Abstract
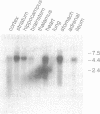
A DNA, cloned after screening a rat genomic bank with probes derived from the sequence of a putative dog histamine H2 receptor [Gantz, I., Schäffer, M., Delvalle, J., Logsdon, C., Campbell, V., Uhler, M. & Yamada, T. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 429-433], was used to prepare a probe for Northern blot analysis and to transfect Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. Distribution of the gene transcripts in guinea pig tissues was consistent with that of H2 receptors. Transfected CHO cells expressed a high density of sites binding [125I]iodoaminopotentidine, a selective H2-receptor ligand. These sites were characterized as typical H2 receptors by using a series of competing agents that displayed apparent dissociation constants closely similar to corresponding values at a reference biological system. In transfected cells, histamine stimulated, with high potency and large receptor reserve, the accumulation of cAMP. In addition, in the same cells, histamine potently inhibited the release of arachidonic acid induced either by stimulation of constitutive purinergic receptors or by application of a Ca2+ ionophore. This inhibition was independent of either cAMP or Ca2+ levels. The results suggest that a single H2 receptor may be linked not only to adenylyl cyclase activation but also to reduction of phospholipase A2 activity. Because H1 receptors have been reported to stimulate arachidonic acid release, inhibition of this release, an unexpected signaling pathway for H2 receptors, may account for the opposing physiological responses elicited in many tissues by stimulation of these two receptors subtypes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):832–837. doi: 10.1038/302832a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baudry M., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. H1 and H2 receptors in the histamine-induced accumulation of cyclic AMP in guinea pig brain slices. Nature. 1975 Jan 31;253(5490):362–364. doi: 10.1038/253362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Duncan W. A., Durant C. J., Ganellin C. R., Parsons E. M. Definition and antagonism of histamine H 2 -receptors. Nature. 1972 Apr 21;236(5347):385–390. doi: 10.1038/236385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron M. G. The guanine nucleotide regulatory protein-coupled receptors for nucleosides, nucleotides, amino acids and amine neurotransmitters. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;1(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooke S. T., Bennett C. F. Mammalian phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C isoenzymes. Cell Calcium. 1989 Jul;10(5):309–323. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam Trung Tuong M., Garbarg M., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacological specificity of brain histamine H2-receptors differs in intact cells and cell-free preparations. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):548–551. doi: 10.1038/287548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajtkowski G. A., Norris D. B., Rising T. J., Wood T. P. Specific binding of 3H-tiotidine to histamine H2 receptors in guinea pig cerebral cortex. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):65–67. doi: 10.1038/304065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantz I., Munzert G., Tashiro T., Schäffer M., Wang L., DelValle J., Yamada T. Molecular cloning of the human histamine H2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):1386–1392. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91047-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantz I., Schäffer M., DelValle J., Logsdon C., Campbell V., Uhler M., Yamada T. Molecular cloning of a gene encoding the histamine H2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. P., Johnson C. L., Weinstein H., Maayani S. Antagonism of histamine-activated adenylate cyclase in brain by D-lysergic acid diethylamide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5697–5701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. K., Diez E., Heasley L. E., Osawa S., Johnson G. L. A G protein mutant that inhibits thrombin and purinergic receptor activation of phospholipase A2. Science. 1990 Aug 10;249(4969):662–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2166341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Wolf P., Palacios J. M., Garbarg M., Barbin G., Schwartz J. C. Hypersensitivity to histamine in the guinea-pig brain: microiontophoretic and biochemical studies. Brain Res. 1978 Nov 10;156(2):275–291. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90509-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegstrand L. R., Kanof P. D., Greengard P. Histamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in mammalian brain. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):163–165. doi: 10.1038/260163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipase A2 activity in bovine rod outer segments by the beta gamma subunits of transducin and its inhibition by the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan H., Sametz W. Histamine-induced release of arachidonic acid and of prostaglandins in the peripheral vascular bed: mode of action. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;314(2):183–190. doi: 10.1007/BF00504536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Kajiyama Y., Nomura Y. Histamine-stimulated and GTP-binding proteins-mediated phospholipase A2 activation in rabbit platelets. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4290–4295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Garbarg M., Barbin G., Schwartz J. C. Pharmacological characterization of histamine receptors mediating the stimulation of cyclic AMP accumulation in slices from guinea-pig hippocampus. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;14(6):971–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli D., Pilon C., Giros B., Sokoloff P., Martres M. P., Schwartz J. C. Dopamine activation of the arachidonic acid cascade as a basis for D1/D2 receptor synergism. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):164–167. doi: 10.1038/353164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruat M., Traiffort E., Arrang J. M., Leurs R., Schwartz J. C. Cloning and tissue expression of a rat histamine H2-receptor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1470–1478. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91738-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruat M., Traiffort E., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C., Hirschfeld J., Buschauer A., Schunack W. Reversible and irreversible labeling and autoradiographic localization of the cerebral histamine H2 receptor using [125I]iodinated probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1658–1662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A., Flower R. J. Extraction and thin-layer chromatography of arachidonic acid metabolites. Methods Enzymol. 1982;86:477–493. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)86219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Shivers B. D., Seeburg P. H. The role of receptor subtype diversity in the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jan;13(1):8–11. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90052-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. C., Arrang J. M., Garbarg M., Pollard H., Ruat M. Histaminergic transmission in the mammalian brain. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jan;71(1):1–51. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankley N. P., Black J. W., Ganellin C. R., Mitchell R. C. Correlation between log POCT/H2O and pKB estimates for a series of muscarinic and histamine H2-receptor antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 May;94(1):264–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff P., Giros B., Martres M. P., Bouthenet M. L., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):146–151. doi: 10.1038/347146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traiffort E., Ruat M., Schwartz J. C. Interaction of mianserin, amitriptyline and haloperidol with guinea pig cerebral histamine H2 receptors studied with [125I]iodoaminopotentidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 19;207(2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90089-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]