Abstract
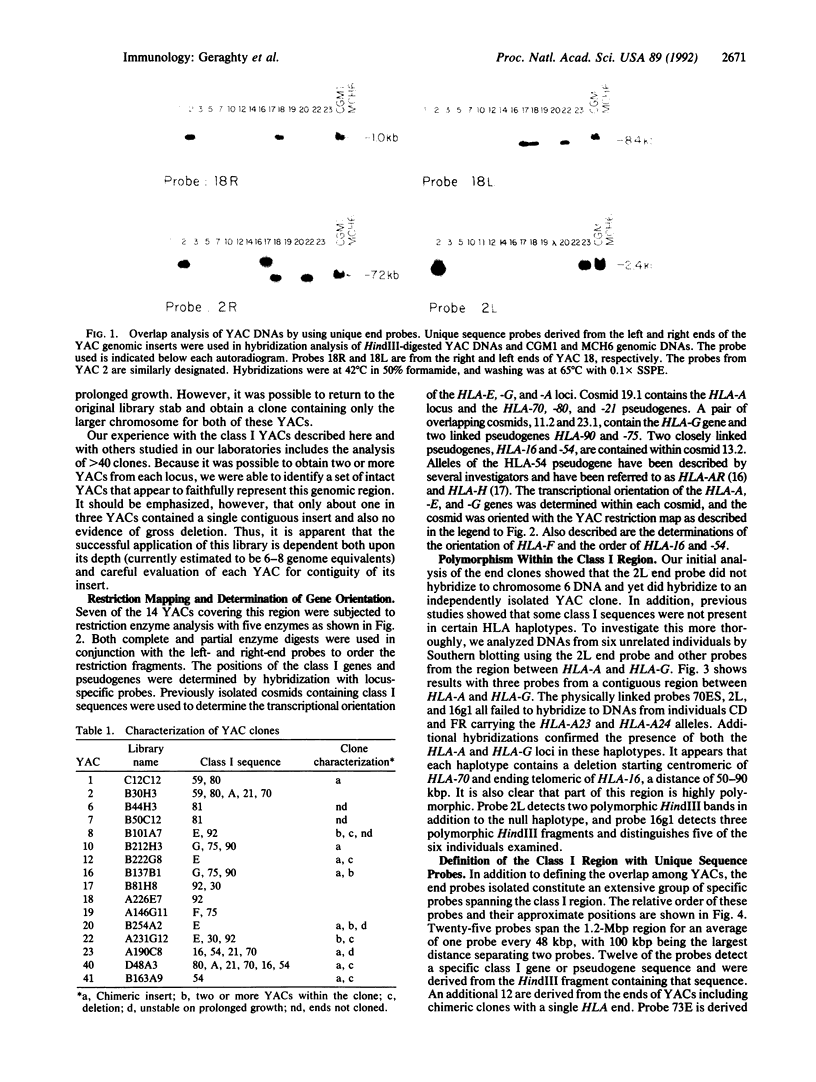
The HLA class I genes are located within a 2-million-base pair (2-Mbp) region constituting the telomeric half of the human major histocompatibility complex. The large majority of the class I sequences, including the HLA-A, -E, -F, and -G genes, is found within the telomeric 1 Mbp. We report here the isolation and characterization of yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones that span a contiguous region of greater than 1.2 Mbp and include 14 of the 18 characterized class I sequences. Restriction enzyme mapping and the use of locus-specific probes have allowed all of the class I genes and sequences to be ordered and positioned within the region. In addition, the transcriptional orientation of the four class I genes has been determined. Using probes derived from the ends of YAC inserts and from class I pseudogenes, we describe a highly polymorphic region between the HLA-A and HLA-G genes. This region appears to be deleted in certain HLA haplotypes, shortening the distance between HLA-A and HLA-G by greater than 50 kilobase pairs (kbp). As part of the characterization of the YAC clones, unique sequence probes derived from the ends of each YAC insert were identified. When combined with probes derived from HLA genes and pseudogenes, 25 locus-specific probes spanning the 1.2-Mbp region have been identified for an average of 1 probe every 48 kbp.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bronson S. K., Pei J., Taillon-Miller P., Chorney M. J., Geraghty D. E., Chaplin D. D. Isolation and characterization of yeast artificial chromosome clones linking the HLA-B and HLA-C loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1676–1680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein B. H., Silverman G. A., Little R. D., Burke D. T., Korsmeyer S. J., Schlessinger D., Olson M. V. Isolation of single-copy human genes from a library of yeast artificial chromosome clones. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1348–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.2544027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. T., Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):806–812. doi: 10.1126/science.3033825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chimini G., Boretto J., Marguet D., Lanau F., Lauquin G., Pontarotti P. Molecular analysis of the human MHC class I region using yeast artificial chromosome clones. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(6):419–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00241636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorney M. J., Sawada I., Gillespie G. A., Srivastava R., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Transcription analysis, physical mapping, and molecular characterization of a nonclassical human leukocyte antigen class I gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Koller B. H., Orr H. T. A human major histocompatibility complex class I gene that encodes a protein with a shortened cytoplasmic segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9145–9149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty D. E., Wei X. H., Orr H. T., Koller B. H. Human leukocyte antigen F (HLA-F). An expressed HLA gene composed of a class I coding sequence linked to a novel transcribed repetitive element. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):1–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Olson M. V. Systematic screening of yeast artificial-chromosome libraries by use of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Lai M. Z., Briner T. J., Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M., Smith J. A., Gefter M. L. Immunological self, nonself discrimination. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):865–870. doi: 10.1126/science.2433769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller C., Pohl F. M. Field inversion gel electrophoresis with different pulse time ramps. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6299–6304. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Geraghty D. E., DeMars R., Duvick L., Rich S. S., Orr H. T. Chromosomal organization of the human major histocompatibility complex class I gene family. J Exp Med. 1989 Feb 1;169(2):469–480. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Geraghty D. E., Shimizu Y., DeMars R., Orr H. T. HLA-E. A novel HLA class I gene expressed in resting T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):897–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu S. J., Day N. E., Degos L., Lepage V., Wang P. C., Chan S. H., Simons M., McKnight B., Easton D., Zeng Y. Linkage of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma susceptibility locus to the HLA region. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):470–471. doi: 10.1038/346470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell L. W., Summers K. M., Board P. G., Axelsen E., Webb S., Halliday J. W. Expression of hemochromatosis in homozygous subjects. Implications for early diagnosis and prevention. Gastroenterology. 1990 Jun;98(6):1625–1632. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)91100-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Bresnahan M., Strominger J. L. Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8955–8958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Winoto A., Minard K., Hood L. Clusters of genes encoding mouse transplantation antigens. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):489–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90203-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X. H., Orr H. T. Differential expression of HLA-E, HLA-F, and HLA-G transcripts in human tissue. Hum Immunol. 1990 Oct;29(2):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(90)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemmour J., Koller B. H., Ennis P. D., Geraghty D. E., Lawlor D. A., Orr H. T., Parham P. HLA-AR, an inactivated antigen-presenting locus related to HLA-A. Implications for the evolution of the MHC. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3619–3629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]