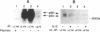Abstract
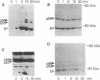
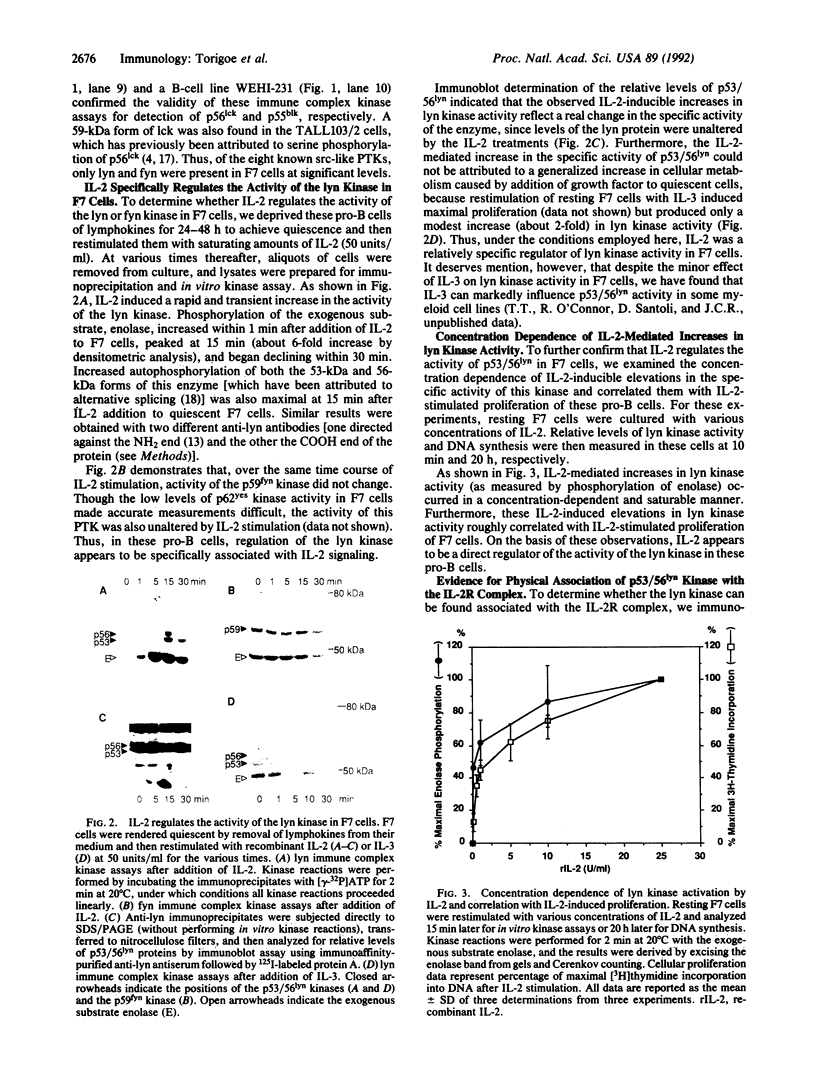
Recently, interleukin 2 (IL-2) has been shown to induce increased activity of the p56lck protein-tyrosine kinase (PTK) in T-cell and natural killer cell lines, and evidence for a direct interaction between the p75 subunit of the IL-2 receptor (IL-2R) and this src-family kinase has been reported. Though these findings suggest a central role for lck in IL-2 signal transduction, one problem with this idea is that not all IL-2-responsive cells express the lck gene. For this reason, we examined the effects of IL-2 on the activity of src-like kinases in a pro-B cell line, F7, that lacks p56lck but that displays high-affinity IL-2Rs and vigorously proliferates in response to this lymphokine. Of the eight known src-family PTKs, F7 cells were shown to contain only p53/56lyn, p59fyn, and a small amount of p62yes. Stimulation of resting F7 cells with IL-2 induced a rapid (detectable within 1 min and maximal at 15 min) and concentration-dependent increase in the specific activity of p53/56lyn kinase, as assessed by in vitro kinase assays. This effect of IL-2 on p53/56lyn kinase was specific, since no IL-2-inducible changes were detected in the activities of the p59fyn and p62yes kinases. Furthermore, by using a monoclonal antibody specific for the approximately 75-kDa beta subunit of the IL-2R (referred to as p75/IL-2R beta), evidence for physical association between the lyn kinase and the IL-2R complex was obtained, in that a small proportion of the p53/56lyn kinase in F7 cells, but no detectable p59fyn kinase, was coimmunoprecipitated with p75/IL-2R beta. When combined with the recent evidence that IL-2 regulates p56lck in T cells, these results indicate that some flexibility exists in the ability of various src-like PTKs to participate in IL-2 signal transduction mechanisms and raise the possibility that lineage-specific (T-versus B-cell) responses to IL-2 may be determined at least in part by the repertoire of src-like PTKs expressed in the cell.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman M. A., Tigges M. A., Minie M. E., Koshland M. E. A model system for peptide hormone action in differentiation: interleukin 2 induces a B lymphoma to transcribe the J chain gene. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):609–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Brunswick M., Bolen J. B., Mond J. J. Anti-immunoglobulin stimulation of B lymphocytes activates src-related protein-tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Thomas W. R., Schrader J. W. Characterization of hemopoietic growth factors from T cells and the myelomonocytic leukemia WEHI-3B. Exp Hematol. 1985 May;13(4):304–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Ultsch M., De Vos A. M., Mulkerrin M. G., Clauser K. R., Wells J. A. Dimerization of the extracellular domain of the human growth hormone receptor by a single hormone molecule. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):821–825. doi: 10.1126/science.1948064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einspahr K. J., Abraham R. T., Dick C. J., Leibson P. J. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation and p56lck modification in IL-2 or phorbol ester-activated human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1490–1497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiseman E., Bolen J. B. src-related tyrosine protein kinases as signaling components in hematopoietic cells. Cancer Cells. 1990 Oct;2(10):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Kobayashi N., Kawahara A., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M., Taniguchi T. Interaction of the IL-2 receptor with the src-family kinase p56lck: identification of novel intermolecular association. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1523–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.2047859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Mori H., Doi T., Taniguchi T. A restricted cytoplasmic region of IL-2 receptor beta chain is essential for growth signal transduction but not for ligand binding and internalization. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):837–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90607-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Tsudo M., Minamoto S., Kono T., Doi T., Miyata T., Miyasaka M., Taniguchi T. Interleukin-2 receptor beta chain gene: generation of three receptor forms by cloned human alpha and beta chain cDNA's. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):551–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2785715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced intermolecular autophosphorylation of the EGF receptors in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4035–4044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Gress R. E., Lucas P. J., Horak E. M., Waldmann T. A., Bolen J. B. T-lymphocyte interleukin 2-dependent tyrosine protein kinase signal transduction involves the activation of p56lck. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1996–2000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the activity and phosphorylation of the lck protein in lymphoid cells. Oncogene. 1989 Mar;4(3):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Cooper J. A., King C. S., Ziegler S. F., Tinker D. A., Overell R. W., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Neoplastic transformation induced by an activated lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (pp56lck). Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):540–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Altman A. Rapid activation of the T-cell tyrosine protein kinase pp56lck by the CD45 phosphotyrosine phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6302–6306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard H. L., Shackelford D. A., Hurley T. R., Johnson P., Hyman R., Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S. Expression of CD45 alters phosphorylation of the lck-encoded tyrosine protein kinase in murine lymphoma T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8959–8963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Meister L., Tanaka S., Cuddy M., Yum S., Geyer C., Pleasure D. Differential expression of bcl2 protooncogene in neuroblastoma and other human tumor cell lines of neural origin. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6529–6538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmage D. A., Riney C., Benjamin T. L. Regulation of pp60c-src expression in rat and mouse fibroblasts by an inducible antisense gene: effects on serum regulation of growth and polyoma virus middle T function. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Jan;2(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Colbert H., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Inhibition of PDGF beta receptor signal transduction by coexpression of a truncated receptor. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):844–848. doi: 10.1126/science.1851331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Horak I. D., Horak E. M., Bookman M. A., Bolen J. B. Alterations of the lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (p56lck) during T-cell activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4353–4361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Fukushige S., Semba K., Sukegawa J., Miyajima N., Matsubara K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. The yes-related cellular gene lyn encodes a possible tyrosine kinase similar to p56lck. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):237–243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Mori S., Yoshida M., Kishimoto T., Inoue K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Selective expression of a protein-tyrosine kinase, p56lyn, in hematopoietic cells and association with production of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6538–6542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Bolen J. B., Ihle J. N. Hematopoietic cells express two forms of lyn kinase differing by 21 amino acids in the amino terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2391–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Levin S. D., Perlmutter R. M. Transformation of NIH 3T3 fibroblasts by an activated form of p59hck. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2724–2727. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Marth J. D., Lewis D. B., Perlmutter R. M. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase gene (hck) preferentially expressed in cells of hematopoietic origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2276–2285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]