Abstract
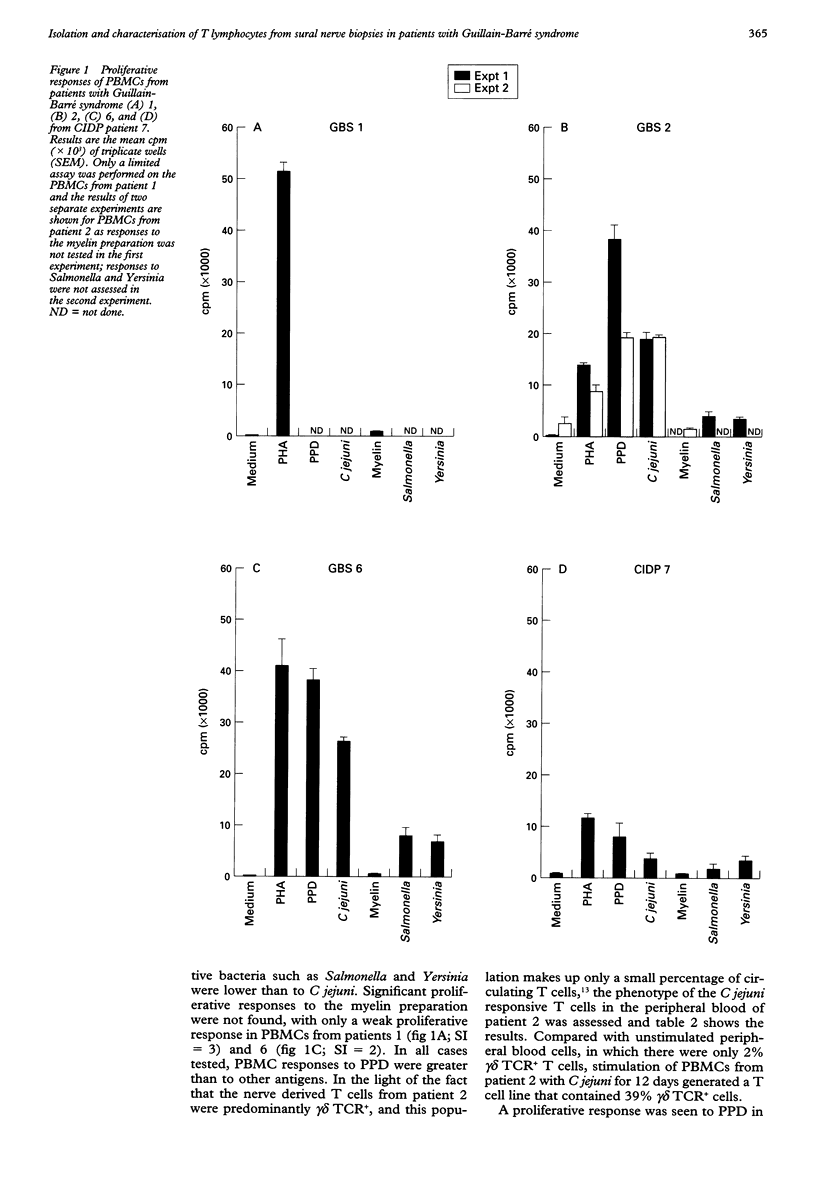
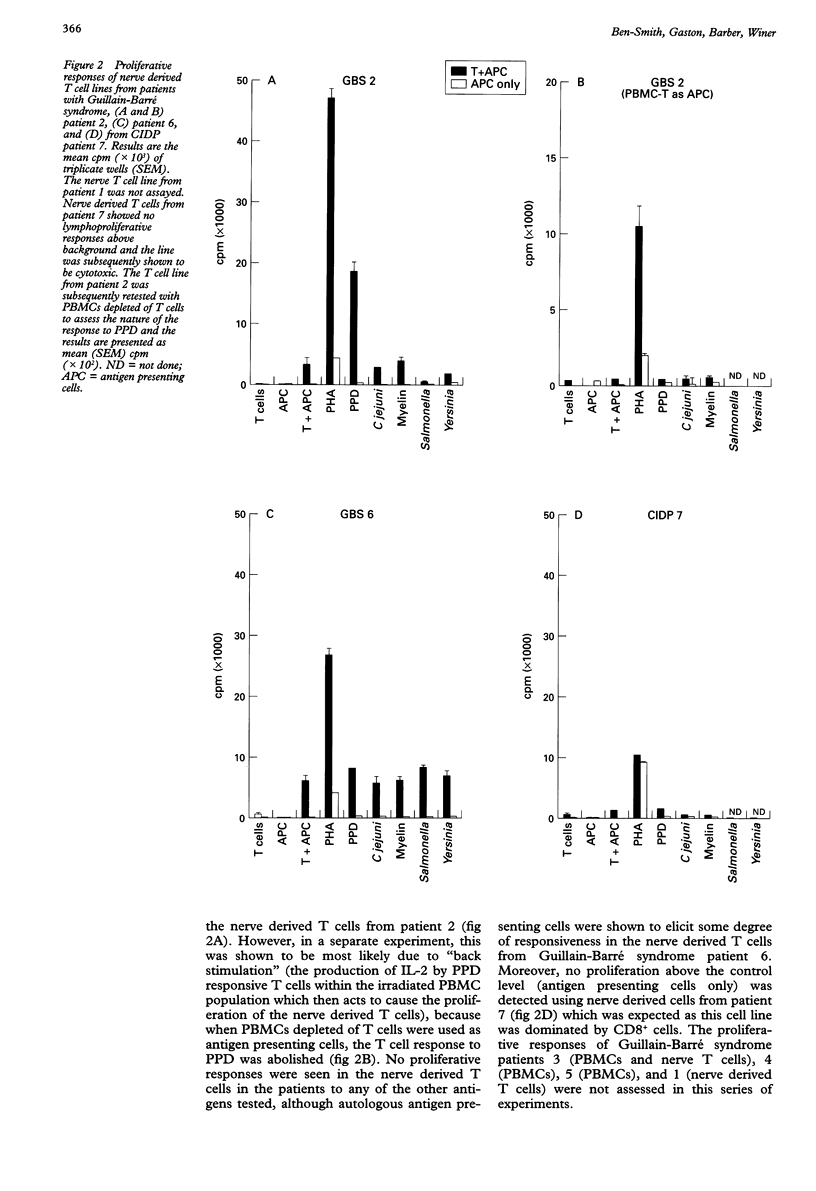
OBJECTIVES: To characterise cultured T lymphocytes from nerve biopsies in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP). METHODS: Sural nerve biopsies, obtained from six patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome, four with CIDP, and six controls with other neuropathies, were cultured with 20 U/ml recombinant interleukin-2 (IL-2) for eight weeks. Flow cytometry was used to determine the phenotype of cultured T lymphocytes. Their proliferative responses to a range of bacterial antigens were also examined. RESULTS: T cell lines were established from four of six patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome, one of four with CIDP, one patient with peripheral nerve vasculitis, and none of five controls with non-inflammatory neuropathies. One of these T cell lines from a patient with Guillain-Barré syndrome, preceded by Campylobacter jejuni infection, consisted entirely of gamma delta TCR+ T lymphocytes. The peripheral blood of this patient also contained an increased frequency of gamma delta T cells when stimulated with C jejuni. The nerve derived T cell lines failed to show a proliferative response to bacterial antigens or to a preparation of myelin proteins. CONCLUSIONS: A new technique to isolate T cells from nerve biopsies in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome and CIDP is reported. This technique may prove to be a useful tool in the investigation of the pathogenesis of other inflammatory neuropathies such as peripheral nerve vasculitis. The isolation of a gamma delta TCR+ nerve T cell line is of interest because of the possibility that these cells might respond to glycolipid epitopes common to C jejuni and peripheral nerve gangliosides.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelmann M., Linington C. Molecular mimicry and the autoimmune response to the peripheral nerve myelin P0 glycoprotein. Neurochem Res. 1992 Sep;17(9):887–891. doi: 10.1007/BF00993264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archelos J. J., Mäurer M., Jung S., Miyasaka M., Tamatani T., Toyka K. V., Hartung H. P. Inhibition of experimental autoimmune neuritis by an antibody to the lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1. Lab Invest. 1994 May;70(5):667–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aspinall G. O., Fujimoto S., McDonald A. G., Pang H., Kurjanczyk L. A., Penner J. L. Lipopolysaccharides from Campylobacter jejuni associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome patients mimic human gangliosides in structure. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):2122–2125. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.2122-2125.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., McLean J., Scheft H., Riberdy J., Ang S. L., Seidman J. G., Devlin P., Krangel M. S. Two forms of the T-cell receptor gamma protein found on peripheral blood cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):689–694. doi: 10.1038/325689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Benjamin D. S., Burks J., Weiner H. L. Myelin basic protein and proteolipid protein reactivity of brain- and cerebrospinal fluid-derived T cell clones in multiple sclerosis and postinfectious encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):68–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn A. F., Feasby T. E., Wilkie L., Lovgren D. Antigalactocerebroside antibody increases demyelination in adoptive transfer experimental allergic neuritis. Muscle Nerve. 1993 Nov;16(11):1174–1180. doi: 10.1002/mus.880161106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Pollard J. D., Harvey G. K., Toyka K. V. Immunopathogenesis and treatment of the Guillain-Barré syndrome--Part II. Muscle Nerve. 1995 Feb;18(2):154–164. doi: 10.1002/mus.880180203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R., Atkinson P., Coates P., Hall S., Leibowitz S. Sural nerve biopsies in Guillain-Barre syndrome: axonal degeneration and macrophage-associated demyelination and absence of cytomegalovirus genome. Muscle Nerve. 1992 May;15(5):568–575. doi: 10.1002/mus.880150506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illa I., Ortiz N., Gallard E., Juarez C., Grau J. M., Dalakas M. C. Acute axonal Guillain-Barré syndrome with IgG antibodies against motor axons following parenteral gangliosides. Ann Neurol. 1995 Aug;38(2):218–224. doi: 10.1002/ana.410380214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W. Mechanism of demyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. Electron microscopic studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Feb;20(2):127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linington C., Izumo S., Suzuki M., Uyemura K., Meyermann R., Wekerle H. A permanent rat T cell line that mediates experimental allergic neuritis in the Lewis rat in vivo. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1946–1950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löhr H., Manns M., Kyriatsoulis A., Lohse A. W., Trautwein C., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Fleischer B. Clonal analysis of liver-infiltrating T cells in patients with LKM-1 antibody-positive autoimmune chronic active hepatitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 May;84(2):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Kato H., Mehra V., Nelson E. E., Fan X. D., Rea T. H., Pattengale P. K., Bloom B. R. Genetically restricted suppressor T-cell clones derived from lepromatous leprosy lesions. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):459–461. doi: 10.1038/322459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano T., Ito M., Mizuno T., Mizutani K., Ihara T., Kamiya H., Sakurai M. Increase of interleukin 2 receptor and CD45RO antigen on lymphocytes cultured with human cytomegalovirus. Cell Immunol. 1993 Mar;147(1):73–80. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcelli S., Brenner M. B., Greenstein J. L., Balk S. P., Terhorst C., Bleicher P. A. Recognition of cluster of differentiation 1 antigens by human CD4-CD8-cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):447–450. doi: 10.1038/341447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Newman W., Tanaka Y., Shaw S. Lymphocyte interactions with endothelial cells. Immunol Today. 1992 Mar;13(3):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90151-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll G., Jander S., Jung S., Archelos J., Tamatani T., Miyasaka M., Toyka K. V., Hartung H. P. Macrophages and endothelial cells express intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in immune-mediated demyelination but not in Wallerian degeneration of the rat peripheral nervous system. Lab Invest. 1993 Jun;68(6):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Morita C. T., Tanaka Y., Nieves E., Brenner M. B., Bloom B. R. Natural and synthetic non-peptide antigens recognized by human gamma delta T cells. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):155–158. doi: 10.1038/375155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. A., Hughes R. A. Responsiveness to P2 of blood- and cauda equina-derived lymphocytes in experimental allergic neuritis in the Lewis rat: preliminary characterisation of a P2-specific cauda equina-derived T cell line. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Oct;19(4):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viner N. J., Bailey L. C., Life P. F., Bacon P. A., Gaston J. S. Isolation of Yersinia-specific T cell clones from the synovial membrane and synovial fluid of a patient with reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Sep;34(9):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A., Lee J. E., Link M. P., Smith S. D., Carroll W., Levy R., Clayberger C., Krensky A. M. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for self tumor immunoglobulin express T cell receptor delta chain. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1557–1564. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuki N., Taki T., Takahashi M., Saito K., Tai T., Miyatake T., Handa S. Penner's serotype 4 of Campylobacter jejuni has a lipopolysaccharide that bears a GM1 ganglioside epitope as well as one that bears a GD1 a epitope. Infect Immun. 1994 May;62(5):2101–2103. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.5.2101-2103.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Link H., Mix E., Olsson T., Huang W. X. Th1-like cell responses to peripheral nerve myelin components over the course of experimental allergic neuritis in Lewis rats. Acta Neurol Scand. 1994 Jul;90(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1994.tb02674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


