Abstract
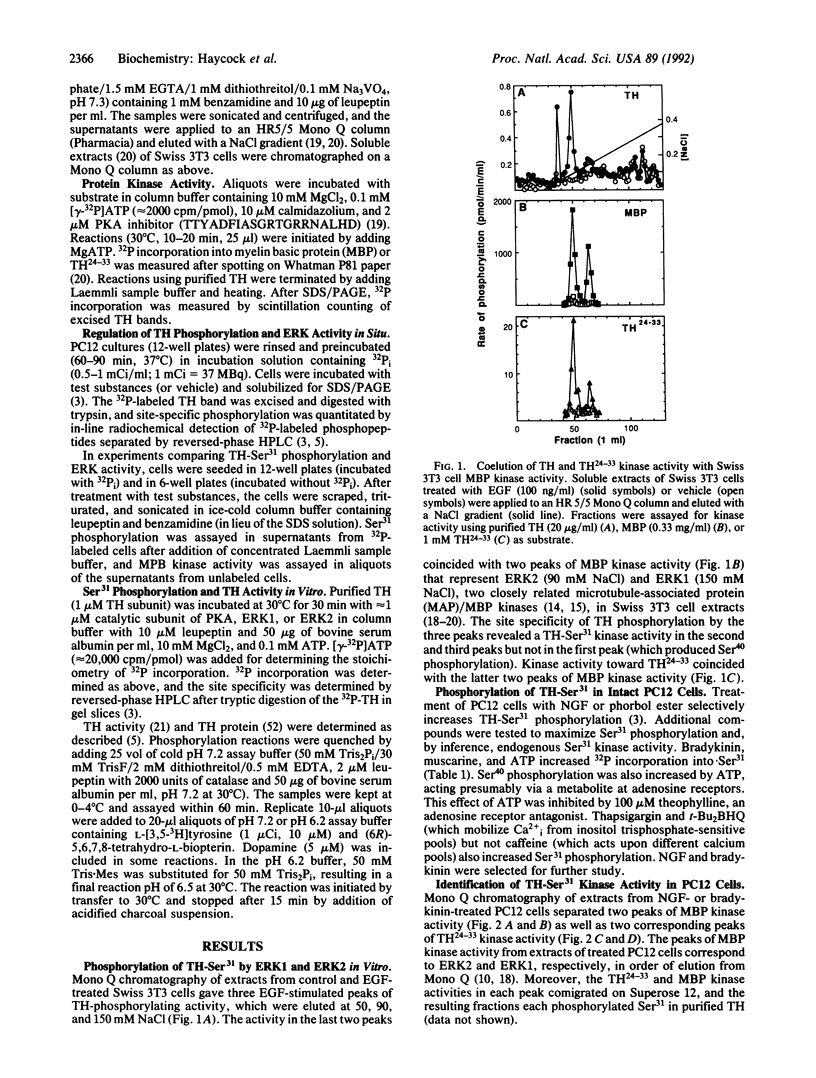
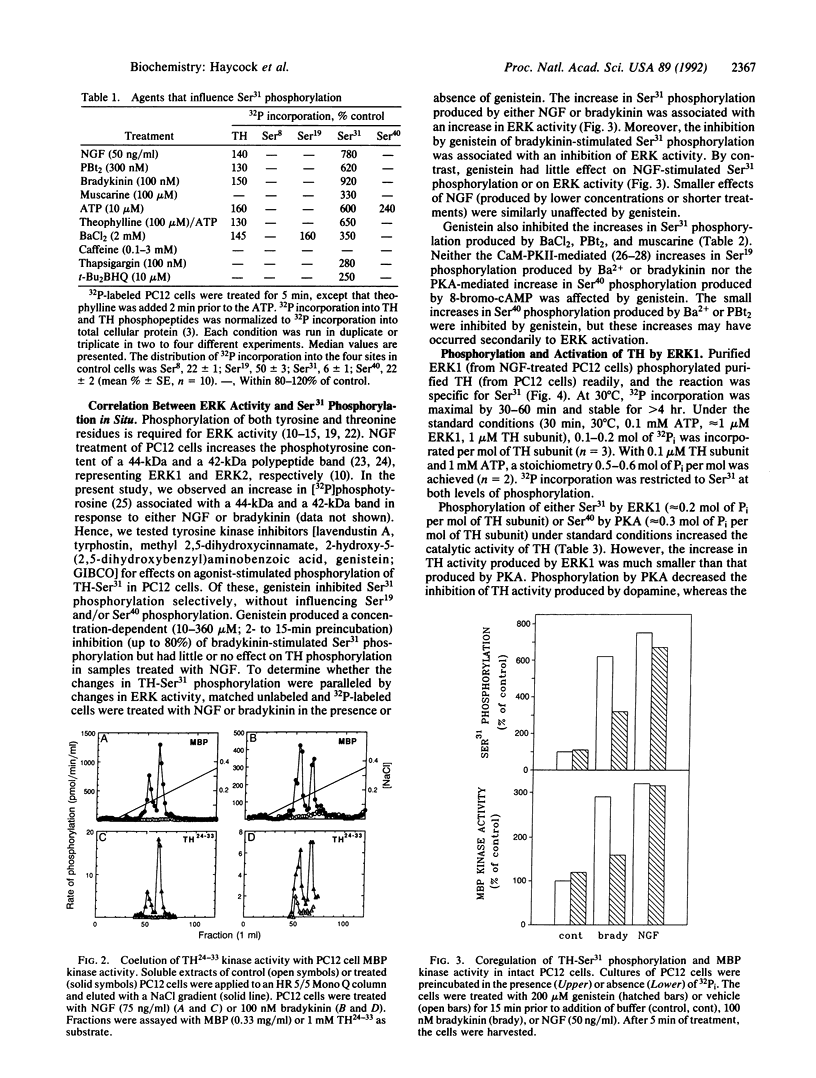
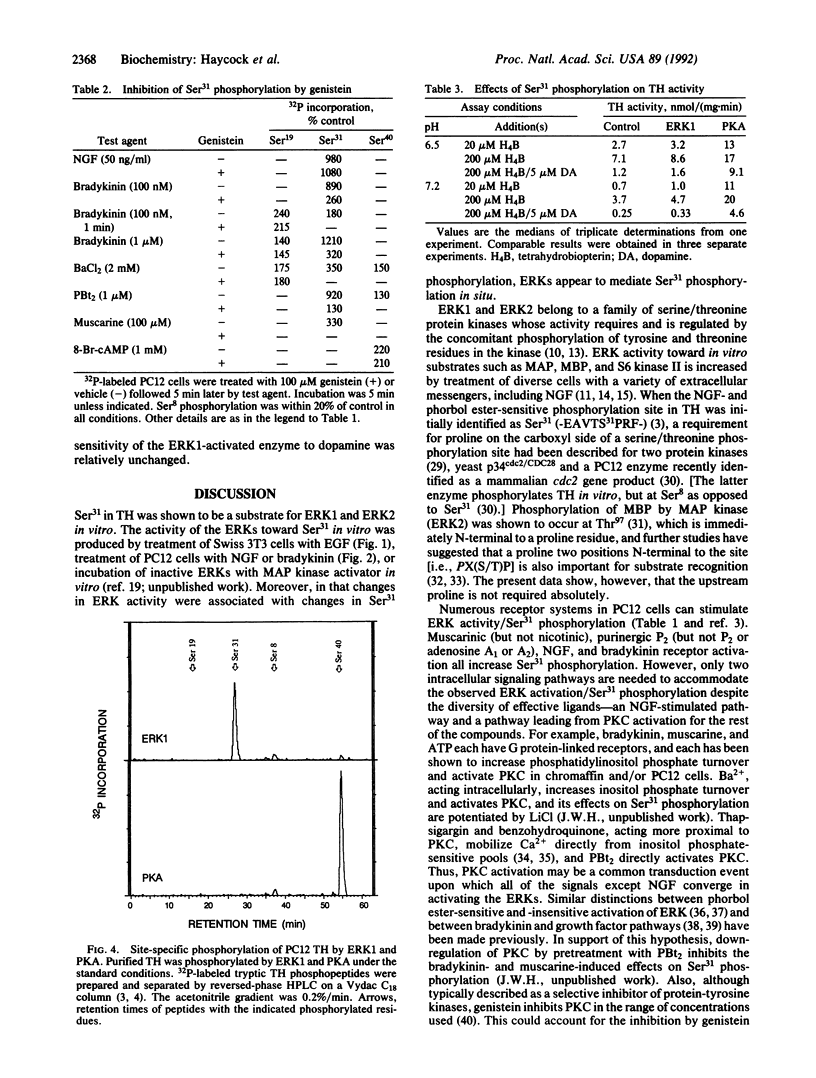
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) is phosphorylated at four sites in situ and in vivo, and the protein kinases that phosphorylate three of these sites (Ser8,Ser19,Ser40) have been identified. In intact cells, the phosphorylation of the fourth site (Ser31) is increased in response to phorbol esters or nerve growth factor (NGF). Here, we show that Ser31 is phosphorylated by ERK1 and ERK2, two myelin basic protein and microtubule-associated protein kinases. Extracts of NGF- or bradykinin-treated PC12 rat pheochromocytoma cells were fractionated on Mono Q columns. Protein kinase activity toward Ser31 in TH was present in two peaks corresponding to myelin basic protein kinase activities previously identified as ERK1 and ERK2. Phosphorylation of purified TH in vitro by both kinases was selective for Ser31 up to at least 0.6 mol of phosphate per mol of TH subunit. Treatment of intact PC12 cells with bradykinin or NGF increased both the phosphorylation of TH-Ser31 in situ and the catalytic activity of ERKs (measured subsequently in vitro with myelin basic protein as substrate). Pretreatment of the cells with genistein (a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor) decreased the bradykinin- but not the NGF-induced changes in both TH-Ser31 phosphorylation and ERK activity. Genistein also inhibited the increases in Ser31 phosphorylation produced by phorbol dibutyrate, muscarine, and Ba2+. The data indicate that ERK activity is responsible for phosphorylating TH at Ser31 in intact cells and suggest that TH-Ser31 phosphorylation may be regulated by multiple signaling pathways that converge at or prior to the activation of the ERKs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Weiel J. E., Chan C. P., Krebs E. G. Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11487–11494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert K. A., Helmer-Matyjek E., Nairn A. C., Müller T. H., Haycock J. W., Greene L. A., Goldstein M., Greengard P. Calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) phosphorylates and activates tyrosine hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7713–7717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altin J. G., Bradshaw R. A. Production of 1,2-diacylglycerol in PC12 cells by nerve growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1666–1676. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Kilgour E., Sturgill T. W. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in BC3H1 myocytes by fluoroaluminate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10131–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson J., Richtand N., Schworer C., Kuczenski R., Soderling T. Phosphorylation of purified rat striatal tyrosine hydroxylase by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: effect of an activator protein. J Neurochem. 1987 Oct;49(4):1241–1249. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb10016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H. Identification of multiple extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) with antipeptide antibodies. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):357–371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Gregory J. S., Cobb M. H. Purification and properties of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1, an insulin-stimulated microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):278–286. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton T. G., Nye S. H., Robbins D. J., Ip N. Y., Radziejewska E., Morgenbesser S. D., DePinho R. A., Panayotatos N., Cobb M. H., Yancopoulos G. D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):663–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90098-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill A. L., Horwitz J., Perlman R. L. Phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase in protein kinase C-deficient PC12 cells. Neuroscience. 1989;30(3):811–818. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Robbins D. J., Boulton T. G. ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated MAP-2 kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. K., Payne D. M., Martino P. A., Rossomando A. J., Shabanowitz J., Weber M. J., Hunt D. F., Sturgill T. W. Identification by mass spectrometry of threonine 97 in bovine myelin basic protein as a specific phosphorylation site for mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19728–19735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasolato C., Pandiella A., Meldolesi J., Pozzan T. Generation of inositol phosphates, cytosolic Ca2+, and ionic fluxes in PC12 cells treated with bradykinin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17350–17359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink D. W., Jr, Guroff G. Nerve growth factor stimulation of arachidonic acid release from PC12 cells: independence from phosphoinositide turnover. J Neurochem. 1990 Nov;55(5):1716–1726. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahn L. G., Roskoski R., Jr Tyrosine hydroxylase purification from rat PC12 cells. Protein Expr Purif. 1991 Feb;2(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/1046-5928(91)90002-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler J. F., Traxler P., Regenass U., Murray B. J., Roesel J. L., Meyer T., McGlynn E., Storni A., Lydon N. B. Thiazolidine-diones. Biochemical and biological activity of a novel class of tyrosine protein kinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22255–22261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Yamashita T., Hoshi M., Kawakami M., Sakai H. Microtubule-associated-protein (MAP) kinase activated by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. Identity with the mitogen-activated MAP kinase of fibroblastic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):661–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19384.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Seeley P. J., Rukenstein A., DiPiazza M., Howard A. Rapid activation of tyrosine hydroxylase in response to nerve growth factor. J Neurochem. 1984 Jun;42(6):1728–1734. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12764.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall F. L., Vulliet P. R. Proline-directed protein phosphorylation and cell cycle regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;3(2):176–184. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90136-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W., Haycock D. A. Tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain dopaminergic nerve terminals. Multiple-site phosphorylation in vivo and in synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5650–5657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W. Phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase in situ at serine 8, 19, 31, and 40. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11682–11691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W. Quantitation of tyrosine hydroxylase, protein levels: spot immunolabeling with an affinity-purified antibody. Anal Biochem. 1989 Sep;181(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W., Wakade A. R. Activation and multiple-site phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase in perfused rat adrenal glands. J Neurochem. 1992 Jan;58(1):57–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heasley L. E., Johnson G. L. Regulation of protein kinase C by nerve growth factor, epidermal growth factor, and phorbol esters in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8646–8652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houchi H., Masserano J. M., Bowyer J. F., Weiner N. Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase activity in pheochromocytoma PC-12 cells by bradykinin. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;37(1):104–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F. Tyrosine phosphorylation and tyrosine kinase activity of the trk proto-oncogene product induced by NGF. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):158–160. doi: 10.1038/350158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim U. H., Fink D., Jr, Kim H. S., Park D. J., Contreras M. L., Guroff G., Rhee S. G. Nerve growth factor stimulates phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Barbacid M. The trk proto-oncogene encodes a receptor for nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90419-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNicol M., Jefferson A. B., Schulman H. Ca2+/calmodulin kinase is activated by the phosphatidylinositol signaling pathway and becomes Ca2(+)-independent in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18055–18058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher P. A. Role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in the NGF response. J Neurosci Res. 1989 Sep;24(1):29–37. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490240106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. P., Hardie D. G., Vulliet P. R. Site-specific phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase after KCl depolarization and nerve growth factor treatment of PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22358–22364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka T., Sternberg D. W., Miyasaka J., Sherline P., Saltiel A. R. Nerve growth factor stimulates protein tyrosine phosphorylation in PC-12 pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Burgoyne R. D. A comparison of bradykinin, angiotensin II and muscarinic stimulation of cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biosci Rep. 1989 Apr;9(2):243–252. doi: 10.1007/BF01116001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldershaw K. A., Taylor C. W. 2,5-Di-(tert-butyl)-1,4-benzohydroquinone mobilizes inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-sensitive and -insensitive Ca2+ stores. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 12;274(1-2):214–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81366-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard J. F., Jr, Smith G. K., Nichol C. A. A rapid and sensitive assay for tyrosine-3-monooxygenase based upon the release of 3H2O and adsorption of [3H]-tyrosine by charcoal. Life Sci. 1986 Dec 8;39(23):2185–2189. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Boulton T. G., Yancopoulos G. D., Panayotatos N., Radziejewska E., Ericsson L., Bratlien R. L., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Microtubule-associated protein 2 kinases, ERK1 and ERK2, undergo autophosphorylation on both tyrosine and threonine residues: implications for their mechanism of activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6142–6146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Wu J. Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):350–357. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thastrup O., Cullen P. J., Drøbak B. K., Hanley M. R., Dawson A. P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2(+)-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter M. L., Martin-Zanca D., Parada L. F., Bishop J. M., Kaplan D. R. Nerve growth factor rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by a kinase activity associated with the product of the trk protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5650–5654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliet P. R., Woodgett J. R., Cohen P. Phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase by calmodulin-dependent multiprotein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13680–13683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulliet P. R., Woodgett J. R., Ferrari S., Hardie D. G. Characterization of the sites phosphorylated on tyrosine hydroxylase by Ca2+ and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase, calmodulin-dependent multiprotein kinase and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80328-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler L. A., Goodrum D. D., Sachs G. Role of protein kinase C in the regulation of cytosolic Ca2+ in A431 cells: separation of growth factor and bradykinin pathways. J Membr Biol. 1990 Oct;118(1):77–91. doi: 10.1007/BF01872206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond R. E., Schwarzschild M. A., Rittenhouse A. R. Acute regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase by nerve activity and by neurotransmitters via phosphorylation. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:415–461. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



