Abstract
Rapid nerve conduction in the CNS is facilitated by insulation of axons with myelin, a specialized oligodendroglial compartment distant from the cell body. Myelin is turned over and adapted throughout life; however, the molecular and cellular basis of myelin dynamics remains elusive. Here we performed a comprehensive transcriptome analysis (RNA-seq) of myelin biochemically purified from mouse brains at various ages and find a surprisingly large pool of transcripts enriched in myelin. Further computational analysis showed that the myelin transcriptome is closely related to the myelin proteome but clearly distinct from the transcriptomes of oligodendrocytes and brain tissues, suggesting a highly selective incorporation of mRNAs into the myelin compartment. The mRNA-pool in myelin displays maturation-dependent dynamic changes of composition, abundance, and functional associations; however ageing-dependent changes after 6 months were minor. We suggest that this transcript pool enables myelin turnover and the local adaptation of individual pre-existing myelin sheaths.
The biogenesis of myelin has long been viewed as a purely developmental process. Indeed, myelin is one of the most long-lived structures of the rodent brain1. However, the finding that several myelin proteins display a half-life of about 6 months indicates that myelin is indeed turned over in normal brains, though slowly. Utilizing the fallout of nuclear bomb tests in the 1950s and 1960s as a global labeling pulse, the normal turnover of oligodendrocytes and myelin has also been assessed in the human brain by quantifying the levels of the carbon isotope 14C in autopsy material from deceased subjects2. In the analyzed white matter tract (the corpus callosum), a continuous but very slow turnover of oligodendrocytes was observed. Indeed, nearly all white matter oligodendrocytes are born in the first five years of human life and afterward turned over remarkably slowly. However, the turnover rate of myelin was considerably higher than what would be predicted if entirely owing to the replacement of old myelin sheaths by adult-born oligodendrocytes. Together, this has suggested that existing oligodendrocytes remodel their myelin over time. Compared to the corpus callosum, the turnover of oligodendrocytes is higher in the grey matter of the human brain2, suggestive of region-dependent myelin changes that may also account for the formation of new myelin sheaths by adult-born oligodendrocytes in the rodent optic nerve3. Additional to what is required for normal myelin turnover, adult myelination by existing mature oligodendrocytes can be triggered by cellular stimuli that induce a net growth of pre-existing myelin sheaths4,5.
Myelin growth occurs at ‘myelin sheath assembly sites’ (MSAS)6, necessitating the presence or biogenesis of future myelin constituents in the non-compact compartments of myelin, which are connected to their distant oligodendroglial cell bodies by tenuous cellular processes. Indeed, two major routes of future constituents into myelin have been identified. First, future myelin membrane can be transported in vesicles7, which is slow owing to the long distance from the oligodendrocytic cell body to the myelin sheath and further limited by the closure of myelinic channels through compact CNS myelin coinciding with its maturation8. Secondly, myelin constituents can be synthesized by local translation, i.e. at MSAS in non-compact myelin. This was shown for Myelin Basic Protein (MBP)9, an abundant structural myelin protein10 that is rate-limiting for CNS myelination11,12. By associating with and thereby neutralizing membrane phospholipids13,14,15, MBP allows the close approximation of adjacent myelin membrane surfaces16. Indeed, oligodendrocytes lacking MBP fail in the formation of compact CNS myelin, e.g., in Mbpshiverer mice17,18. The trafficking of Mbp-mRNA along microtubules into oligodendroglial processes19,20 and the inhibition of its premature translation are tightly controlled by a multitude of factors contained in transport granules21,22,23. Consequently, Mbp-mRNA has been found at MSAS24 and enriched in biochemically purified myelin compared to brain lysates, along with transcripts encoding the unrelated myelin-oligodendrocyte basic protein (MOBP) and ferritin heavy chain (FTH1)6.
Considering that the turnover and adaptation of myelin require the availability and selective incorporation of many more proteins into the future myelin sheath we sought to systematically determine by RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq) the mRNAs present in CNS myelin. Surprisingly, we find that adult CNS myelin comprises an unexpectedly large number of mRNAs. Developmentally, the myelin transcriptome reaches maturity by six months of age. According to functional genomic analysis, myelin is enriched for mRNAs encoding myelin proteins, components of the translational machinery, and molecules required for protein transport and localization.
Results
Purified myelin is enriched for myelin markers both at the protein and transcript level
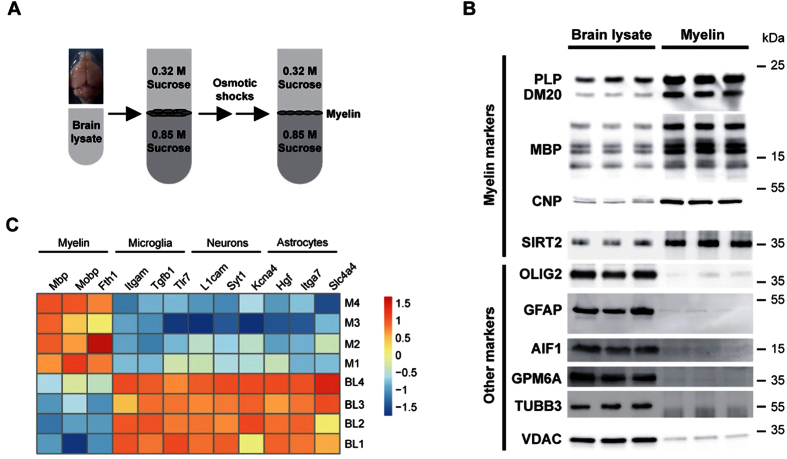
We have biochemically enriched myelin from mouse brains by sucrose density gradient centrifugation (Fig. 1A), reproducibly yielding a myelin fraction enriched for classical marker proteins of both the compact (PLP, MBP) and the non-compact compartments of myelin (CNP, SIRT2) (Fig. 1B)25,26,27. In contrast, marker proteins for the oligodendroglial nuclear/cytoplasmic compartment (OLIG2), astrocytes (GFAP), microglia (AIF1), neurons (GPM6A, TUBB3), and mitochondria (VDAC) were reduced in purified myelin compared to brain lysates (Fig. 1B). When subjecting purified myelin to RNA isolation, reverse transcription, and qRT-PCR, the abundance of the myelin-related mRNAs Mbp, Mopb, and Fth1 was strongly increased compared to brain lysates (Fig. 1C), in agreement with a previous report using Northern blots6. Importantly, transcripts specific to neurons (L1cam, Syt1, Kcn4), astrocytes (Hgf, Itga7, Slc4a4) or microglia (Itgam, Tgfb1, Tlr7) were diminished in myelin compared to brain lysate according to qRT-PCR analysis (Fig. 1C). Together, both myelin proteins and myelin-related transcripts are strongly enriched in biochemically purified myelin.
Figure 1. Myelin proteins and mRNAs are enriched in purified myelin compared to brain homogenate.
(A) Scheme illustrating the biochemical purification of a light-weight membrane fraction enriched for myelin by homogenizing mouse brains in 0.32 M sucrose, sequential sucrose density gradient centrifugation, and osmotic shocks. Myelin accumulates at the interface between 0.32 M and 0.85 M sucrose. (B) Immunoblot analysis of myelin-enriched fractions and equal amounts of brain lysate to compare the abundance of marker proteins for compact myelin (PLP/DM20, MBP), non-compact myelin (CNP, SIRT2), the oligodendroglial nuclear/cytoplasmic compartment (OLIG2), astrocytes (GFAP), microglia (AIF1/IBA1), neuronal plasma membrane (GPM6A), axonal microtubules (TUBB3/TUJ1), and mitochondria (VDAC). Blot represents three biological replicates (male c57Bl6/N mice, age P75). Note that myelin markers were enriched in purified myelin while markers of other cellular sources were reduced. (C) Heatmap displaying reverse CT values from qRT-PCRs for three markers each specific for myelin, migroglia, neurons and astrocytes performed on myelin biochemically purified from the brains of 4 individual mice (M1–4) compared to the respective brain lysates (BL1–4) at six month of age.
The myelin transcriptome displays a distinct composition
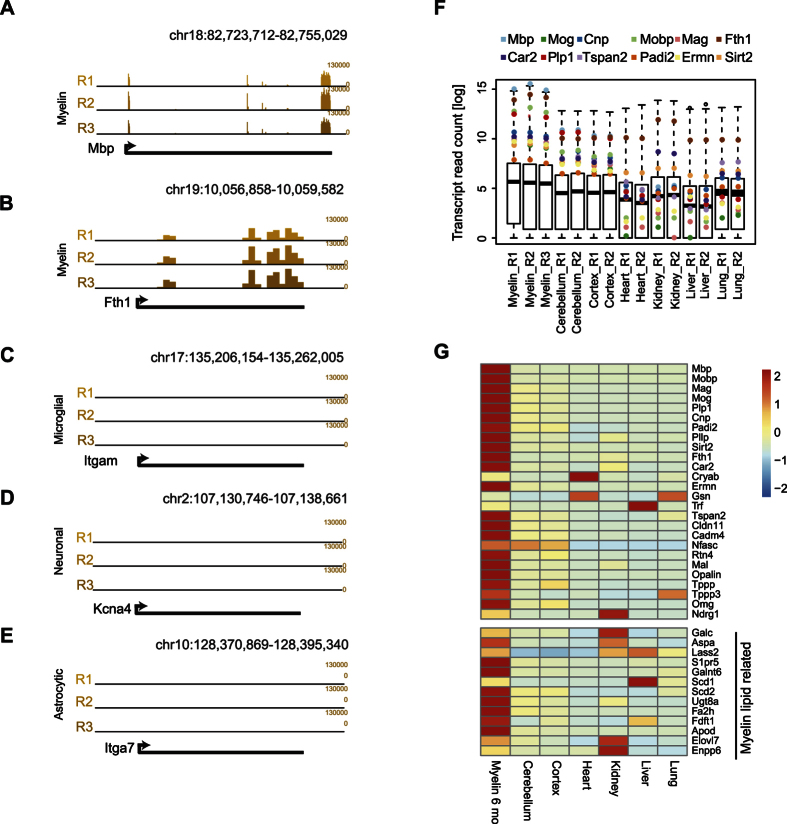
To determine the composition of the entire mRNA-pool present in CNS myelin, we performed RNA-Seq on myelin extracted from three individual mouse brains (male c57Bl6/N, age 6 months) (Supplementary Table 1). We observed a very strong replicate correlation (Fig. S1A,B). The reads reproducibly mapped to the exons of selected myelin-related genes (Fig. 2A,B and Fig. S1 D–O), indicating that indeed mature transcripts were detected. However, the abundance of transcripts ageencoding for microglial, neuronal and astrocytic marker genes was very low (Fig. 2C–E), implying the detection of myelin-specific transcripts with low contamination by transcripts originating from neighboring cells.
Figure 2. Transcripts encoding known myelin proteins are enriched in mature CNS myelin.
(A–E) UCSC browser tracks of selected RNA-seq mRNA-reads on purified myelin. Displayed are two myelin-related genes (Mbp, Fth1), one microglial marker (Itgam), one neuronal marker (Kcn4a) and one astrocytic marker (Itga7). Note that mature myelin-related mRNAs were detected. Also see Fig S1C-K. (F) Box-Whisker plots showing transcript read count of all mRNAs identified in myelin purified from male c57Bl6/N mice (age 6 months) compared to total cerebellum, cortex, heart, kidney, liver, and lung. The three biological replicates display similar transcript distribution (R1-R3) and selected myelin-related mRNAs (highlighted) are enriched in myelin compared to the other samples. (G) Heat map showing the abundance of selected myelin-related transcripts in myelin (age 6 months), cerebellum, cortex, heart, kidney, liver, and lung. Note that mRNAs encoding enzymes related to myelin lipids are also enriched in myelin.
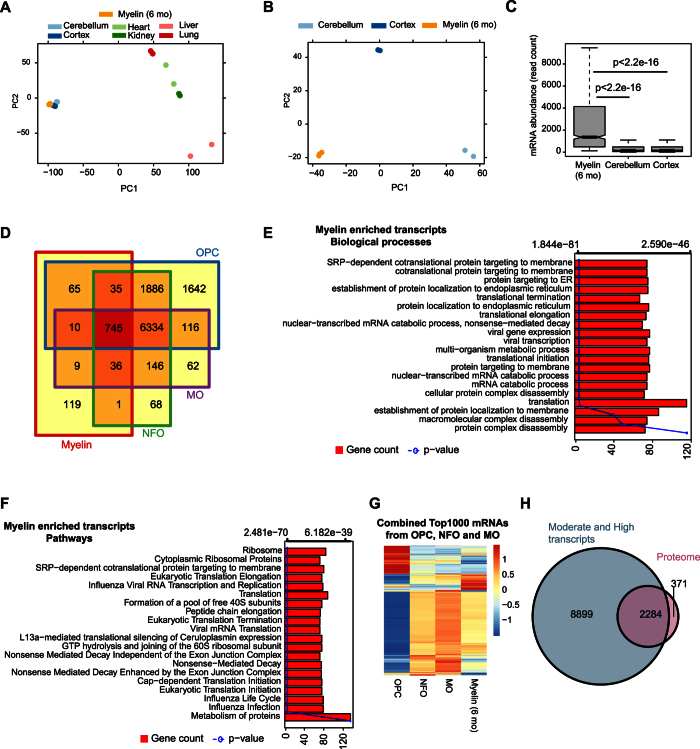
The transcript pool of myelin is overall more similar to that of total brain regions (cerebellum, cortex) compared to tissues derived from other germ layers (Fig. 2F,G and Fig. S2 and Fig. S3A and Fig. 3A). Importantly, in depth analysis confirmed the strong enrichment in myelin of mRNAs (Mbp, Mobp, Fth1) previously analyzed in a small-scale study6. For a surprising number of known myelin proteins, the abundance of the corresponding mRNA in purified myelin was considerably higher compared to cerebellum and cortex homogenates, as well as to non-neuronal tissues (Fig. 2F,G). Also many transcripts encoding myelin lipid-related enzymes were enriched in myelin (Fig. 2G). Interestingly, the transcripts most abundant in myelin (Fig. S2) comprise several mRNAs for which to the best of our knowledge no relation to central myelination has yet been reported, including Plekhb1, Bcas1, Trp53inp2, and Ptgds. Together, myelin displays a specific transcript composition and abundance profile clearly distinct from other transcriptomes (Fig. 2F,G and Fig S2 and Fig. 3A,B).
Figure 3. The transcriptome of mature CNS myelin.
(A) Principal component analysis (PCA) comparing the transcriptome of myelin with that of total cerebellum, cortex, heart, kidney, liver, and lung. First two principal components (PC) are represented as distances on x- and y-axis to display variation between samples. Myelin and brain samples cluster away from those of other germ layers. (B) PCA comparing the myelin transcriptome with cerebellum and cortex. Note the similarity of the three biological replicates of myelin. (C) Box-Whisker plots displaying the relative abundance of mRNAs that are at least 2-fold enriched in myelin compared to cerebellum and cortex (n = 1020). (D) Comparison of mRNAs that are at least 2-fold enriched in myelin compared to cerebellum and cortex with the mRNAs expressed in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPC), newly formed oligodendrocytes (NFO), and myelinating oligodendrocytes (MO) according to Zhang et al. 2014. Only a subset of the mRNAs expressed in the oligodendrocyte lineage is enriched in myelin. (E) Bar plot showing biological processes associated with myelin-enriched transcripts. Bars indicate the number of genes in a category (x-axis); the line gives the p-value for each biological process. (F) Bar plot showing biological pathways associated with myelin-enriched transcripts. Bars indicate the number of genes in a category (x-axis); the line gives the p-value for each pathway. (G) Heat map of the top 1000 most abundant mRNAs expressed in the oligodendrocyte lineage (combined OPC, NFO, and MO) to compare their abundance with that in myelin. mRNAs expressed in the oligodendrocyte lineage are not necessarily enriched in myelin, and myelin-enriched mRNAs are not necessarily among the most abundantly expressed oligodendroglial mRNAs. (H) Venn diagram comparing the mass spectrometrically identified proteins in purified myelin with the mRNAs detected in myelin at a high or moderate level at the same age (6 months).
To further elucidate the composition of the myelin transcriptome we focused on myelin-enriched transcripts, i.e. those mRNAs with a normalized read count of >100 and that were at least 2-fold more abundant in myelin compared to total cerebellum (1141 transcripts), cortex (846), or both (1020) (Fig. S3B) (Supplementary Table 2, 3). Many of these transcripts were enriched in myelin to an unexpectedly high degree (Fig. 3C and Fig. S3C,D).
Next we compared the myelin transcriptome with that of the myelinating cells of the CNS. Here, we took advantage of recently published genome-wide expression data28 for oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPC), newly formed oligodendrocytes (NFO), and myelinating oligodendrocytes (MO) purified by immunopanning. Density plots of these datasets revealed overall similarly distributed transcript abundances, allowing to categorize mRNAs as not expressed, lowly expressed, moderately expressed, or highly expressed (Fig. S3E). When comparing all moderately and highly abundant transcripts (i.e., with an FPKM >2 at any stage of the oligodendrocyte lineage; n = 11155) with mRNAs enriched in myelin compared to both cerebellum and cortex (n = 1020) we found that most myelin-enriched transcripts are expressed at all stages of oligodendroglial maturation (n = 745) (Fig. 3D). A minority of myelin-enriched mRNAs was found expressed only after the OPC stage (n = 46); this category includes many of the classical myelin markers. The myelin-enriched mRNAs (n = 1020) largely represent biological processes and pathways strongly associated with protein translation and targeting (Fig. 3E,F), suggesting that the myelin sheath comprises transcripts required for its own translation machinery.
Notably, a very large number of mRNAs expressed in oligodendrocytes are not enriched in myelin (n = 10254) (Fig. 3D). We thus compared in a heat map the top 1000 most abundant oligodendroglial mRNAs with their abundance in myelin (Fig. 3G and Fig. S3F) (Supplementary Table 4). As expected, the mRNA-abundance profiles of NFO and MO were more similar to each other than to OPC. Strikingly, mRNAs highly abundant in NFO and MO were not necessarily among the most abundant mRNAs in myelin, and vice versa mRNAs highly abundant in myelin were not necessarily among the most abundant oligodendroglial mRNAs (Fig. 3G and Fig S3F). For example, when comparing the mRNAs highly expressed in myelinating oligodendrocytes (FPKM > 64) (according to the dataset by Zhang and colleagues28) with those that are of low abundance or below threshold in myelin (Supplementary Table 5), the strongest depletion was found for BC002163, Gm6682, Fam57a, and Gm6788. On the other hand, the most abundant mRNAs in myelin (Mbp, Fth1, Plekhb1, and Mobp) were all enriched in myelin compared to myelinating oligodendrocytes. Together, oligodendroglial cells and the myelin compartment display clearly distinct mRNA-profiles, suggesting that the mechanisms to transport mRNAs into the myelin sheath are selective. Importantly, the most abundant myelin mRNAs largely clustered away from the mRNAs most abundant in neurons, astrocytes and microglia (according to the dataset by Zhang and colleagues) (Fig. S3G), thereby supporting qRT-PCR data gained for individual marker genes (Fig. 1C) and thus the notion that myelin displays a distinct transcriptome.
To systematically assess whether mRNAs present in myelin can be ultimately translated into myelin proteins, we mass spectrometrically analyzed myelin purified from the brains of 6 months old mice (male, c57Bl/6N) in which 2655 distinct proteins were identified (Supplementary Table 6). For the vast majority of them (n = 2284; 86%), the corresponding mRNA was detected in myelin at a moderate or high level (Fig. 3H) (Supplementary Table 7). Among those were a considerable number of metabolic proteins largely associated with the nucleotide metabolism, as well as proteins associated with biological processes like membrane organization, protein localization and transport (Fig. S3H). When comparing the myelin proteome with the entire myelin transcriptome including mRNAs of low abundance, 88% (n = 2327) of the identified myelin proteins were also detected at the level of the corresponding mRNA (Fig. S3I). Together this indicates that the transcriptome and the proteome of CNS myelin correspond with each other surprisingly well.
Developmental maturation of the myelin transcriptome
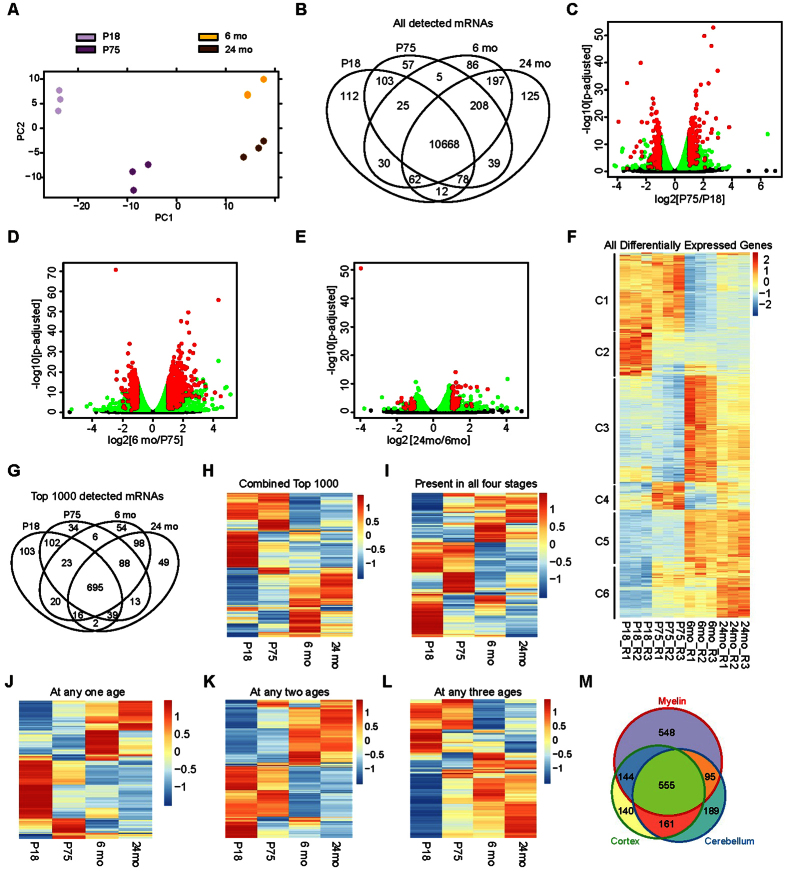
We next asked whether the myelin transcriptome is fully matured already in newly formed myelin or if it undergoes developmental changes. Therefore we determined the myelin transcriptome of mouse brains at different ages (P18, P75, 6 and 24 months). Interestingly, the myelin transcriptome was very similar when comparing the latter ages while we observed clear developmental differences between P18, P75, and 6 months of age (Fig. 4A). This suggests that the myelin transcriptome in mice reaches a mature state by about 6 months of age.
Figure 4. Developmental maturation of the myelin transcriptome.
(A) PCA plot showing transcriptome dynamics of myelin at four different ages (postnatal day 18 (P18), P75, 6 months and 24 months). (B) Venn diagram comparing all myelin mRNAs at specified ages (normalized read count; threshold >100 reads). (C) Volcano plot displaying transcripts with abundance change in myelin >2-fold between P18 and P75. X-axis displays log2-fold change between P18 and P75, and y-axis shows respective adjusted p-value as -log10. Red dots: transcripts that display fold-change abundance of at least 2-fold (203 increasing; 158 decreasing), green dots: other significantly changing transcripts, black dots: transcripts without significant change in abundance. (D) Same as in Fig. 4C showing mRNAs of which the abundance in myelin changes over 2-fold between P75 and 6 months of age. (E) Same as Fig. 4C showing mRNAs of which the abundance in myelin changes over 2-fold between 6 and 24 months of age. (F) Heat map of all mRNAs of which the abundance in myelin changes over 2-fold in any of the analyzed subsequent ages. (G) Venn diagram comparing the transcripts in myelin that are among the top 1000 most abundant at any of the analyzed ages (n = 1342) revealing 695 mRNAs among the top 1000 at all ages. (H) Heat map showing relative abundance of the combined top 1000 most abundant transcripts in myelin at any analyzed age (n = 1342 as in Fig. 3G). (I) Heat map of transcripts that were among the top 1000 most abundant mRNAs in myelin at all four analyzed ages (n = 695, subset of Fig. 3H, as in Fig. 3G). (J) Heat map of transcripts that were among the top 1000 mRNAs in myelin at only one of the analyzed ages (n = 240, subset of Fig. 3H). (K) Heat map of transcripts among the top 1000 at any two ages (n = 241, subset of Fig. 3H). (L) Heat map of transcripts among the top 1000 at any three ages (n = 166, subset of Fig. 3H). (M) Venn diagram comparing combined top 1000 myelin transcripts at any age (n = 1342 as in Fig. 3G) with the top 1000 transcripts cortex and cerebellum.
To elucidate the transcript profile in myelin irrespective of age-dependent changes we compared all transcripts (normalized read count >100) of each analyzed age. As expected, a large number of transcripts (n = 10668) was present at all analyzed ages (Fig. 4B). The top 1000 most abundant among these transcripts were preferentially associated with biological processes as protein translation, transport, and localization (Fig. S4A), biological pathways as ribosome biogenesis and assembly (Fig. S4B), and known mouse mutant phenotypes as abnormal nervous system physiology and morphology (Fig. S4C).
To further explore developmental changes affecting the mRNA-abundance profile of myelin in the context of the observation that the myelin transcriptome reaches maturity at 6 months of age we performed more detailed differential analysis of the consecutive ages. Indeed, considerable changes of the myelin transcriptome were observed until 6 months of age (Fig. 4C,D), whereas changes were comparatively minor between 6 and 24 months of age (Fig. 4E) (Supplementary Table 8–10).
By gene ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis, the mRNAs differentially present in the myelin transcriptome at P18 and P75 are associated with protein targeting and localization, translational termination, and cell adhesion (Fig. S4D). The transcripts that distinguish myelin at P75 and at 6 months of age are preferentially associated with ion transport, cell-signaling, protein transport and localization (Fig. S4E). Importantly, although the myelin transcriptome was largely similar at 6 and 24 months of age (Fig. 4E), a class of transcripts that distinguished both ages was associated with immune response (Fig. S4F).
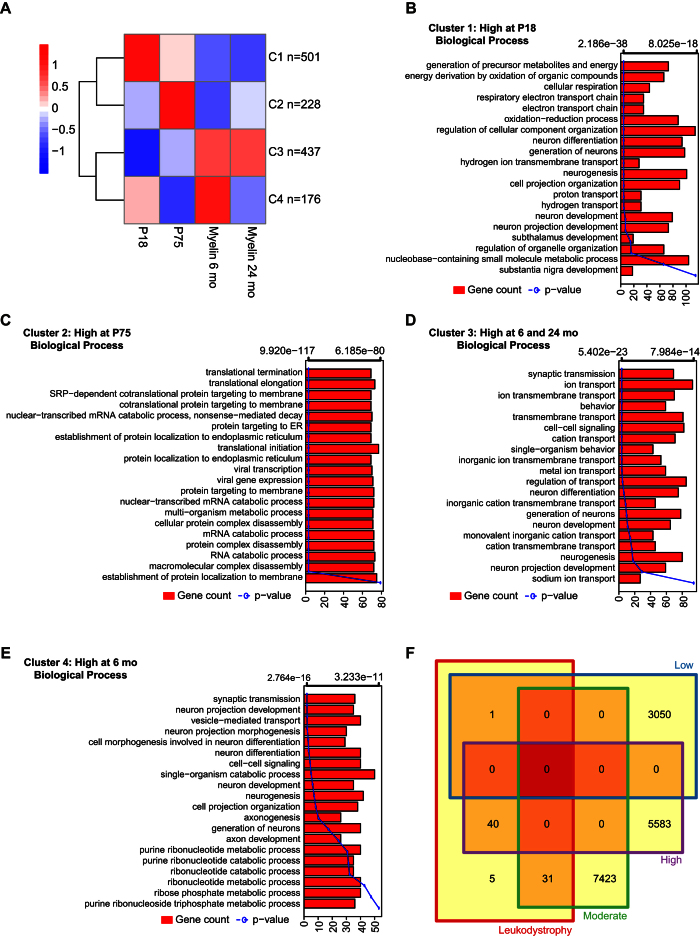
To better resolve the maturation of the myelin transcriptome we visualized in a heat map all mRNAs that displayed significant abundance changes in any pairwise comparison (Fig. 4F). Hierarchical clustering resulted in six clusters of mRNAs based on their developmental abundance kinetics (Fig. 4F). We observed transcripts that are only highly abundant in newly formed myelin (P18: cluster 2, C2) or myelin at both P18 and P75 (C1). The cluster of transcripts most abundant at only P75 (C4) was comparatively small. A consistent increase in mRNA abundance was seen for another comparatively small cluster (C6). The largest clusters consisted of mRNAs with the highest abundance at 6 or 24 months with only moderate changes between these ages (C3, C5) (Fig. 4F). To further elucidate changes of the myelin transcriptome between the four analyzed ages we also performed k-means clustering (Fig. 5A), which yielded defined clusters for myelin at P18 (C1), P75 (C2), and 6 months (C4), as well as a cluster at both 6 and 24 months of age (C3) (Supplementary Table 11). Interestingly, no distinct cluster was gained for myelin at 24 months of age, supporting the observation that the myelin transcriptome has largely reached maturity by 6 months of age.
Figure 5. Functional genomics of the myelin transcriptome.
(A) Heat map showing distinct k-means clusters of transcripts in myelin of which the abundance differentially changes between any analyzed age. (B) Bar plot showing enrichment of biological processes for mRNAs in cluster 1 obtained from k-means clustering (compare Fig. S3G) representing abundant transcripts in myelin at age P18. Bars indicate numbers of mRNAs in the respective biological process (lower x-axis) while the line represents the respective p-value (upper x-axis). (C) Same as in Fig. 5B but for k-means clustered transcripts abundant in myelin at age P75. (D) Same as in Fig. 5B but for k-means clustered transcripts abundant in myelin at 6 and 24 months of age. (E) Same as in Fig. 5B but for k-means clustered transcripts abundant in myelin at 6 months of age. (F) Comparison of the mRNAs detected in myelin with the genes causing (when mutated) heritable disorders preferentially affecting the white matter of the brain (leukodystrophies/leukoencephalopathies). Note that surprisingly many leukodystrophy-associated mRNAs were identified in myelin at least at moderate or high abundance (see also supplemental Fig. S5).
To further explore the transcripts highly abundant in myelin (Supplementary Table 12) at particular or all analyzed ages (compare Fig. 4G), we plotted only these mRNAs and observed dynamically changing transcript levels coinciding with myelin maturation but comparatively moderate changes between 6 and 24 months of age (Fig. 4H,I). Among the analyzed ages, myelin at P18 comprises the largest group of uniquely abundant transcripts, which appear specific to newly formed myelin (Fig. 4J). A small cluster comprises transcripts specifically abundant in myelin at P75 (Fig. 4J). The transcripts constituting the larger clusters in myelin at 6 or 24 months are commonly also present at high abundance in the respective other later age but not in myelin at P18 or P75 (Fig. 4J and Fig. S4G), again supporting that the myelin transcriptome matures by 6 months of age. The gradual maturation of the myelin transcriptome up to the age of 6 months is also indicated by plotting the transcripts that are of particular abundance at any two (Fig. 4K and Fig. S4G) or three (Fig. 4L and Fig. S4G) of the analyzed ages.
To analyze how similar the top 1000 most abundant transcripts in myelin at any of the analyzed ages are to those in total brain regions we compared these transcriptomes and found about half of them (n = 555) also highly abundant in both cortex and cerebellum (Fig. 4M). Conversely, 548 transcripts are specifically enriched in myelin. Indeed, overall abundance in myelin is manifold higher compared to the homogenates of the analyzed brain regions (Fig. S4H).
Stage specific expression kinetics suggest functional remodeling of the myelin transcriptome during development
Considering that the myelin transcriptome matures in mRNA composition and abundance during postnatal brain development we were curious whether this remodeling would indicate changes of the functional relevance of the mRNA-pool. We thus performed GO-term enrichment analysis for those transcripts that display a stage-specifically differential abundance (compare k-means clusters in Fig. 5A). Indeed, the clusters correspond to distinct biological processes (Fig. 5B–E). Transcripts most abundant in myelin at P18 are preferentially associated with biological processes involved in energy metabolism and nervous system development (Fig. 5B). Transcripts highly abundant in myelin at P75 display a strong association with protein translation, protein targeting, and RNA catabolism (Fig. 5C). The transcripts abundant in mature myelin at 6 and 24 months are preferentially associated with ion homeostasis and cellular signaling (Fig. 5D,E). The comparatively fewer transcripts most abundant in myelin at 6 months of age (n = 176) are also associated with vesicle-mediated transport and ribonucleotide metabolic processes (Fig. 5E).
Finally, we compared the myelin transcriptome with 77 genes causing (when mutated) brain disorders preferentially affecting the white matter (leukodystrophies/leukoencephalopathies). Surprisingly, most of the respective mRNAs were found in myelin at least at moderate abundance (Fig. 5F) (Supplementary Table 13); indeed, the majority of them were enriched in myelin compared to other tissues (Fig. S5).
Taken together, we report the existence of an unexpectedly large mRNA-pool in CNS myelin, which displays a maturation-dependent dynamic modulation with respect to composition, abundance, and functional associations.
Discussion
In this study we obtained the first RNA-Seq transcriptome database of myelin purified from wild-type mouse brains at various ages (P18, P75, 6mo and 24mo). We report that CNS myelin comprises an unexpectedly large number of mRNAs, with transcripts of >13000 mRNAs present at least at a moderate abundance level; a surprising finding when considering that only very few mRNAs have been previously recognized in myelin using a small-scale approach6. Indeed, >1000 transcripts were specifically enriched in myelin compared to other brain tissues. The selectivity of mRNA incorporation into myelin and thus the specificity of the myelin transcriptome is also indicated by our finding that myelin-enriched transcripts are not necessarily among those most abundantly expressed in oligodendrocytes when analyzed by comparing our dataset with the previously determined transcriptomes of various cell types of the brain28. Vice versa, mRNAs highly expressed in the oligodendrocyte lineage are not necessarily enriched in myelin. As expected, mRNA markers of neurons, astrocytes and microglia are diminished in purified myelin. Together this indicates that the identified mRNA-pool in the myelin compartment is unique and distinct from that in surrounding brain tissue and in oligodendroglial cell bodies.
Incorporation of transcripts into myelin is mediated by the microtubule-dependent transport of RNA-granules that contain ribosomes, regulatory proteins, and a selection of mRNAs9,29. Considering that MBP is rate-limiting for myelination11,12, the molecular control of Mbp-mRNA translation appears crucial to regulate the precise extent of myelin biogenesis. Indeed, Mbp-mRNA is transported into myelin sheaths along microtubules19,20,30. Its translation is confined to MSAS by translation-inhibitory factors, including ribonucleoproteins21,22,23 and the small non-coding RNA 71531. Considering that MBP is the second-most abundant structural myelin protein32, it is not surprising that Mbp-mRNA is strongly enriched in myelin. We note that Mobp-mRNA, which is also highly enriched in myelin, is also recognized by trans-acting ribonucleoproteins and transported in RNA-trafficking granules along microtubules33. Excessive microtubule accumulation in oligodendrocytes in the hypomyelinating taiep mutant rat34, causes impaired RNA-granule dynamics35 and the accumulation of both, Mbp and Mobp mRNAs in oligodendroglial cell bodies36. Together, the mechanisms underlying the incorporation of transcripts into myelin have largely been established using Mbp-mRNA but probably apply to other myelin-related transcripts as well. This has most recently been exemplified for the mRNA encoding the small heat-shock protein α-B-crystallin (CRYAB, also termed HspB5). The rapidly increased abundance of CRYAB upon a neuroinflammatory challenge protects myelin and neurons from degeneration37. By in situ-hybridization, Cryab-mRNA in oligodendrocytes localized away from the cell bodies38, in resemblance of Mbp-mRNA24. Indeed, Cryab-mRNA is enriched in myelin according to the present analysis. Its continuous availability for rapid local protein translation in the individual internode may be advantageous upon an immunological challenge.
Myelin remodeling is now recognized as a mechanism of life-long brain plasticity39 with consequences for the velocity of nerve conduction and thus cognitive and motor capabilities. Indeed, it has long been known that neuronal activity can stimulate central myelination5,40. It is hypothesized that the en passent release of glutamatergic vesicles from active axons towards adjacent cells of the oligodendrocyte lineage41,42 enhances the synthesis of MBP locally43,44, i.e. in the individual internode. Apparently, thus, electrically active axons have an advantage over neighboring silent axons in the induction of active myelination by their associated oligodendroglial processes. Considering that individual oligodendrocytes commonly myelinate segments of numerous axons, the local control of myelination at the level of the individual internode appears well suited to modulate the local extent of myelination in dependence of axonal activity.
The locally controlled translation of myelin-enriched Mbp-mRNA facilitates the MBP-dependent compaction of newly synthesized myelin membrane at MSAS distant from the oligodendroglial cell body45. Indeed, the existence of many additional myelin-enriched mRNAs (as reported here) may thus indicate the existence of a reservoir for the local translation of further myelin proteins for the turnover or adaptive modulation of myelin. More speculatively, the substantial overlap between the myelin transcriptome and the myelin proteome may reflect that most myelin constituents can be biosynthesized locally at MSAS. Interestingly, beyond myelin-related mRNAs, mRNAs encoding proteins required for protein translation and trafficking are also enriched in myelin. This may enable myelin to extend its own protein translation machinery without an immediate requirement for the comparatively slower intracellular transport7 from the cell body through the oligodendroglial processes to the MSAS in non-compact myelin. It is interesting to note that the mRNA-pool of CNS myelin displays considerable changes in composition and abundance during myelin maturation whereas ageing-dependent changes at over six months of age were minor.
The present RNA-Seq dataset provides a valuable reference for investigating oligodendroglial mRNA transport mechanisms, as well as myelin maturation, turnover, adaptive modulation, and ageing. Considering the robustness and reproducibility of both, biochemical myelin purification and RNA-Seq, the methods will be useful for applications beyond wild-type myelin. For example, myelin can be biochemically purified from mutant mice32 that model neurological disorders. In recent years it has become increasingly evident that myelin and myelinating cells are pathophysiologically involved in many neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis, leukodystrophies, Rett syndrome, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and psychiatric diseases25,46,47,48,49,50. We believe that the combination of myelin purification with unbiased transcriptome and proteome analysis can provide molecular profiles that hold great promise for better understanding their pathomechanisms.
Exeprimental Procedure
Biochemical analysis
A light-weight membrane fraction enriched for myelin was purified from mouse brains as described51. Male c57Bl6/N mice from the breeding colony of the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine (MPIEM, Göttingen, Germany) were used. For immunoblot, mice were 75 days old. For proteome analysis and qRT-PCR, mice were 6 months old. For RNA-Seq, indicated ages were used. Animal experiments were performed in accordance with the animal policies of the Max Planck Institute of Experimental Medicine (Göttingen, Germany) approved by the institute's animal welfare officer and the Landesamt für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit (LAVES), the responsible authority for the German Federal State of Niedersachsen. The protein concentration was determined using the DC protein assay (BioRad). Immunoblotting was as described52. Antibodies were specific for PLP/DM20 (A43153, 1:5000), MBP (Dako A0623, 1:500), CNP (Sigma C 5922, 1:1000), SIRT2 (Abcam ab67299, 1:500), OLIG2 (DF30854, 1:200, kindly provided by J. Alberta and C. Stiles, Boston, MA, USA) GFAP (Novocastra NCL-GFAP-GA5, 1:500), AIF (also termed IBA1; Abcam ab107159, 1:500), GPM6A (#2492455, 1:1000), TUBB3 (also termed TUJ1; Covance MMS-435P, 1:1000), and VDAC (Rockland 600-401-882, 1:2000). Immunoblots were scanned using the Intas ChemoCam system.
qRT-PCR
RNA was extracted from brain lysates and purified myelin using the miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). cDNA was synthesized using the Transcriptor High Fidelity Reverse Transcription Kit and Random Hexameric Primers (Roche Applied Science). qRT-PCR was performed using the TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix according to manufacturer’s protocol in a 96-well plate StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR System (both Applied Biosystems). Primers and Universal Probe Library (UPL) probes were specific for Mbp (forward 5′-AACATTGTGA CACCTCGAACA, reverse 5′-TGTCTCTTCC TCCCCAGCT, UPL probe #58), Mobp (forward 5′-GGCTCTCCAA GAACCAGAAG, reverse 5′-GCTTGGAGTT GAGGAAGGTG, UPL probe #74), Fth1 (forward 5′-TGGAGTTGTA TGCCTCCTACG, reverse 5′-TGGAGAAAGT ATTTGGCAAAGTT, UPL probe #21), Itgam (forward 5′-GGAGCCCCAC ACTAGCATCAA, reverse 5′-CAAAGGGAGG CCCCAAAATAAG), Tgfb1 (forward 5′-CAAGTGTGGA GCAACATGTGGAA, reverse 5′-CGTATCAGTG GGGGTCAGCAG), Tlr7 (forward 5′-GGATGATCCT GGCCTATCTCTGA, reverse 5′-TCCGTGTCCA CATCGAAAACAC), L1cam (forward 5′-CAGCCTGCCT TCAGACCATCA, reverse 5′-ATGTTCTGGG GATTCTTGTCTGG), Syt1 (forward 5′-GCGATCTCCA GAGTGCTGAGAAA, reverse 5′-ACAGTCAGCT TGCCGGCAGTA), Kcna4 (forward 5′-GAAGGCACTG GGGGTTCTGGT, reverse 5′-AGTAGGCCCC ACGTGTCTGATG), Slc4a4 (forward 5′-CACGAAGAAC GCCAGGAC, reverse 5′-TCCGGTACTT CCTGTGGAAC), Itga7 (forward 5′-GTCCGTGCTC TGGACTCTGTGG, reverse 5′-CCCAGCTCAC ACTCGACATGA), and Hgf (forward 5′-CACTGACCCA AACATCCGAGTTG, reverse 5′-TCCCATTGCCACGATAACAATCT).
RNA-Seq data analysis
RNA-Seq data was generated using Illumina sequencing. Reads were aligned to mouse genome (mm9) using TopHat56 (version 2.0.9) with default options. The aligned reads were then provided as an input for the HTSeq_count utility from the HTSeq package. The raw read count files obtained from HTSeq-count were then processed for differential expression using the DESeq package57. Expression was quantified after library size normalization using DESeq57. Differential expression analysis was performed using the DESeq package with a FDR rate of 0.157.
Accession numbers
The next generation sequencing datasets generated in this study have already been submitted to GEO and will be publically available under accession number GSE78151. Tissue-specific datasets for cerebellum, cortex, heart, kidney, liver and lung were obtained from the ENCODE project deposited in Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) with accession GSE36026. All these data sets were processed as described above.
Myelin proteome analysis
Myelin purified from the brains of 6 months old mice (see above) was homogenized in RIPA buffer and samples were boiled at 70 °C for 10 minutes in 1x NuPAGE LDS Sample Buffer (Life technologies) supplemented with 100 mM DTT. The samples were separated on a 10% NuPAGE Bis-Tris gel (Life technologies) for 20 minutes at 180V in MOPS running buffer (Life technologies), fixated in 7% acetic acid containing 40% methanol and subsequently stained for 30 minutes using Colloidal Blue staining kit (Life technologies) and excised from the gel. Protein lane was divided into four slices. Each slice was chopped and destained (50% ethanol in 25 mM NH4HCO3) for 15 minutes rotating at room temperature and dehydrated for 10 minutes rotating in 100% acetonitrile. Vacuum dried samples were rehydrated and reduced for 60 minutes in reduction buffer (10 mM DTT in 50 mM NH4HCO3 pH 8.0) at 56 °C and subsequently alkylated in 50 mM iodoacetamide in 50 mM NH4HCO3 pH 8.0 for 45 minutes at room temperature in the dark. Dehydrated (10 minutes rotating in 100% acetonitrile) and vacuum dried samples were subjected to trypsin digestion (1 μg trypsin/sample in 50 mM NH4HCO3 pH 8.0) at 37 °C over night. Peptides were extracted twice in extraction solution (30% acetonitrile) and once in 100% acetonitrile for 15 minutes at 25 °C shaking at 1400 rpm, purified and desalted using C18 stage tips. Peptides were separated on C18 columns (New Objective) with inner diameter of 75 μm packed with 1.9 μm Reprosil beads (Dr. Maisch) that was mounted to an EasyLC1000 HPLC (Thermo). Eluting peptides (Buffer A: 0.1% formic acid, Buffer B: 80% acetonitrile and 0.1% formic acid, Gradient: 0–67 min 0–22% buffer B, 68–89 min 22–40% buffer B, 90–95 min 40–95% buffer B) were directly sprayed into a Q Exactive Plus mass spectrometer from Thermo operating in positive scan mode with a full scan resolution of 70,000; AGC target 3 × 10^6; max IT = 20ms; Scan range 300–1650 m/z and a Top10 MSMS method. Database search was performed using MaxQuant Version 1.5.2.858 against Mouse Uniprot database downloaded on 8. January 2015 (75,403 entries), with Trypsin/P as digestion enzyme allowing 2 missed cleavages. As settings the following was applied: variable modification: Acetyl (Protein N-term);Oxidation (M), fixed modifications: Carbamidomethyl (C), FDR of 1% on peptide and protein level was applied. Proteins with at least two peptides (one of them unique) were considered as identified. Proteins matching reverse database or common contamination list as well as proteins with peptides only identified by peptides with modification were filtered out.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Thakurela, S. et al. The transcriptome of mouse central nervous system myelin. Sci. Rep. 6, 25828; doi: 10.1038/srep25828 (2016).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank members of the Tiwari lab for their cooperation and critical feedback during the project. Tiwari lab gratefully acknowledges support from the Core Facilities of the Institute of Molecular Biology (IMB), Mainz, and especially from the proteomics, genomics and bioinformatics core facilities. R.B.J., S.G., and H.B.W. thank K.-A. Nave for financial support made possible by an European Research Council (ERC) Advanced Grant to K.-A. Nave. Research in the laboratory of H.B.W. is supported by DFG grant WE2720/2-1. Research in the laboratory of S.G. is supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) grant GO 2463/1-1. Research in the laboratory of V.K.T. is supported by the Wilhelm Sander Stiftung 2012.009.2; the EpiGeneSys RISE1 program; Marie Curie CIG 322210 and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Grant TI 799/1-1.
Footnotes
Author Contributions S.T. conceived novel approaches for bioinformatics analysis and performed entire computational analysis under supervision of V.K.T. and A.G. performed experiments and provided critical inputs under supervision of V.K.T. and R.B.J. performed myelin purification and immunoblotting with supervision by H.B.W. and C.M. performed qRT-PCRs under supervision of R.W. who also conceived the project. S.T., A.G., S.G., H.B.W. and V.K.T. wrote the manuscript. All authors have contributed to and approved the manuscript.
References
- Toyama B. H. et al. Identification of long-lived proteins reveals exceptional stability of essential cellular structures. Cell 154, 971–982 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung M. S. et al. Dynamics of oligodendrocyte generation and myelination in the human brain. Cell 159, 766–774 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. M. et al. Oligodendrocyte dynamics in the healthy adult CNS: evidence for myelin remodeling. Neuron 77, 873–885 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebbels S. et al. Elevated phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in glia triggers cell-autonomous membrane wrapping and myelination. J Neurosci 30, 8953–8964 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson E. M. et al. Neuronal activity promotes oligodendrogenesis and adaptive myelination in the mammalian brain. Science 344, 1252304 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. M., Freund C. M., Palmer F. & Feinstein D. L. Messenger RNAs located in myelin sheath assembly sites. J Neurochem 75, 1834–1844 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. & Kramer-Albers E. M. Axon-glia interaction and membrane traffic in myelin formation. Front Cell Neurosci 7, 284 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snaidero N. et al. Myelin membrane wrapping of CNS axons by PI(3,4,5)P3-dependent polarized growth at the inner tongue. Cell 156, 277–290 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller C., Bauer N. M., Schafer I. & White R. Making myelin basic protein -from mRNA transport to localized translation. Front Cell Neurosci 7, 169 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn O., Tenzer S. & Werner H. B. Myelin proteomics: molecular anatomy of an insulating sheath. Mol Neurobiol 40, 55–72 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popko B. et al. Myelin deficient mice: expression of myelin basic protein and generation of mice with varying levels of myelin. Cell 48, 713–721 (1987). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Readhead C. et al. Expression of a myelin basic protein gene in transgenic shiverer mice: correction of the dysmyelinating phenotype. Cell 48, 703–712 (1987). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min Y. et al. Interaction forces and adhesion of supported myelin lipid bilayers modulated by myelin basic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 3154–3159 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz S. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-dependent interaction of myelin basic protein with the plasma membrane in oligodendroglial cells and its rapid perturbation by elevated calcium. J Neurosci 29, 4794–4807 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz S., Schweitzer J., Jahn O. & Werner H. B. Molecular evolution of myelin basic protein, an abundant structural myelin component. Glia 61, 1364–1377 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal S. et al. Myelin membrane assembly is driven by a phase transition of myelin basic proteins into a cohesive protein meshwork. PLos Biol 11, e1001577 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach A., Takahashi N., Pravtcheva D., Ruddle F. & Hood L. Chromosomal mapping of mouse myelin basic protein gene and structure and transcription of the partially deleted gene in shiverer mutant mice. Cell 42, 149–155 (1985). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobius W., Nave K. A. & Werner H. B. Electron microscopy of myelin: structure preservation by high-pressure freezing. Brain research (2016). in press, (doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.027). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman D. R., Kreibich G., Frey A. B. & Sabatini D. D. Synthesis and incorporation of myelin polypeptides into CNS myelin. J Cell Biol 95, 598–608 (1982). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainger K. et al. Transport and localization of exogenous myelin basic protein mRNA microinjected into oligodendrocytes. J Cell Biol 123, 431–441 (1993). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. et al. Activation of oligodendroglial Fyn kinase enhances translation of mRNAs transported in hnRNP A2-dependent RNA granules. J Cell Biol 181, 579–586 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laursen L. S., Chan C. W. & Ffrench-Constant C. Translation of myelin basic protein mRNA in oligodendrocytes is regulated by integrin activation and hnRNP-K. J Cell Biol 192, 797–811 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torvund-Jensen J., Steengaard J., Reimer L., Fihl L. B. & Laursen L. S. Transport and translation of MBP mRNA is regulated differently by distinct hnRNP proteins. J Cell Sci 127, 1550–1564 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessert D. A. & Skoff R. P. High-resolution in situ hybridization and TUNEL staining with free-floating brain sections. The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry : official journal of the Histochemistry Society 47, 693–702 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A. & Werner H. B. Myelination of the nervous system: mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30, 503–533 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar J. M. et al. Early ultrastructural defects of axons and axon-glia junctions in mice lacking expression of Cnp1. Glia 57, 1815–1824 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H. B. et al. Proteolipid protein is required for transport of sirtuin 2 into CNS myelin. J Neurosci 27, 7717–7730 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. et al. An RNA-sequencing transcriptome and splicing database of glia, neurons, and vascular cells of the cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 34, 11929–11947 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. L. & Brophy P. J. Mechanisms of axon ensheathment and myelin growth. Nat Rev Neurosci 6, 683–690 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson J. H. & Barbarese E. Systems analysis of RNA trafficking in neural cells. Biol Cell 97, 51–62 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer N. M. et al. Myelin basic protein synthesis is regulated by small non-coding RNA 715. EMBO Rep 13, 827–834 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Monasterio-Schrader P. et al. Systematic approaches to central nervous system myelin. Cell Mol Life Sci 69, 2879–2894 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson J. H. et al. Multiplexed RNA trafficking in oligodendrocytes and neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta 1779, 453–458 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. D., Lunn K. F., Holmgren B., Urba-Holmgren R. & Brignolo-Holmes L. The taiep rat: a myelin mutant with an associated oligodendrocyte microtubular defect. J Neurocytol 21, 870–884 (1992). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song J., Carson J. H., Barbarese E., Li F. Y. & Duncan I. D. RNA transport in oligodendrocytes from the taiep mutant rat. Mol Cell Neurosci 24, 926–938 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor L. T., Goetz B. D., Couve E., Song J. & Duncan I. D. Intracellular distribution of myelin protein gene products is altered in oligodendrocytes of the taiep rat. Mol Cell Neurosci 16, 396–407 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ousman S. S. et al. Protective and therapeutic role for alphaB-crystallin in autoimmune demyelination. Nature 448, 474–479 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quraishe S. et al. Selective and compartmentalized myelin expression of HspB5. Neuroscience 316, 130–142 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban M., Mensch S. & Lyons D. A. Adaptive myelination from fish to man. Brain research (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demerens C. et al. Induction of myelination in the central nervous system by electrical activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93, 9887–9892 (1996). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensch S. et al. Synaptic vesicle release regulates myelin sheath number of individual oligodendrocytes in vivo. Nat Neurosci 18, 628–630 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines J. H., Ravanelli A. M., Schwindt R., Scott E. K. & Appel B. Neuronal activity biases axon selection for myelination in vivo. Nat Neurosci 18, 683–689 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake H. et al. Nonsynaptic junctions on myelinating glia promote preferential myelination of electrically active axons. Nat Commun 6, 7844 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake H., Lee P. R. & Fields R. D. Control of local protein synthesis and initial events in myelination by action potentials. Science 333, 1647–1651 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassall K. A., Bamm V. V. & Harauz G. MyelStones: the executive roles of myelin basic protein in myelin assembly and destabilization in multiple sclerosis. Biochem J 472, 17–32 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A. & Ehrenreich H. Myelination and oligodendrocyte functions in psychiatric diseases. JAMA Psychiatry 71, 582–584 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubetzki C. & Stankoff B. Demyelination in multiple sclerosis. Handb Clin Neurol 122, 89–99 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen M. V. et al. Oligodendrocyte lineage cells contribute unique features to Rett syndrome neuropathology. J Neurosci 33, 18764–18774 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. et al. Oligodendroglia metabolically support axons and contribute to neurodegeneration. Nature 487, 443–448 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang S. H. et al. Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Neurosci 16, 571–579 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn O., Tenzer S., Bartsch N., Patzig J. & Werner H. B. Myelin proteome analysis: methods and implications for the myelin cytoskeleton. Neuromethods 79, 335–353 (2013). [Google Scholar]
- Werner H. B. et al. A critical role for the cholesterol-associated proteolipids PLP and M6B in myelination of the central nervous system. Glia 61, 567–586 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung M., Sommer I., Schachner M. & Nave K. A. Monoclonal antibody O10 defines a conformationally sensitive cell-surface epitope of proteolipid protein (PLP): evidence that PLP misfolding underlies dysmyelination in mutant mice. J Neurosci 16, 7920–7929 (1996). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligon K. L. et al. The oligodendroglial lineage marker OLIG2 is universally expressed in diffuse gliomas. Journal of neuropathology and experimental neurology 63, 499–509 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S. et al. Transcallosal Projections Require Glycoprotein M6-Dependent Neurite Growth and Guidance. Cereb Cortex 25, 4111–4125 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapnell C., Pachter L. & Salzberg S. L. TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25, 1105–1111 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders S. & Huber W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11, R106 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. & Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26, 1367–1372 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.