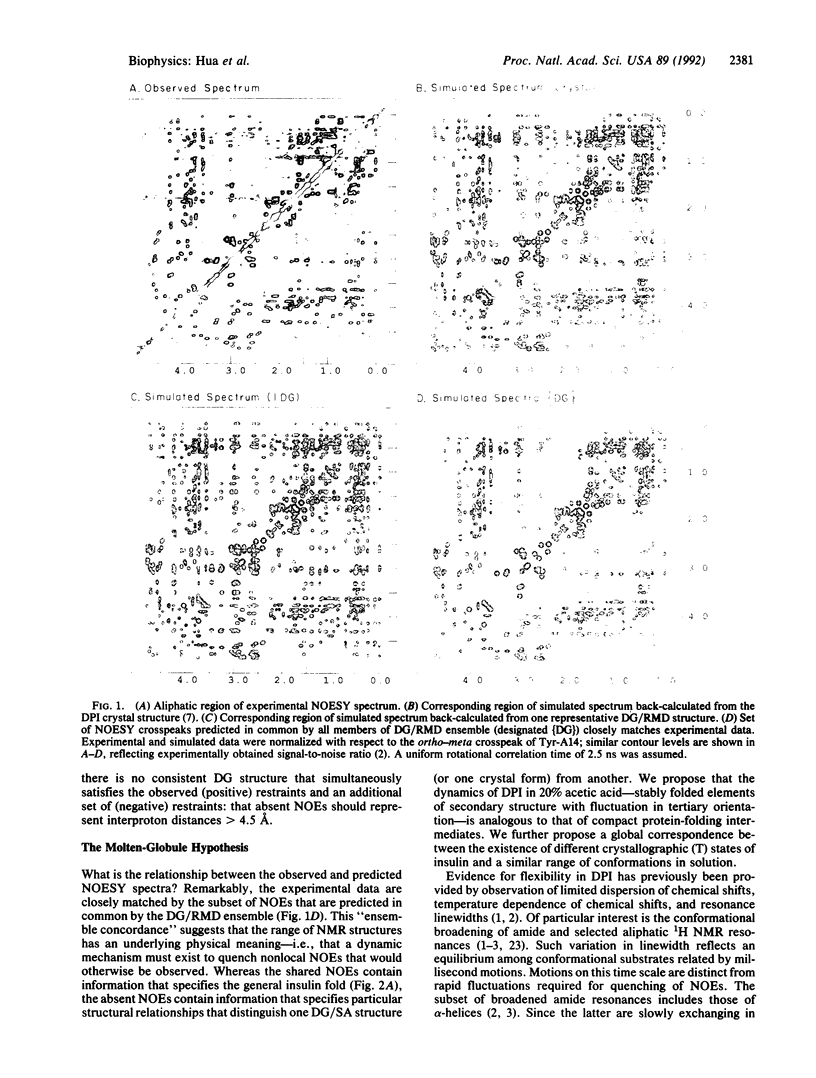
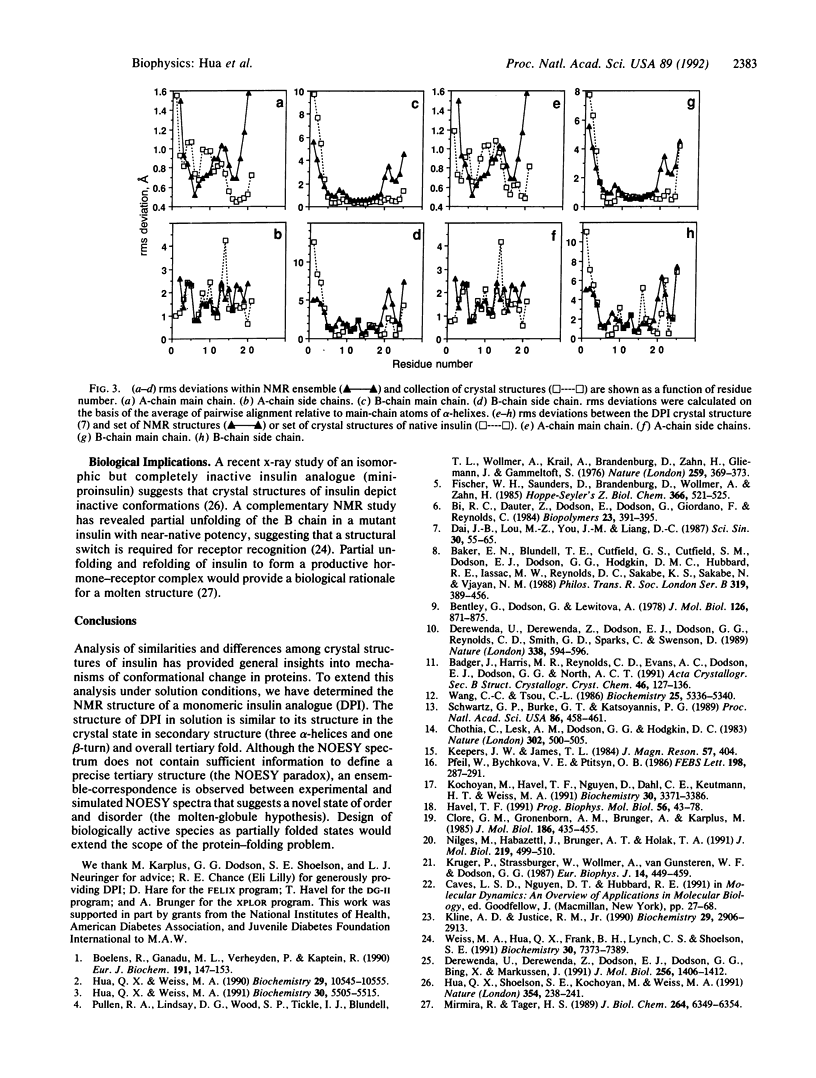
Abstract
Structures of insulin in different crystal forms exhibit significant local and nonlocal differences, including correlated displacement of elements of secondary structure. Here we describe the solution structure and dynamics of a monomeric insulin analogue, des-pentapeptide-(B26-B30)-insulin (DPI), as determined by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy and distance geometry/restrained molecular dynamics (DG/RMD). Although the solution structure of DPI exhibits a general similarity to its crystal structure, individual DG/RMD structures in the NMR ensemble differ by rigid-body displacements of alpha-helices that span the range of different crystal forms. These results suggest that DPI exists as a partially folded state formed by coalescence of distinct alpha-helix-associated microdomains. The physical reality of this model is investigated by comparison of the observed two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement (NOE) spectroscopy (NOESY) spectrum with that predicted from crystal and DG/RMD structures. The observed NOESY spectrum contains fewer tertiary contacts than predicted by any single simulation, but it matches their shared features; such "ensemble correspondence" is likely to reflect the effect of protein dynamics on observed NOE intensities. We propose (i) that the folded state of DPI is analogous to that of a compact protein-folding intermediate rather than a conventional native state and (ii) that the molten state is the biologically active species. This proposal (the molten-globule hypothesis) leads to testable thermodynamic predictions and has general implications for protein design.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Badger J., Harris M. R., Reynolds C. D., Evans A. C., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., North A. C. Structure of the pig insulin dimer in the cubic crystal. Acta Crystallogr B. 1991 Feb 1;47(Pt 1):127–136. doi: 10.1107/s0108768190009570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. N., Blundell T. L., Cutfield J. F., Cutfield S. M., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. M., Hubbard R. E., Isaacs N. W., Reynolds C. D. The structure of 2Zn pig insulin crystals at 1.5 A resolution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 6;319(1195):369–456. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley G., Dodson G., Lewitova A. Rhombohedral insulin crystal transformation. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):871–875. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boelens R., Ganadu M. L., Verheyden P., Kaptein R. Two-dimensional NMR studies on des-pentapeptide-insulin. Proton resonance assignments and secondary structure analysis. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 20;191(1):147–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. C. Transmission of conformational change in insulin. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):500–505. doi: 10.1038/302500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Brünger A. T., Karplus M. Solution conformation of a heptadecapeptide comprising the DNA binding helix F of the cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli. Combined use of 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and restrained molecular dynamics. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 20;186(2):435–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derewenda U., Derewenda Z., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Reynolds C. D., Smith G. D., Sparks C., Swenson D. Phenol stabilizes more helix in a new symmetrical zinc insulin hexamer. Nature. 1989 Apr 13;338(6216):594–596. doi: 10.1038/338594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W. H., Saunders D., Brandenburg D., Wollmer A., Zahn H. A shortened insulin with full in vitro potency. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 May;366(5):521–525. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.1.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel T. F. An evaluation of computational strategies for use in the determination of protein structure from distance constraints obtained by nuclear magnetic resonance. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1991;56(1):43–78. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(91)90007-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua Q. X., Shoelson S. E., Kochoyan M., Weiss M. A. Receptor binding redefined by a structural switch in a mutant human insulin. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):238–241. doi: 10.1038/354238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua Q. X., Weiss M. A. Comparative 2D NMR studies of human insulin and des-pentapeptide insulin: sequential resonance assignment and implications for protein dynamics and receptor recognition. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5505–5515. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua Q. X., Weiss M. A. Toward the solution structure of human insulin: sequential 2D 1H NMR assignment of a des-pentapeptide analogue and comparison with crystal structure. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 20;29(46):10545–10555. doi: 10.1021/bi00498a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline A. D., Justice R. M., Jr Complete sequence-specific 1H NMR assignments for human insulin. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 27;29(12):2906–2913. doi: 10.1021/bi00464a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochoyan M., Havel T. F., Nguyen D. T., Dahl C. E., Keutmann H. T., Weiss M. A. Alternating zinc fingers in the human male associated protein ZFY: 2D NMR structure of an even finger and implications for "jumping-linker" DNA recognition. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3371–3386. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger P., Strassburger W., Wollmer A., van Gunsteren W. F., Dodson G. G. The simulated dynamics of the insulin monomer and their relationship to the molecule's structure. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(8):449–459. doi: 10.1007/BF00293254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirmira R. G., Tager H. S. Role of the phenylalanine B24 side chain in directing insulin interaction with its receptor. Importance of main chain conformation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6349–6354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilges M., Habazettl J., Brünger A. T., Holak T. A. Relaxation matrix refinement of the solution structure of squash trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90189-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeil W., Bychkova V. E., Ptitsyn O. B. Physical nature of the phase transition in globular proteins. Calorimetric study of human alpha-lactalbumin. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 31;198(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen R. A., Lindsay D. G., Wood S. P., Tickle I. J., Blundell T. L., Wollmer A., Krail G., Brandenburg D., Zahn H., Gliemann J. Receptor-binding region of insulin. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):369–373. doi: 10.1038/259369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. P., Burke G. T., Katsoyannis P. G. A highly potent insulin: des-(B26-B30)-[AspB10,TyrB25-NH2]insulin(human). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):458–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Tsou C. L. Interaction and reconstitution of carboxyl-terminal-shortened B chains with the intact A chain of insulin. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5336–5340. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Hua Q. X., Lynch C. S., Frank B. H., Shoelson S. E. Heteronuclear 2D NMR studies of an engineered insulin monomer: assignment and characterization of the receptor-binding surface by selective 2H and 13C labeling with application to protein design. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 30;30(30):7373–7389. doi: 10.1021/bi00244a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]