Abstract
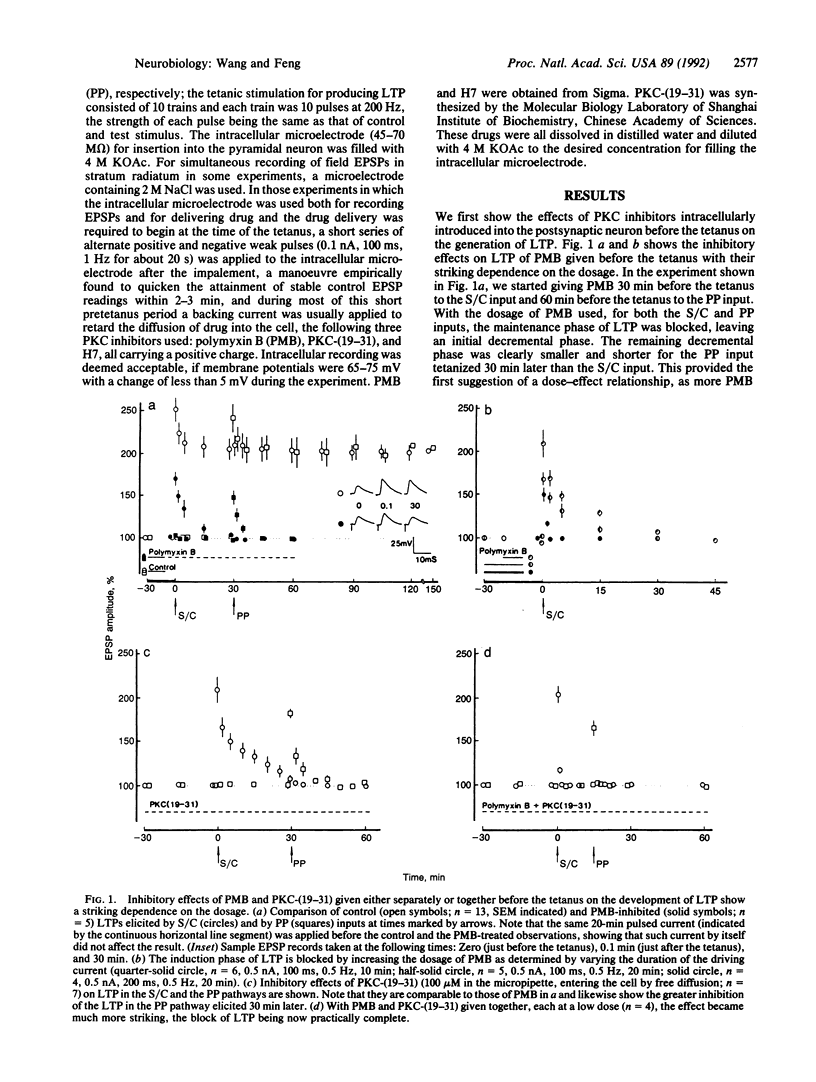
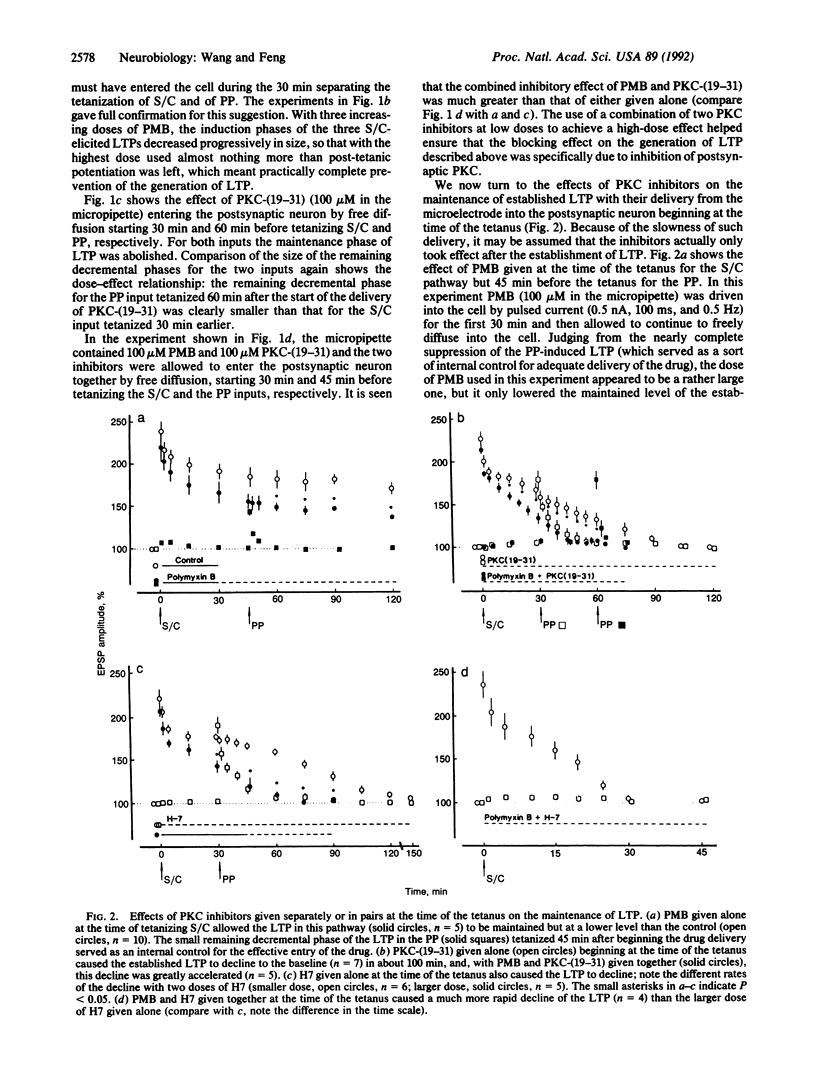
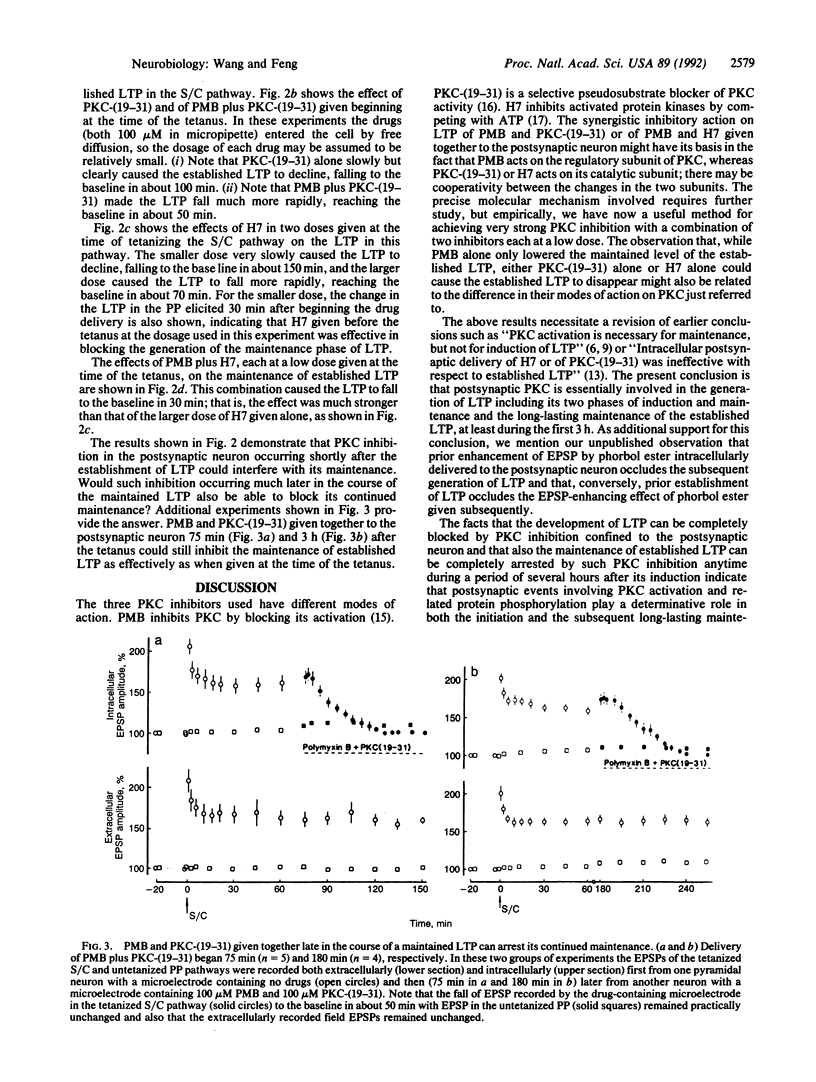
Previous studies on the effects of protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors intracellularly introduced into the postsynaptic neuron on long-term potentiation (LTP) in the hippocampal CA1 region showed that given before the tetanic stimulation they only blocked the development of the maintenance phase of LTP and that given after the tetanus they did not affect the continued maintenance of established LTP. We now report different results in such experiments obtained by looking into the dose-effect relationship of the inhibitors given to the postsynaptic neuron and making use of a synergistic effect of two inhibitors given together. We used the following three PKC inhibitors: polymyxin B (PMB), PKC-(19-31), and H7. With the intracellular delivery of the inhibitor(s) beginning 30 min before the tetanus, PMB in adequate dosage or a combination of PMB and PKC-(19-31), each at a low dosage, could block the development of LTP completely including its initial induction phase. With the delivery beginning at the time of the tetanus, PKC-(19-31) or H7 slowly caused the established LTP to decline to the baseline; this decline was greatly accelerated when PMB and PKC-(19-31) or PMB and H7 were given together. PMB and PKC-(19-31) given together 75-90 min or even 3 h after the tetanus caused a decline of the maintained LTP similar to the decline observed when both inhibitors were given at the time of the tetanus. These results show that postsynaptic PKC is essentially involved in both the initial induction and the subsequent maintenance of LTP, contrary to current views on the subject.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwyl R. Protein kinase C and long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jun;10(6):236–239. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ascher P., Nowak L. The role of divalent cations in the N-methyl-D-aspartate responses of mouse central neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:247–266. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. Presynaptic mechanism for long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):724–729. doi: 10.1038/346724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. N., Lester R. A., Reymann K. G., Collingridge G. L. Temporally distinct pre- and post-synaptic mechanisms maintain long-term potentiation. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):500–503. doi: 10.1038/338500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H. Physiological mechanisms underlying long-term potentiation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Apr;11(4):156–162. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauer J. A., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A persistent postsynaptic modification mediates long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Neuron. 1988 Dec;1(10):911–917. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. Mechanisms underlying long-term potentiation of synaptic transmission. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:379–397. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A., Perkel D. J., Mauk M. D., Kelly P. T., Nicoll R. A., Waxham M. N. An essential role for postsynaptic calmodulin and protein kinase activity in long-term potentiation. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):554–557. doi: 10.1038/340554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C. Postsynaptic factors control the duration of synaptic enhancement in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90121-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Madison D. V., Tsien R. W. Persistent protein kinase activity underlying long-term potentiation. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):820–824. doi: 10.1038/335820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Schulman H., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.2549638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Tsien R. W. Presynaptic enhancement shown by whole-cell recordings of long-term potentiation in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):177–180. doi: 10.1038/346177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei G. J., Katoh N., Kuo J. F. Polymyxin B is a more selective inhibitor for phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase than for calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91894-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller D., Buchs P. A., Dunant Y., Lynch G. Protein kinase C activity is not responsible for the expression of long-term potentiation in hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4073–4077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymann K. G., Davies S. N., Matthies H., Kase H., Collingridge G. L. Activation of a K-252b-Sensitive Protein Kinase is Necessary for a Post-Synaptic Phase of Long-Term Potentiation in Area CA1 of Rat Hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(6):481–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00439.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymann K. G., Frey U., Jork R., Matthies H. Polymyxin B, an inhibitor of protein kinase C, prevents the maintenance of synaptic long-term potentiation in hippocampal CA1 neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 9;440(2):305–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91000-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. F. Strengthening the synapses. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):460–461. doi: 10.1038/338460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



