Abstract
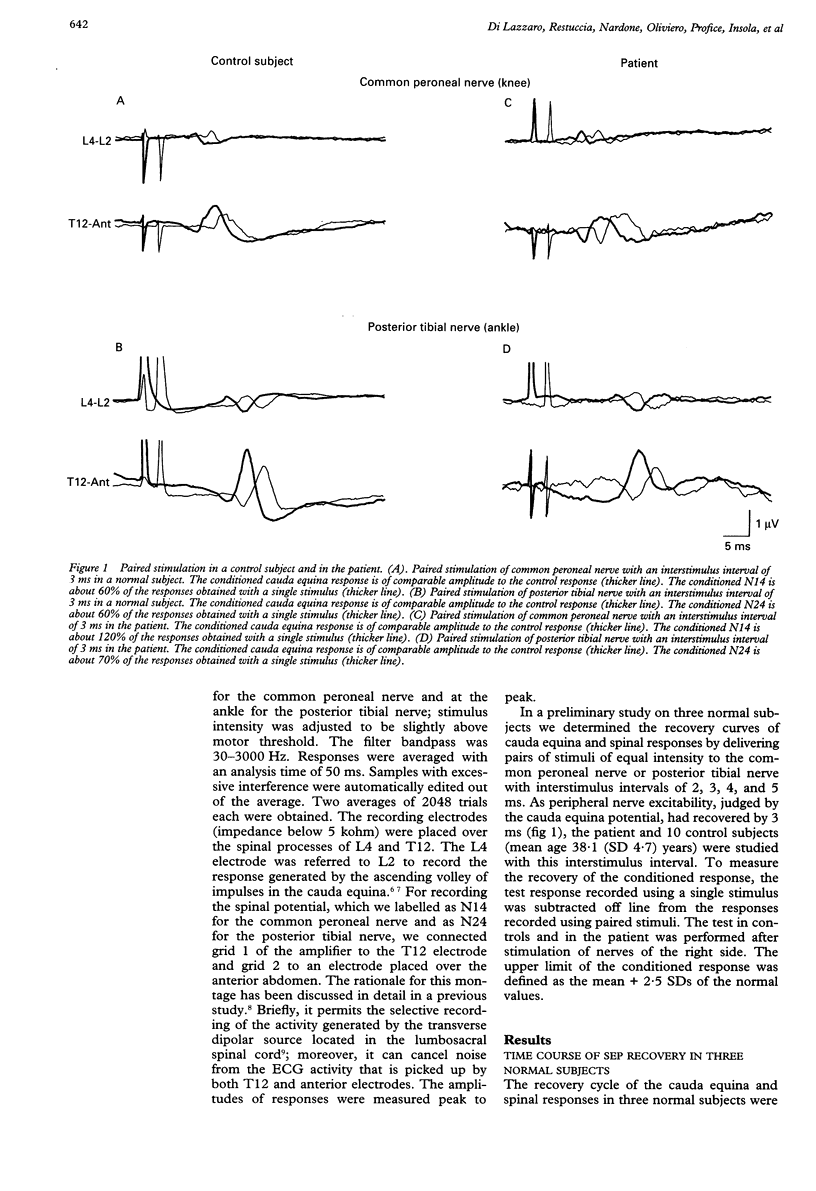
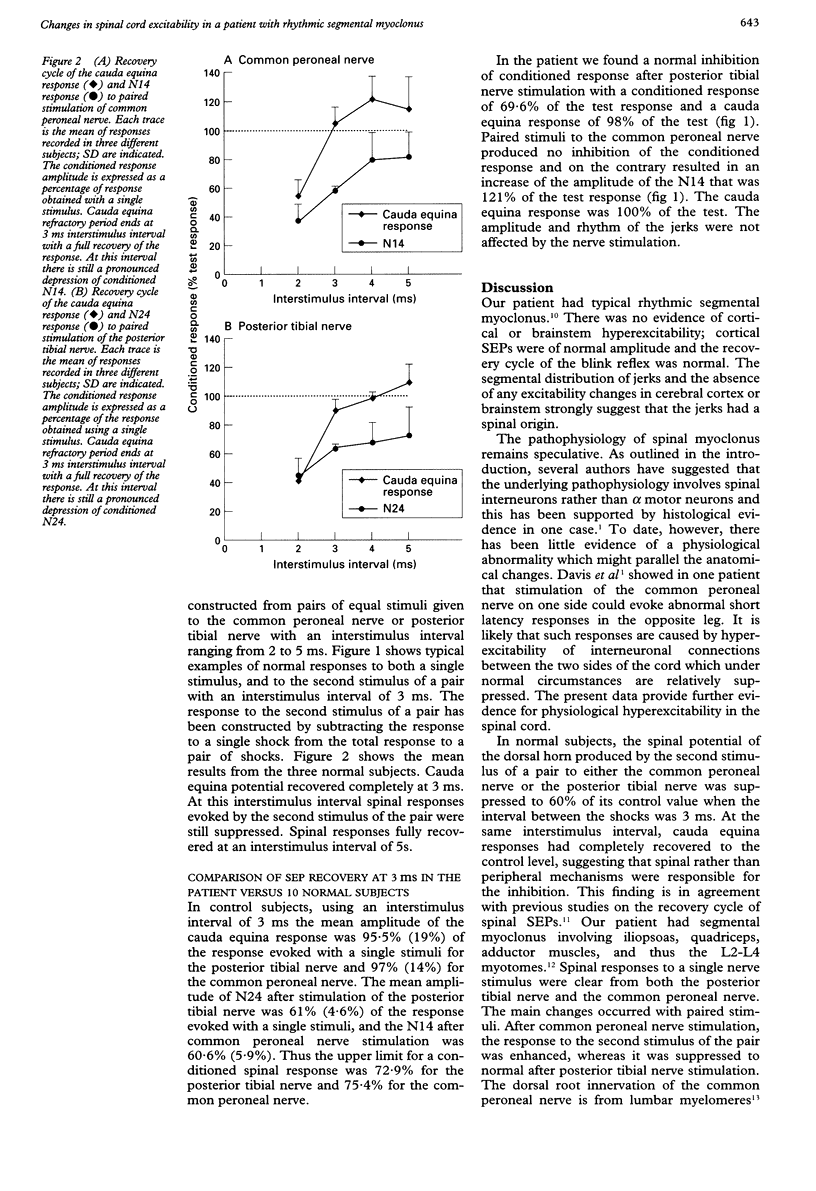
Paired stimulation of the common peroneal and posterior tibial nerve was used to study the recovery cycle of lumbosacral somatosensory evoked potentials in 10 control subjects and in one patient with rhythmic segmental myoclonus of the leg involving the L2-L4 myotomes. In normal subjects the peripheral nerve volley in the cauda equina had recovered at an interstimulus interval of 3 ms whereas the postsynaptic dorsal horn potential was reduced to about 60% of its control size. Similar results were found in the patient after posterior tibial nerve but not common peroneal nerve stimulation. The second, which evokes afferent input to the affected lumbar segments, produced facilitation of the postsynaptic response at 3 ms. This finding suggests that the physiological suppression of dorsal horn interneurons which usually takes place after paired stimulation fails to occur in segmental myoclonus. This may indicate that dorsal horn interneurons are abnormally hyperactive and are involved in the pathophysiology of spinal myoclonus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall J. E., Applebaum A. E., Foreman R. D., Willis W. D. Spinal cord potentials evoked by cutaneous afferents in the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Mar;40(2):199–211. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.2.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cracco J. B., Cracco R. Q., Graziani L. J. The spinal evoked response in infants and children. Neurology. 1975 Jan;25(1):31–36. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. M., Murray N. M., Diengdoh J. V., Galea-Debono A., Kocen R. S. Stimulus-sensitive spinal myoclonus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Oct;44(10):884–888. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.10.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Cheron G. Spinal and far-field components of human somatosensory evoked potentials to posterior tibial nerve stimulation analysed with oesophageal derivations and non-cephalic reference recording. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1983 Dec;56(6):635–651. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(83)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins A. P., Michael W. F. Spinal myoclonus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Oct;37(10):1112–1115. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.10.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanmonod D., Sindou M., Mauguière F. Three transverse dipolar generators in the human cervical and lumbo-sacral dorsal horn: evidence from direct intraoperative recordings on the spinal cord surface. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1989 May-Jun;74(3):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(89)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGLADERY J. W., PORTER W. E., PARK A. M., TEASDALL R. D. Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. IV. The two-neurone reflex and identification of certain action potentials from spinal roots and cord. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1951 Jun;88(6):499–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohl M., Doose H., Gross-Selbeck G., Jensen H. P. Sinal myoclonus. Eur Neurol. 1978;17(3):129–135. doi: 10.1159/000114935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restuccia D., Di Lazzaro V., Valeriani M., Colosimo C., Tonali P. N24 spinal response to tibial nerve stimulation and magnetic resonance imaging in lesions of the lumbosacral spinal cord. Neurology. 1993 Nov;43(11):2269–2275. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.11.2269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risius B., Modic M. T., Hardy R. W., Jr, Duchesneau P. M., Weinstein M. A. Sector computed tomographic spine scanning in the diagnosis of lumbar nerve root entrapment. Radiology. 1982 Apr;143(1):109–114. doi: 10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



