Abstract
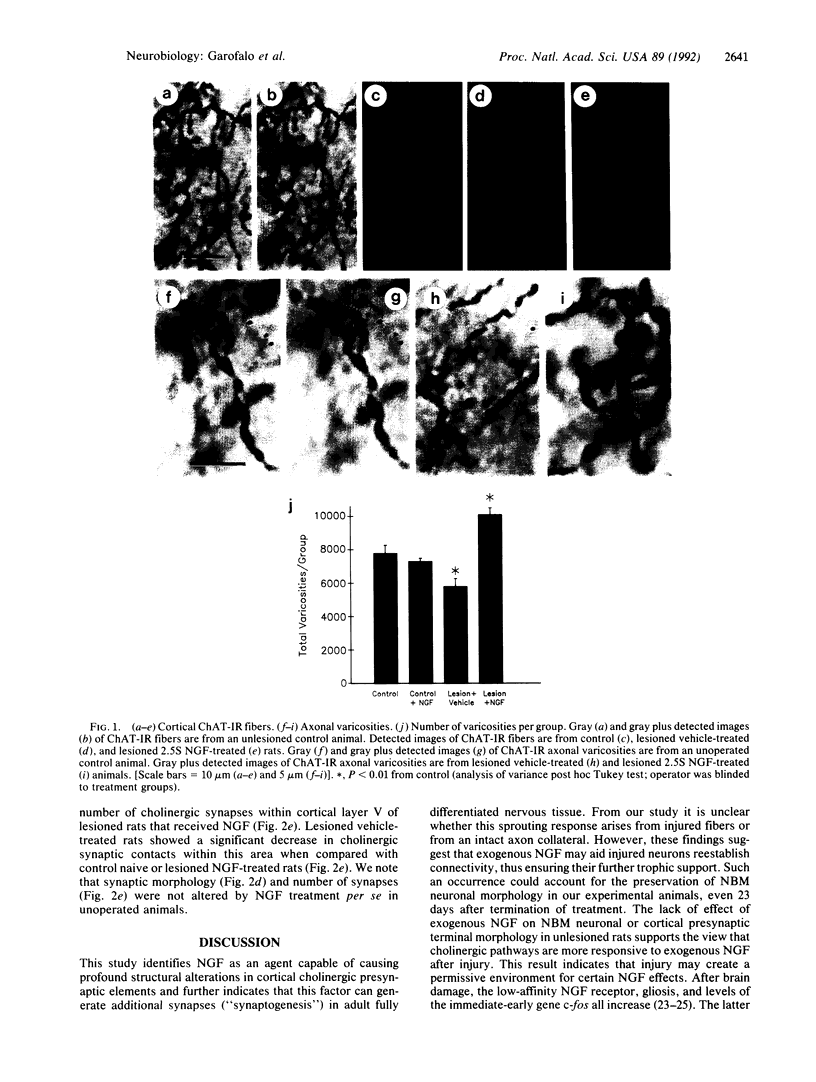
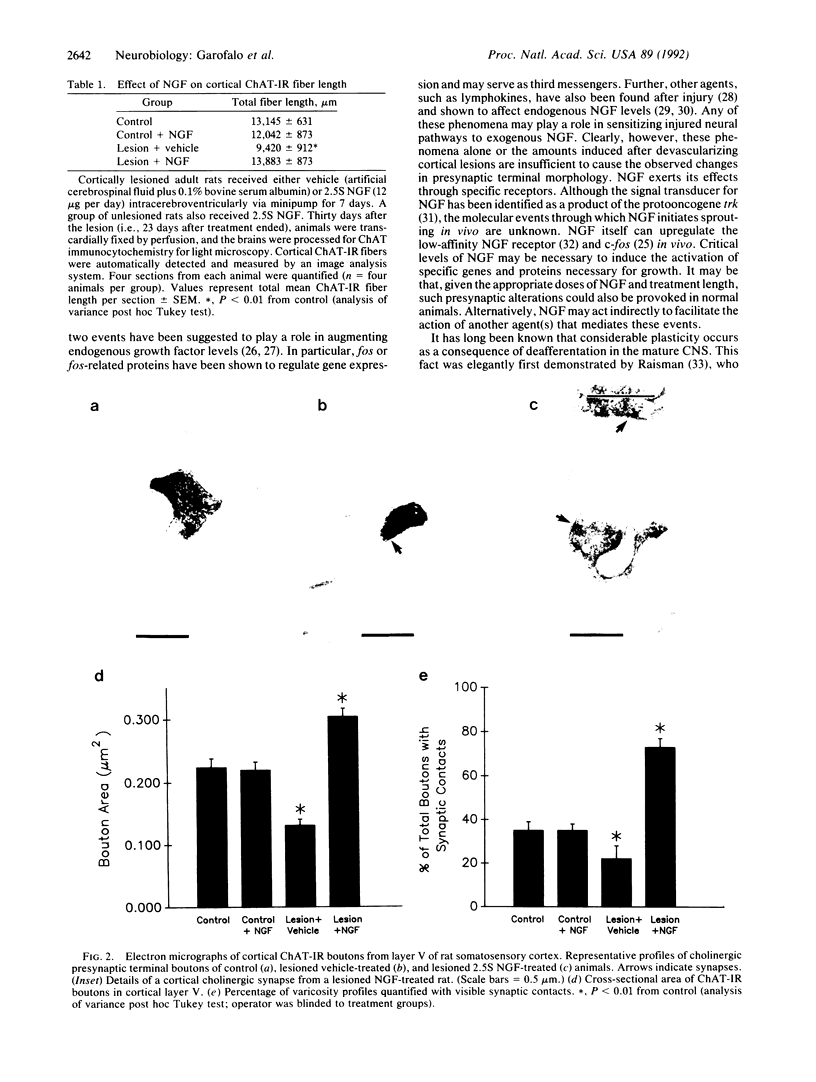
In this study light and EM quantitative analysis were used to examine whether exogenous nerve growth factor (NGF) could affect terminal fields and synaptic connections in the adult rat brain in vivo. Adult rats received, immediately after unilateral decortication, 2.5S NGF (12 micrograms/day) or vehicle intracerebroventricularly for 7 days. Thirty days after the lesion cholinergic fiber length was quantified, using image analysis, in the remaining cortical area adjacent to the lesion site in each animal. Rats that had received vehicle showed a significantly reduced cortical choline acetyl-transferase-immunoreactive fiber network in the remaining cortex when compared with control animals. By contrast, the network in lesioned rats that had received 2.5S NGF was not different from control animals. Furthermore, the number of cortical choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive varicosities, which decreased in vehicle-treated lesioned rats, significantly increased above control in lesioned rats that had received 2.5S NGF. At the ultrastructural level, 30 days after the lesion, animals that had received vehicle showed shrunken cholinergic boutons in cortical layer V and fewer synapses compared with control animals. Exogenous NGF, administered to lesioned rats, increased to supernormal levels both size of cholinergic boutons and number of synaptic contacts. These parameters were unaltered in unlesioned rats treated with NGF. This study demonstrates that exogenous NGF can cause significant compensatory changes in terminal fields and synaptic connections in the adult fully differentiated central nervous system.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applegate M. D., Kerr D. S., Landfield P. W. Redistribution of synaptic vesicles during long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1987 Jan 20;401(2):401–406. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartus R. T., Dean R. L., 3rd, Beer B., Lippa A. S. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982 Jul 30;217(4558):408–414. doi: 10.1126/science.7046051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavicchioli L., Flanigan T. P., Vantini G., Fusco M., Polato P., Toffano G., Walsh F. S., Leon A. NGF Amplifies Expression of NGF Receptor Messenger RNA in Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons of Rats. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 May;1(3):258–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C., Gentry C., Steward O. Synaptic replacement in the dentate gyrus after unilateral entorhinal lesion: electron microscopic analysis of the extent of replacement of synapses by the remaining entorhinal cortex. J Neurocytol. 1977 Aug;6(4):455–464. doi: 10.1007/BF01178228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello A. C., Garofalo L., Kenigsberg R. L., Maysinger D. Gangliosides potentiate in vivo and in vitro effects of nerve growth factor on central cholinergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2056–2060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibiger H. C. The organization and some projections of cholinergic neurons of the mammalian forebrain. Brain Res. 1982 Nov;257(3):327–388. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(82)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Batchelor P., Chen K. S., Chin D., Higgins G. A., Koh S., Deputy S., Rosenberg M. B., Fischer W., Bjorklund A. NGF receptor reexpression and NGF-mediated cholinergic neuronal hypertrophy in the damaged adult neostriatum. Neuron. 1989 Feb;2(2):1177–1184. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Olejniczak P., Armstrong D. M. Astrocytes are important for sprouting in the septohippocampal circuit. Exp Neurol. 1988 Oct;102(1):2–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(88)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall C. M., Isackson P. J. Limbic seizures increase neuronal production of messenger RNA for nerve growth factor. Science. 1989 Aug 18;245(4919):758–761. doi: 10.1126/science.2549634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Lachman L. B. Interleukin-1 stimulation of astroglial proliferation after brain injury. Science. 1985 Apr 26;228(4698):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.3872478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagg T., Vahlsing H. L., Manthorpe M., Varon S. Nerve growth factor infusion into the denervated adult rat hippocampal formation promotes its cholinergic reinnervation. J Neurosci. 1990 Sep;10(9):3087–3092. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-09-03087.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F. Nerve growth factor promotes survival of septal cholinergic neurons after fimbrial transections. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2155–2162. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02155.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengerer B., Lindholm D., Heumann R., Rüther U., Wagner E. F., Thoenen H. Lesion-induced increase in nerve growth factor mRNA is mediated by c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Crawford G. D., Salvaterra P. M., Vaughn J. E. Immunocytochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase in rat cerebral cortex: a study of cholinergic neurons and synapses. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Apr 1;234(1):17–34. doi: 10.1002/cne.902340103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Hempstead B. L., Martin-Zanca D., Chao M. V., Parada L. F. The trk proto-oncogene product: a signal transducing receptor for nerve growth factor. Science. 1991 Apr 26;252(5005):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1850549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S., Auburger G., Heumann R., Scott J., Thoenen H. Levels of nerve growth factor and its mRNA in the central nervous system of the rat correlate with cholinergic innervation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1389–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kromer L. F. Nerve growth factor treatment after brain injury prevents neuronal death. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):214–216. doi: 10.1126/science.3798108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibrock J., Lottspeich F., Hohn A., Hofer M., Hengerer B., Masiakowski P., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):149–152. doi: 10.1038/341149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Heumann R., Hengerer B., Thoenen H. Interleukin 1 increases stability and transcription of mRNA encoding nerve growth factor in cultured rat fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16348–16351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Heumann R., Meyer M., Thoenen H. Interleukin-1 regulates synthesis of nerve growth factor in non-neuronal cells of rat sciatic nerve. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):658–659. doi: 10.1038/330658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luiten P. G., Gaykema R. P., Traber J., Spencer D. G., Jr Cortical projection patterns of magnocellular basal nucleus subdivisions as revealed by anterogradely transported Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. Brain Res. 1987 Jun 16;413(2):229–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysakowski A., Wainer B. H., Bruce G., Hersh L. B. An atlas of the regional and laminar distribution of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience. 1989;28(2):291–336. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Squinto S., Ip N. Y., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1446–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathewson A. J., Berry M. Observations on the astrocyte response to a cerebral stab wound in adult rats. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 18;327(1-2):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91499-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mize R. R., Holdefer R. N., Nabors L. B. Quantitative immunocytochemistry using an image analyzer. I. Hardware evaluation, image processing, and data analysis. J Neurosci Methods. 1988 Nov;26(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(88)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto-Sampedro M., Manthrope M., Barbin G., Varon S., Cotman C. W. Injury-induced neuronotrophic activity in adult rat brain: correlation with survival of delayed implants in the wound cavity. J Neurosci. 1983 Nov;3(11):2219–2229. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-11-02219.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pioro E. P., Cuello A. C. Distribution of nerve growth factor receptor-like immunoreactivity in the adult rat central nervous system. Effect of colchicine and correlation with the cholinergic system--I. Forebrain. Neuroscience. 1990;34(1):57–87. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90304-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D., Njå A. Effect of nerve growth factor on synaptic depression after axotomy. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):535–536. doi: 10.1038/260535a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raisman G. Neuronal plasticity in the septal nuclei of the adult rat. Brain Res. 1969 Jun;14(1):25–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-da-Silva A., Cuello A. C. Choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive profiles are presynaptic to primary sensory fibers in the rat superficial dorsal horn. J Comp Neurol. 1990 May 15;295(3):370–384. doi: 10.1002/cne.902950303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. B., Friedmann T., Robertson R. C., Tuszynski M., Wolff J. A., Breakefield X. O., Gage F. H. Grafting genetically modified cells to the damaged brain: restorative effects of NGF expression. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.3201248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp F. R., Gonzalez M. F., Hisanaga K., Mobley W. C., Sagar S. M. Induction of the c-fos gene product in rat forebrain following cortical lesions and NGF injections. Neurosci Lett. 1989 May 22;100(1-3):117–122. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90670-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofroniew M. V., Pearson R. C., Powell T. P. The cholinergic nuclei of the basal forebrain of the rat: normal structure, development and experimentally induced degeneration. Brain Res. 1987 May 19;411(2):310–331. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. H., Cuello A. C., Sofroniew M. V., Pearson R. C., Tagari P. Effect of unilateral decortication on choline acetyltransferase activity in the nucleus basalis and other areas of the rat brain. J Neurochem. 1985 Oct;45(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutula T., He X. X., Cavazos J., Scott G. Synaptic reorganization in the hippocampus induced by abnormal functional activity. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1147–1150. doi: 10.1126/science.2449733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahlsing H. L., Varon S., Hagg T., Fass-Holmes B., Dekker A., Manley M., Manthorpe M. An improved device for continuous intraventricular infusions prevents the introduction of pump-derived toxins and increases the effectiveness of NGF treatments. Exp Neurol. 1989 Sep;105(3):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90125-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Harreveld A., Fifkova E. Swelling of dendritic spines in the fascia dentata after stimulation of the perforant fibers as a mechanism of post-tetanic potentiation. Exp Neurol. 1975 Dec;49(3):736–749. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. R., Varon S., Peterson G. M., Wictorin K., Fischer W., Bjorklund A., Gage F. H. Continuous infusion of nerve growth factor prevents basal forebrain neuronal death after fimbria fornix transection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9231–9235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]