Abstract
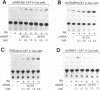
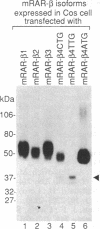
An isoform of retinoic acid receptor beta, RAR-beta 4, has been identified. RAR-beta 4 is expressed under the control of the same retinoic acid-responsive promoter as RAR-beta 2. RAR-beta 4, which is generated by alternative splicing from the same primary transcripts as RAR-beta 2, is initiated by a non-AUG codon, CUG. The amino acid sequence of RAR-beta 4 in regions B-F is identical to that of the other RAR-beta isoforms beta 1, beta 2, and beta 3. However, the RAR-beta 4 A region is much shorter (4 amino acids long) than those of these isoforms. RAR-beta 4 exhibits a tissue-specific pattern of expression and distinct transcriptional activation properties when compared with the other RAR-beta isoforms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acland P., Dixon M., Peters G., Dickson C. Subcellular fate of the int-2 oncoprotein is determined by choice of initiation codon. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):662–665. doi: 10.1038/343662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H. Transcription activation by estrogen and progesterone receptors. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:89–123. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Krust A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Zelent A., Leroy P., Staub A., Chambon P. Murine isoforms of retinoic acid receptor gamma with specific patterns of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Krust A., Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Kastner P., Dierich A., Chambon P. Multiple isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha are generated by alternative splicing and differential induction by retinoic acid. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):59–69. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C., Ruberte E., LeMeur M., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Developmental analysis of the retinoic acid-inducible RAR-beta 2 promoter in transgenic animals. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):723–734. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochette-Egly C., Lutz Y., Saunders M., Scheuer I., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Retinoic acid receptor gamma: specific immunodetection and phosphorylation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):535–545. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Dolle P., Chambon P., Morriss-Kay G. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):45–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Nakshatri H., Leroy P., Rees J., Chambon P. A retinoic acid response element is present in the mouse cellular retinol binding protein I (mCRBPI) promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2223–2230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Baltimore D. Id proteins Id1 and Id2 selectively inhibit DNA binding by one class of helix-loop-helix proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5603–5611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasset D., Tora L., Fromental C., Scheer E., Chambon P. Distinct classes of transcriptional activating domains function by different mechanisms. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1177–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90394-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., Gronemeyer H., Turcotte B., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The N-terminal region of the chicken progesterone receptor specifies target gene activation. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):185–188. doi: 10.1038/333185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., White J., Brou C., Tasset D., Webster N., Scheer E., Chambon P. The human estrogen receptor has two independent nonacidic transcriptional activation functions. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Kastner P., Krust A., Garnier J. M., Ruffenach F., Leroy P., Chambon P. Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor beta generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]