Abstract
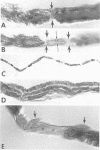
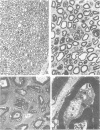
OBJECTIVE: To develop and characterise an animal model of paralytic neuropathy after Campylobacter jejuni infection. Campylobacter infection precedes development of many cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome and is particularly associated with cases having prominent axonal degeneration. Understanding the pathogenesis of Guillain-Barré syndrome after C jejuni infection has been slowed by the lack of animal models. METHODS: A spontaneous paralytic neuropathy is described that developed in chickens from the farms of four patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. The production of paralytic neuropathy in chickens experimentally fed Campylobacter jejuni isolated from one of these patients is reported. The sciatic nerves of the spontaneously paralysed chickens were examined pathologically in teased fibres, in plastic embedded sections, and by electron microscopy. Two large groups of chickens were then fed cultures of a C jejuni (Penner type O:19) isolated from one of these patients. RESULTS: The chickens with spontaneous paralysis had pathologically noninflammatory neuropathy. Pathology in the sciatic nerves ranged from no detectable changes to severe Wallerian-like degeneration. In the experimentally inoculated groups, an average of 33% of the chickens became paralysed. The median time after inoculation to paralysis was 12 days. The lesions found in the first few days of paralysis included nodal lengthening and paranodal demyelination. In those animals that survived for several days after onset of weakness, the pathology was dominated by extensive Wallerian-like degeneration. Animals that survived for weeks with no clinically apparent neuropathy had paranodal remyelination in some teased nerve fibres, reflecting earlier paranodal demyelination. CONCLUSION: Experimental inoculation with C jejuni may provide a new model for understanding some forms of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J. Is there an axonal variety of GBS? Neurology. 1993 Jul;43(7):1277–1280. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.7.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders U., Karch H., Toyka K. V., Michels M., Zielasek J., Pette M., Heesemann J., Hartung H. P. The spectrum of immune responses to Campylobacter jejuni and glycoconjugates in Guillain-Barré syndrome and in other neuroimmunological disorders. Ann Neurol. 1993 Aug;34(2):136–144. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feasby T. E., Gilbert J. J., Brown W. F., Bolton C. F., Hahn A. F., Koopman W. F., Zochodne D. W. An acute axonal form of Guillain-Barré polyneuropathy. Brain. 1986 Dec;109(Pt 6):1115–1126. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.6.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feasby T. E., Hahn A. F., Brown W. F., Bolton C. F., Gilbert J. J., Koopman W. J. Severe axonal degeneration in acute Guillain-Barré syndrome: evidence of two different mechanisms? J Neurol Sci. 1993 Jun;116(2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90324-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto S., Yuki N., Itoh T., Amako K. Specific serotype of Campylobacter jejuni associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):183–183. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. W., Li C. Y., Ho T. W., Tian M., Gao C. Y., Xue P., Mishu B., Cornblath D. R., Macko C., McKhann G. M. Pathology of the motor-sensory axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1996 Jan;39(1):17–28. doi: 10.1002/ana.410390105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. W., Li C. Y., Ho T. W., Xue P., Macko C., Gao C. Y., Yang C., Tian M., Mishu B., Cornblath D. R. Guillain-Barré syndrome in northern China. The spectrum of neuropathological changes in clinically defined cases. Brain. 1995 Jun;118(Pt 3):577–595. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.3.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. W., Li C. Y., Macko C., Ho T. W., Hsieh S. T., Xue P., Wang F. A., Cornblath D. R., McKhann G. M., Asbury A. K. Early nodal changes in the acute motor axonal neuropathy pattern of the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J Neurocytol. 1996 Jan;25(1):33–51. doi: 10.1007/BF02284784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho T. W., Mishu B., Li C. Y., Gao C. Y., Cornblath D. R., Griffin J. W., Asbury A. K., Blaser M. J., McKhann G. M. Guillain-Barré syndrome in northern China. Relationship to Campylobacter jejuni infection and anti-glycolipid antibodies. Brain. 1995 Jun;118(Pt 3):597–605. doi: 10.1093/brain/118.3.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaldor J., Pritchard H., Serpell A., Metcalf W. Serum antibodies in Campylobacter enteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jul;18(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.1.1-4.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusunoki S., Chiba A., Kon K., Ando S., Arisawa K., Tate A., Kanazawa I. N-acetylgalactosaminyl GD1a is a target molecule for serum antibody in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1994 May;35(5):570–576. doi: 10.1002/ana.410350510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G. M., Cornblath D. R., Griffin J. W., Ho T. W., Li C. Y., Jiang Z., Wu H. S., Zhaori G., Liu Y., Jou L. P. Acute motor axonal neuropathy: a frequent cause of acute flaccid paralysis in China. Ann Neurol. 1993 Apr;33(4):333–342. doi: 10.1002/ana.410330402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees J. H., Gregson N. A., Hughes R. A. Anti-ganglioside GM1 antibodies in Guillain-Barré syndrome and their relationship to Campylobacter jejuni infection. Ann Neurol. 1995 Nov;38(5):809–816. doi: 10.1002/ana.410380516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees J. H., Soudain S. E., Gregson N. A., Hughes R. A. Campylobacter jejuni infection and Guillain-Barré syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 23;333(21):1374–1379. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511233332102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriesendorp F. J., Mishu B., Blaser M. J., Koski C. L. Serum antibodies to GM1, GD1b, peripheral nerve myelin, and Campylobacter jejuni in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome and controls: correlation and prognosis. Ann Neurol. 1993 Aug;34(2):130–135. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winer J. B., Hughes R. A., Anderson M. J., Jones D. M., Kangro H., Watkins R. P. A prospective study of acute idiopathic neuropathy. II. Antecedent events. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1988 May;51(5):613–618. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.51.5.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki N., Sato S., Fujimoto S., Yamada S., Tsujino Y., Kinoshita A., Itoh T. Serotype of Campylobacter jejuni, HLA, and the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1992 Aug;15(8):968–969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki N., Yoshino H., Sato S., Miyatake T. Acute axonal polyneuropathy associated with anti-GM1 antibodies following Campylobacter enteritis. Neurology. 1990 Dec;40(12):1900–1902. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.12.1900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki N., Yoshino H., Sato S., Shinozawa K., Miyatake T. Severe acute axonal form of Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with IgG anti-GD1a antibodies. Muscle Nerve. 1992 Aug;15(8):899–903. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]