Abstract
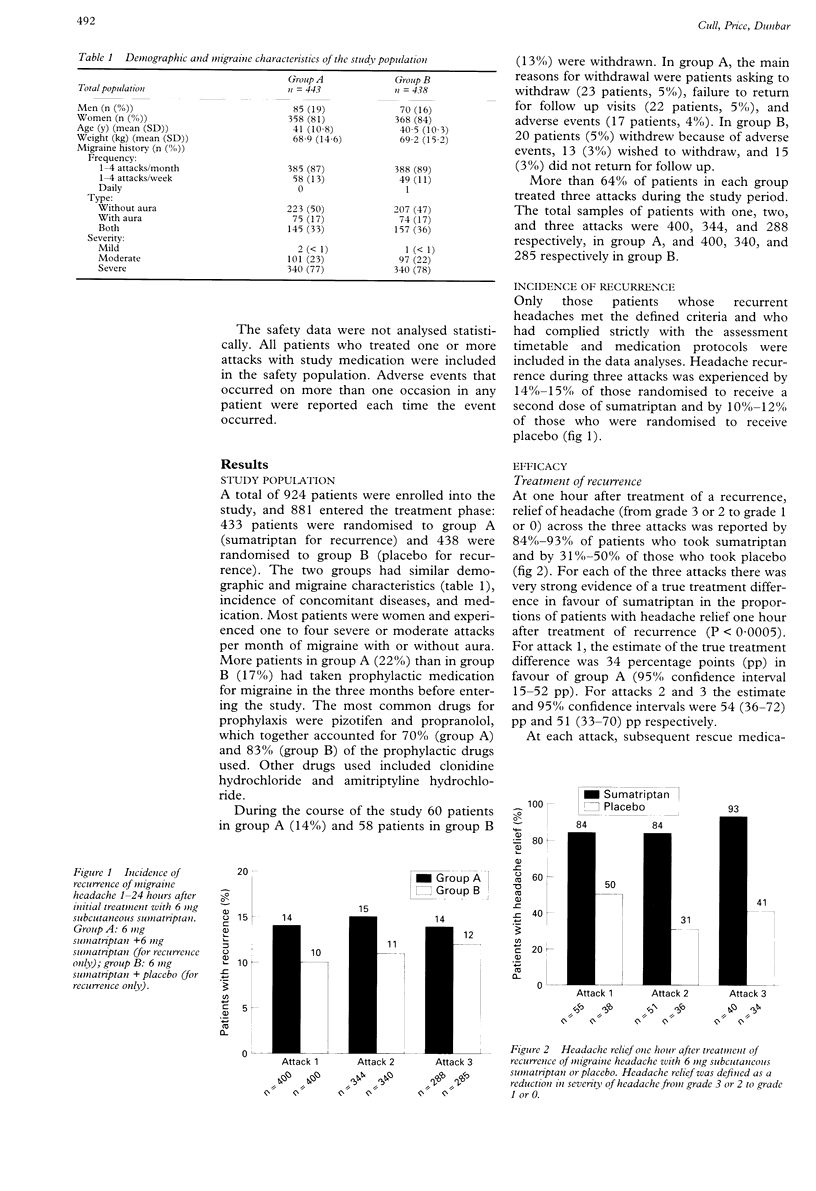
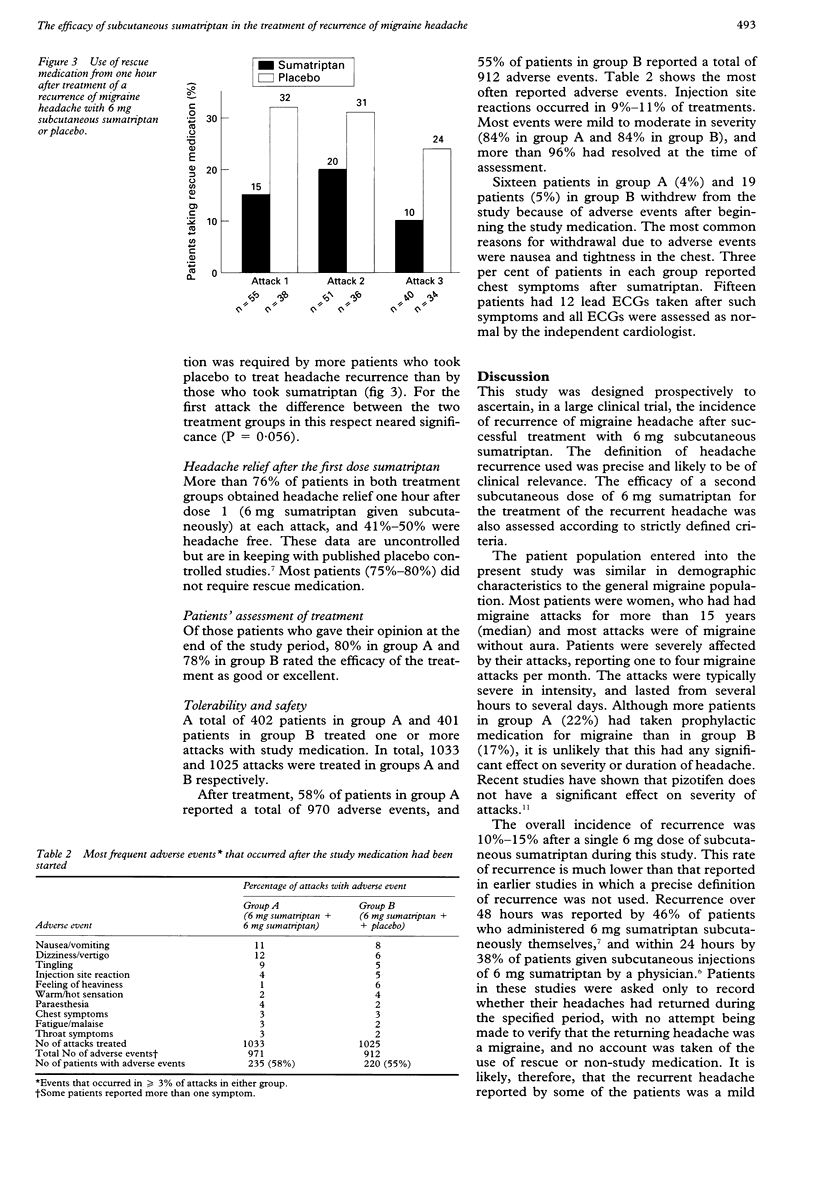
OBJECTIVES: To investigate the efficacy of a second subcutaneous dose of 6 mg sumatriptan in the treatment of recurrence of headache after successful treatment of a migraine attack with an initial 6 mg dose. METHODS: In a prospective, randomised, placebo controlled, double blind, parallel group study, 803 patients were treated for one to three migraine attacks with severe or moderate headache with a subcutaneous injection of 6 mg sumatriptan. Any subsequent recurrence of migraine headache was treated with a randomised second injection of sumatriptan or placebo. Recurrence was defined as a headache of moderate or severe intensity occurring 1-24 hours after the initial dose in a patient whose headache had been relieved by sumatriptan (reduction of headache severity from severe or moderate to mild or none after one hour). RESULTS: Headache recurrence was reported by 10%-15% of patients. At each attack, 6 mg sumatriptan given subcutaneously was significantly (P < 0.0005) more effective than placebo at relieving recurrent headache after one hour (84%-93% v 31%-50% of patients); 76%-83% of patients reported headache relief one hour after the initial dose of sumatriptan. Sumatriptan was generally well tolerated. CONCLUSIONS: Up to 15% of patients with migraine experience significant recurrence of headache after successful treatment with subcutaneous sumatriptan, and this recurrence is effectively treated by a further dose of subcutaneous sumatriptan.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blau J. N. Sumatriptan and recurrence of migraine. Lancet. 1992 Oct 31;340(8827):1110–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cady R. K., Wendt J. K., Kirchner J. R., Sargent J. D., Rothrock J. F., Skaggs H., Jr Treatment of acute migraine with subcutaneous sumatriptan. JAMA. 1991 Jun 5;265(21):2831–2835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catarci T., Fiacco F., Argentino C., Sette G., Cerbo R. Ergotamine-induced headache can be sustained by sumatriptan daily intake. Cephalalgia. 1994 Oct;14(5):374–375. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-2982.1994.1405374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catarci T., Lenzi G. L., Cerbo R., Fieschi C. Sumatriptan and daily headache. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995 Apr;58(4):508–508. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.58.4.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler P. A., Lacey L. F., Thomas M., Keene O. N., Tanner R. J., Baber N. S. The clinical pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and metabolism of sumatriptan. Eur Neurol. 1991;31(5):291–294. doi: 10.1159/000116756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Fan E., Linville D., Ting V., Villemure J. G., Chia L. S. Expression of mRNA for the serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine1D beta receptor subtype in human and bovine cerebral arteries. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;44(2):242–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey P. P., Feniuk W. Mode of action of the anti-migraine drug sumatriptan. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Dec;12(12):444–446. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90630-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew N. T. Drug-induced headache. Neurol Clin. 1990 Nov;8(4):903–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew N. T., Kurman R., Perez F. Drug induced refractory headache--clinical features and management. Headache. 1990 Oct;30(10):634–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1990.hed3010634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tansey M. J., Pilgrim A. J., Martin P. M. Long-term experience with sumatriptan in the treatment of migraine. Eur Neurol. 1993;33(4):310–315. doi: 10.1159/000116960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


