A12 (URAT1) loss-of-function mutation causes endothelial dysfunction in hypouricemia. Circ J. 2015;79:1125–1132. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-14-1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kuwabara M, Niwa K, Nishi Y, et al. Relationship between serum uric acid levels and hypertension among Japanese individuals not treated for hyperuricemia and hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2014;37:785–789. doi: 10.1038/hr.2014.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kuwabara M, Niwa K, Nishi Y, Hisatome I, et al. The positive relationship between uric acid and hypertension in Japanese people not taking antihypertensive drugs. J Hypertens. 2011;29:e32–e33. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Loeffler LF, Navas-Acien A, Brady TM, Miller ER, 3rd, Fadrowski JJ. Uric acid level and elevated blood pressure in US adolescents: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2006. Hypertension. 2012;59:811–817. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.183244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Feig DI, Soletsky B, Johnson RJ. Effect of allopurinol on blood pressure of adolescents with newly diagnosed essential hypertension: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008;300:924–932. doi: 10.1001/jama.300.8.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Soletsky B, Feig DI. Uric acid reduction rectifies prehypertension in obese adolescents. Hypertension. 2012;60:1148–1156. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.196980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Agarwal V, Hans N, Messerli FH. Effect of allopurinol on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2013;15:435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kuwabara M, Kume I. Review ‘uric acid and hypertension’. Kidney. 2011;34:29–34. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Atar AI, Yilmaz OC, Akin K, Selcoki Y, Er O, Eryonucu B. Serum uric acid level is an independent risk factor for presence of calcium in coronary arteries: an observational case-controlled study. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2013;13:139–145. doi: 10.5152/akd.2013.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tomiyama H, Higashi Y, Takase B, et al. Relationships among hyperuricemia, metabolic syndrome, and endothelial function. Am J hypertens. 2011;24:770–774. doi: 10.1038/ajh.2011.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mehta T, Nuccio E, McFann K, Madero M, Sarnak MJ, Jalal D. Association of uric acid with vascular stiffness in the Framingham Heart Study. Am J hypertens. 2015;28:877–883. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpu253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bos MJ, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Breteler MM. Uric acid is a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke: the Rotterdam study. Stroke. 2006;37:1503–1507. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000221716.55088.d4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fang J, Alderman MH. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular mortality the NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study, 1971-1992. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. JAMA. 2000;283:2404–2410. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.18.2404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Culleton BF, Larson MG, Kannel WB, Levy D. Serum uric acid and risk for cardiovascular disease and death: the Framingham Heart Study. Ann Intern Med. 1999;131:7–13. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-131-1-199907060-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sakata K, Hashimoto T, Ueshima H, Okayama A, et al. Absence of an association between serum uric acid and mortality from cardiovascular disease: NIPPON DATA 80, 1980-1994. National Integrated Projects for Prospective Observation of Non-communicable Diseases and its Trend in the Aged. Eur J Epidemiol. 2001;17:461–468. doi: 10.1023/a:1013735717961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Alderman MH, Cohen H, Madhavan S, Kivlighn S. Serum uric acid and cardiovascular events in successfully treated hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 1999;34:144–150. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.34.1.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Alderman MH. Serum uric acid as a cardiovascular risk factor for heart disease. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2001;3:184–189. doi: 10.1007/s11906-001-0036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ward HJ. Uric acid as an independent risk factor in the treatment of hypertension. Lancet. 1998;352:670–671. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)60816-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hoieggen A, Alderman MH, Kjeldsen SE, et al. The impact of serum uric acid on cardiovascular outcomes in the LIFE study. Kidney Int. 2004;65:1041–1049. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Franse LV, Pahor M, Di Bari M, et al. Serum uric acid, diuretic treatment and risk of cardiovascular events in the Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program (SHEP). J Hypertens. 2000;18:1149–1154. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200018080-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang JG, Staessen JA, Fagard RH, Birkenhager WH, Gong L, Liu L. Prognostic significance of serum creatinine and uric acid in older Chinese patients with isolated systolic hypertension. Hypertension. 2001;37:1069–1074. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.37.4.1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Okura T, Higaki J, Kurata M, et al. Elevated serum uric acid is an independent predictor for cardiovascular events in patients with severe coronary artery stenosis: subanalysis of the Japanese Coronary Artery Disease (JCAD) Study. Circ J. 2009;73:885–891. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-08-0828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ioachimescu AG, Brennan DM, Hoar BM, Hazen SL, Hoogwerf BJ. Serum uric acid is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease: a preventive cardiology information system (PreCIS) database cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:623–630. doi: 10.1002/art.23121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hsu PF, Chuang SY, Cheng HM, Sung SH, Ting CT, Lakatta EG, et al. Associations of serum uric acid levels with arterial wave reflections and central systolic blood pressure. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168:2057–2063. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.01.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Goicoechea M, de Vinuesa SG, Verdalles U, et al. Effect of allopurinol in chronic kidney disease progression and cardiovascular risk. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:1388–1393. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01580210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Noman A, Ang DS, Ogston S, Lang CC, Struthers AD. Effect of high-dose allopurinol on exercise in patients with chronic stable angina: a randomised, placebo controlled crossover trial. Lancet. 2010;375:2161–2167. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60391-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Filippatos GS, Ahmed MI, Gladden JD, et al. Hyperuricaemia, chronic kidney disease, and outcomes in heart failure: potential mechanistic insights from epidemiological data. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:712–720. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Givertz MM, Anstrom KJ, Redfield MM, Deswal A, Haddad H, Butler J, et al. Effects of xanthine oxidase inhibition in hyperuricemic heart failure patients: The Xanthine Oxidase Inhibition for Hyperuricemic Heart Failure Patients (EXACT-HF) Study. Circulation. 2015;131:1763–1771. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.014536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Konstam MA, Neaton JD, Dickstein K, et al. Effects of high-dose versus low-dose losartan on clinical outcomes in patients with heart failure (HEAAL study): a randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1840–1848. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61913-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kang SM, Oh J, Hong N. High-dose versus low-dose losartan in patients with heart failure. Lancet. 2010;375(1079):1079–1080. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60473-4. author reply. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]