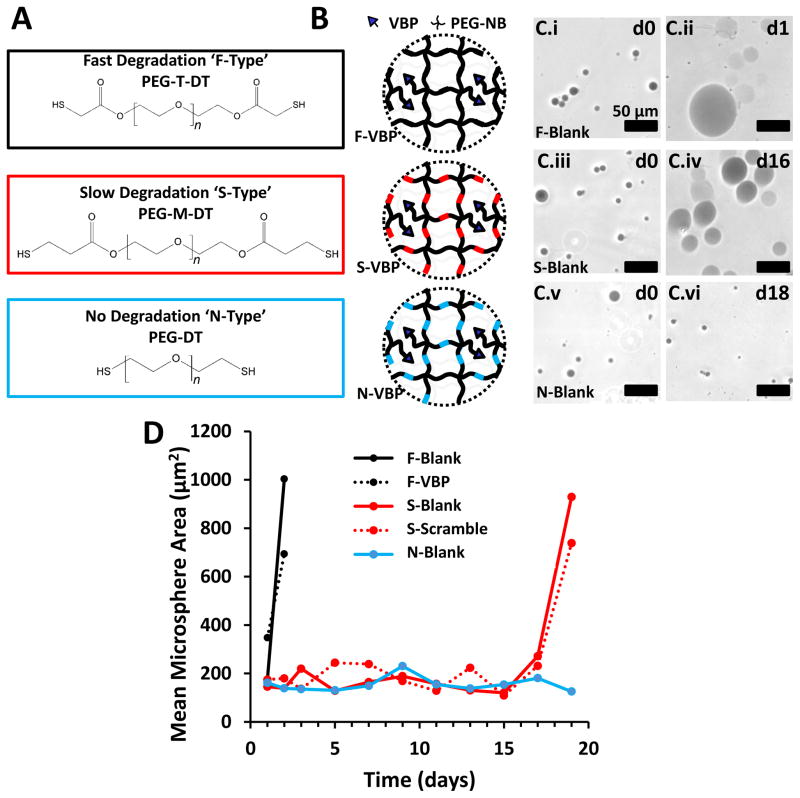
Figure 1.
Influence of chemical crosslinker identity on PEG microsphere degradation rate. A: Chemical structure of PEG-T-DT, PEG-M-DT, and PEG-DT. The molecular weight of each PEG chain is 3.4 kDa, thus the number of repeat ethylene glycol units, ‘n’, in each schematic is approximately 77. B: Schematic of VBP microspheres crosslinked with fast-degrading PEG-T-DT crosslinker (F-Type), slow-degrading PEG-M-DT crosslinker (S-Type), and non-degrading PEG-DT (N-Type). C: Phase contrast images of Trypan-stained Blank F-Type microspheres at day 0 (C.i) and day 1 (C.ii), S-Type microspheres at day 0 (C.iii) and day 16 (C.iv), and N-Type microspheres at day 0 (C.v) and day 18 (C.vi). Scale bar represents 50 μm. D: Line graph represents mean microsphere area (μm2) over time for F-Blank (Black), S-Blank (Red), and N-Blank (Blue) microspheres. Peptide-containing microspheres are represented for F-VBP microspheres (Dashed Black) and S-Scramble microspheres (Dashed Red). F-Scramble, S-VBP, N-VBP, and N-Scramble were omitted for brevity, as the degradation profiles for microspheres of each crosslinker type was independent of the presence of peptide.