Figure 2.
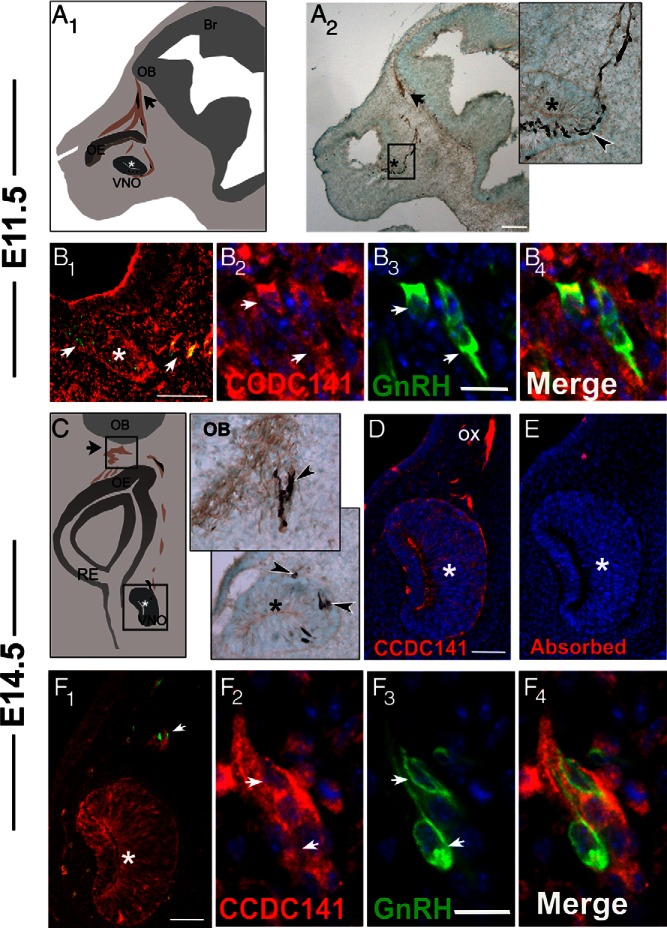
Ccdc141 is expressed in migrating GnRH neurons in the developing mouse. A1, Schematic of an E11.5 parasagittal mouse head; *, developing VNO; OE, olfactory epithelium, arrow points to nasal forebrain junction; OB, olfactory bulb. Peripherin-positive olfactory axons (in brown) are shown extending to the olfactory bulb. GnRH neurons (shown in black) migrate on these axon bundles until they cross the nasal forebrain junction (black arrow) and enter the brain. A2, E11.5 embryo stained for peripherin (brown) and GnRH (black), with high-magnification image of boxed area on right. Arrowhead indicates GnRH neurons streaming out from the VNO (*). B1–B4, Fluorescent staining for Ccdc141 (red), GnRH (green), and nuclear staining with DAPI (blue) at E11.5. B1, Ccdc141 staining is expressed in GnRH neurons and in mesenchymal cells. Robust staining is evident in the axonal tracts leaving the VNO where GnRH neurons are located (arrows). B2–B4, Higher magnification showing GnRH/Ccdc141 neurons in the VNO. C1, Schematic of a coronal section of an E14.5 embryo nose; VNO (*), respiratory epithelium (RE), OE, nasal forebrain junction (arrow), and OB. C2, Magnified coronal sections from an E14.5 embryo stained for GnRH (black) and peripherin (brown), showing GnRH neurons at the nasal/forebrain junction (upper box in schematic) and leaving the VNO (*, bottom box in schematic). D, Fluorescent staining of Ccdc141 red at E14.5 showing staining in VNO (*) and olfactory axons (OX). E, Serial section stained with antibody + blocking peptide (10 μg/mL). After primary antibody/primary antibody + blocking peptide, D and E were stained together. No specific staining was detected after blocking peptide was added to the primary antibody. F1–F4, Fluorescent staining for Ccdc141 (red), GnRH (green), and nuclear staining with DAPI (blue) at E14.5. By E14.5, Ccdc141 levels appeared to decrease in mesenchyme cells (F1) yet remained clearly present in sensory axons and GnRH neurons (F2–F4). Scale bars: 100 μm (A), 50 μm (B1 and F1), and 10 μm (B2–B4 and F2–F4).