Abstract
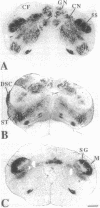
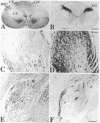
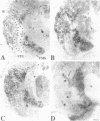
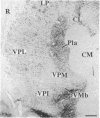
Chronic deafferentation of skin and peripheral tissues is associated with plasticity of representational maps in cerebral cortex and with perturbations of sensory experience that include severe "central" pain. This study shows that in normal monkeys the nonnociceptive, lemniscal component of the somatosensory pathways at spinal, brainstem, and thalamic levels is distinguished by cells and fibers immunoreactive for the calcium-binding protein parvalbumin, whereas cells of the nociceptive component at these levels are distinguished by immunoreactivity for 28-kDa calbindin. Long-term dorsal rhizotomies in monkeys lead to transneuronal degeneration of parvalbumin cells at brainstem and thalamic sites accompanied in the thalamus by a down-regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors and an apparent increase in activity of calbindin cells preferentially innervated by central pain pathways. Release from inhibition and imbalance in patterns of somatosensory inputs from thalamus to cerebral cortex may constitute subcortical mechanisms for inducing changes in representational maps and perturbations of sensory perception, including central pain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson D. L., Isackson P. J., Gall C. M., Jones E. G. Differential effects of monocular deprivation on glutamic acid decarboxylase and type II calcium-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase gene expression in the adult monkey visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1991 Jan;11(1):31–47. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-01-00031.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Adler J. E., Dreyfus C. F., Jonakait G. M., Katz D. M., LaGamma E. F., Markey K. M. Neurotransmitter plasticity at the molecular level. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1266–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.6147894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boivie J. An anatomical reinvestigation of the termination of the spinothalamic tract in the monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Aug 1;186(3):343–369. doi: 10.1002/cne.901860304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R. Calbindin D-28k and parvalbumin in the rat nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;35(2):375–475. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90091-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R. Parvalbumin in most gamma-aminobutyric acid-containing neurons of the rat cerebral cortex. Science. 1986 Feb 28;231(4741):995–997. doi: 10.1126/science.3945815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celio M. R., Schärer L., Morrison J. H., Norman A. W., Bloom F. E. Calbindin immunoreactivity alternates with cytochrome c-oxidase-rich zones in some layers of the primate visual cortex. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):715–717. doi: 10.1038/323715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFelipe J., Hendry S. H., Hashikawa T., Molinari M., Jones E. G. A microcolumnar structure of monkey cerebral cortex revealed by immunocytochemical studies of double bouquet cell axons. Neuroscience. 1990;37(3):655–673. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90097-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devor M., Wall P. D. Reorganisation of spinal cord sensory map after peripheral nerve injury. Nature. 1978 Nov 2;276(5683):75–76. doi: 10.1038/276075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Fuchs J., deBlas A. L., Jones E. G. Distribution and plasticity of immunocytochemically localized GABAA receptors in adult monkey visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2438–2450. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02438.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G. Activity-dependent regulation of GABA expression in the visual cortex of adult monkeys. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):701–712. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry S. H., Jones E. G., Emson P. C., Lawson D. E., Heizmann C. W., Streit P. Two classes of cortical GABA neurons defined by differential calcium binding protein immunoreactivities. Exp Brain Res. 1989;76(2):467–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00247904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks T. P., Metherate R., Landry P., Dykes R. W. Bicuculline-induced alterations of response properties in functionally identified ventroposterior thalamic neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1986;63(2):248–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00236843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C. A., Pang D. Z., Jones E. G. Distribution and density of GABA cells in intralaminar and adjacent nuclei of monkey thalamus. Neuroscience. 1991;43(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90426-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Friedman D. P. Projection pattern of functional components of thalamic ventrobasal complex on monkey somatosensory cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1982 Aug;48(2):521–544. doi: 10.1152/jn.1982.48.2.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Hendry S. H. C. Differential Calcium Binding Protein Immunoreactivity Distinguishes Classes of Relay Neurons in Monkey Thalamic Nuclei. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 May;1(3):222–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G., Schwark H. D., Callahan P. A. Extent of the ipsilateral representation in the ventral posterior medial nucleus of the monkey thalamus. Exp Brain Res. 1986;63(2):310–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00236848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaas J. H., Merzenich M. M., Killackey H. P. The reorganization of somatosensory cortex following peripheral nerve damage in adult and developing mammals. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:325–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaas J. H., Nelson R. J., Sur M., Dykes R. W., Merzenich M. M. The somatotopic organization of the ventroposterior thalamus of the squirrel monkey, Saimiri sciureus. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jun 10;226(1):111–140. doi: 10.1002/cne.902260109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewy A. D. Transneuronal changes in the gracile nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Feb 15;147(4):497–510. doi: 10.1002/cne.901470405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEHLER W. R., FEFERMAN M. E., NAUTA W. J. Ascending axon degeneration following anterolateral cordotomy. An experimental study in the monkey. Brain. 1960 Dec;83:718–750. doi: 10.1093/brain/83.4.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matute C., Streit P. Monoclonal antibodies demonstrating GABA-like immunoreactivity. Histochemistry. 1986;86(2):147–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00493380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POGGIO G. F., MOUNTCASTLE V. B. THE FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES OF VENTROBASAL THALAMIC NEURONSSTUDIED IN UNANESTHETIZED MONKEYS. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Sep;26:775–806. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny G. R., Fitzpatrick D., Schmechel D. E., Diamond I. T. Glutamic acid decarboxylase-immunoreactive neurons and horseradish peroxidase-labeled projection neurons in the ventral posterior nucleus of the cat and Galago senegalensis. J Neurosci. 1983 Sep;3(9):1868–1887. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-09-01868.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons T. P., Garraghty P. E., Ommaya A. K., Kaas J. H., Taub E., Mishkin M. Massive cortical reorganization after sensory deafferentation in adult macaques. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1857–1860. doi: 10.1126/science.1843843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmusson D. D. Projections of digit afferents to the cuneate nucleus in the raccoon before and after partial deafferentation. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Nov 22;277(4):549–556. doi: 10.1002/cne.902770408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausell E., Jones E. G. Chemically distinct compartments of the thalamic VPM nucleus in monkeys relay principal and spinal trigeminal pathways to different layers of the somatosensory cortex. J Neurosci. 1991 Jan;11(1):226–237. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-01-00226.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rausell E., Jones E. G. Histochemical and immunocytochemical compartments of the thalamic VPM nucleus in monkeys and their relationship to the representational map. J Neurosci. 1991 Jan;11(1):210–225. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-01-00210.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruda M. A., Iadarola M. J., Cohen L. V., Young W. S., 3rd In situ hybridization histochemistry and immunocytochemistry reveal an increase in spinal dynorphin biosynthesis in a rat model of peripheral inflammation and hyperalgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):622–626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitorica J., Park D., Chin G., de Blas A. L. Monoclonal antibodies and conventional antisera to the GABAA receptor/benzodiazepine receptor/Cl- channel complex. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):615–622. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00615.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D., Egger M. D. Formation of new connexions in adult rat brains after partial deafferentation. Nature. 1971 Aug 20;232(5312):542–545. doi: 10.1038/232542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Riley M. Changes in the visual system of monocularly sutured or enucleated cats demonstrable with cytochrome oxidase histochemistry. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 27;171(1):11–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90728-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]