Abstract
Lettuce drop, caused by the soil borne pathogen Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, is one of the most common and serious diseases of lettuce worldwide. Increased concerns about the side effects of chemical pesticides have resulted in greater interest in developing biocontrol strategies against S. sclerotiorum. However, relatively little is known about the mechanisms of Streptomyces spp. as biological control agents against S. sclerotiorum on lettuce. Two Streptomyces isolates, S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I, inhibit mycelial growth of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by more than 75% in vitro. We evaluated their biocontrol activity against S. sclerotiorum in vivo, and compared them to Streptomyces lydicus WYEC 108, isolated from Actinovate®. When Streptomyces spp. (106 CFU/mL) were applied to S. sclerotiorum inoculated substrate in a growth chamber 1 week prior lettuce sowing, they significantly reduced the risk of lettuce drop disease, compared to the inoculated control. Interestingly, under field conditions, S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I protected lettuce from drop by 40 and 10% respectively, whereas S. lydicus WYEC 108 did not show any protection. We further labeled S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I with the enhanced GFP (EGFP) marker to investigate their rhizosphere competence and ability to colonize lettuce roots using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The abundant colonization of young lettuce seedlings by both strains demonstrated Streptomyces' capability to interact with the host from early stages of seed germination and root development. Moreover, the two strains were detected also on 2-week-old roots, indicating their potential of long-term interactions with lettuce. Additionally, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations showed EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W endophytic colonization of lettuce root cortex tissues. Finally, we determined its viability and persistence in the rhizosphere and endorhiza up to 3 weeks by quantifying its concentration in these compartments. Based on these results we conclude that S. exfoliatus FT05W has high potential to be exploited in agriculture for managing soil borne diseases barely controlled by available plant protection products.
Keywords: biocontrol, hazard ratio, lettuce, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Streptomyces, rhizosphere competence, endophytes
Introduction
The world population will continue to grow until at least 2050, and possibly increase from 7 to 11 billion people (Van Den Bergh and Rietveld, 2004). For this reason, food security has become one of the main challenges to human development, and therefore any plant pathogen causing substantial crop yield losses needs to be minimized. Drop, caused by Sclerotinia species, is globally one of the most destructive soil borne diseases of important horticultural crops. Three are the possible Sclerotinia species involved in lettuce drop, S. sclerotiorum, S. minor, and S. nivalis (Van Beneden et al., 2009). On lettuce, the pathogens can survive in the soil as sclerotia for years, or as mycelium on dead plants. Sclerotinia can infect the lettuce crown, roots, and leaves at any stage of plant development (Rabeendran et al., 2006). The hyphae arising from sclerotia penetrate lettuce directly through senescent leaves and root tissues, and can cause wilting and complete plant collapse in less than 2 days (Subbarao, 1998). In Lombardy, northern Italy, commercial lettuce cultivation is threatened by S. sclerotiorum infections (Bonaldi et al., 2014) and different strategies and methods are being used to prevent and manage lettuce drop epidemics. So far, fungicides have been extensively used, however, the adverse side effects of chemicals represent a serious threat to living organisms including human and the environment (Kohler and Triebskorn, 2013; Lamberth et al., 2013). In addition, for many plant pathogens, fungicide resistant populations have made many molecules ineffective. Therefore, there is an increasing demand for alternative and sustainable methods of disease management (Spadaro and Gullino, 2004; Ishii, 2006). An up-and-coming alternative to chemicals is the use of biological control agents (BCAs). Coniothyrium, Trichodema, Bacillus, and Pseudomonas spp. have been used for the management of numerous diseases (Walsh et al., 2001; Howell, 2003; Jacobsen et al., 2004). In comparison to these well-known BCAs, there is only limited application of Streptomyces in agriculture, contrary to its exploitation in pharmaceutical industry.
Streptomyces are Gram-positive bacteria ubiquitously found in soil, where they significantly contribute to the turnover of organic matter. They are the largest genus of Streptomycetaceae family (order Actinomycetales), comprising more than 500 species (Labeda et al., 2012). Very few species are pathogenic to human or plants. S. scabies and S. turgidiscabies cause scab disease on tuber and taproot crops, such as potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots or beet (Lehtonen et al., 2004; Loria et al., 2006). On the contrary, many species produce a variety of bioactive secondary metabolites and enzymes, which gives them potential in biocontrol and plant growth promotion. It has been hypothesized that high levels of antagonistic Streptomyces in naturally-occurring or induced suppressive soils significantly contribute to disease suppression (Kinkel et al., 2012). Similarly, organic soil amendments resulted in shift and increase of the density of indigenous Streptomyces populations and led to disease suppression (Cohen et al., 2005; Mazzola and Zhao, 2010). The current research, however, focused mainly on evaluating biocontrol activity of individual antagonistic Streptomyces spp.: S. globisporus JK-1 inhibited Pyricularia oryzae, reducing thus rice blast severity (Li et al., 2011); S. rochei ACTA1551 protected tomato seeds from F. oxysporum infection (Kanini et al., 2013); the metabolites of S. bikiniensis HD-087 effectively suppressed F. oxysporum and induced resistance in cucumber (Zhao et al., 2012); three endophytic Streptomyces isolates significantly promoted tomato plant growth by producing auxins and siderophores (Verma et al., 2011). Until now, only few commercial Streptomyces-based biocontrol products have been developed for the market, e.g., Mycostop® based on S. griseoviridis strain K61, or Actinovate® and Micro108® based on S. lydicus strain WYEC 108 (Palaniyandi et al., 2013). They showed moderate protection of different plants against various pathogens (Paulitz and Belanger, 2001; Zeng et al., 2012; Tian and Zheng, 2013). Although vast array of secondary metabolites have been assumed to act in the biocontrol and plant growth promoting activity of streptomycetes (Trejo-Estrada et al., 1998; Prapagdee et al., 2008; Schrey and Tarkka, 2008; Tarkka and Hampp, 2008), only in few cases the exact mechanism was elucidated, e.g., disruption of geldanamycin production in recombinant S. melanosporofaciens strain FP-60 resulted in the loss of its activity against S. scabies (Agbessi et al., 2003), or the involvement of siderophores in rice growth promotion by Streptomyces sp. GMKU 3100 (Rungin et al., 2012). Moreover, priming by streptomycetes to activate plant defense responses through induced and/or acquired systemic resistance pathways could be an additional mechanism of action involved in disease suppression (Conn et al., 2008; Lehr et al., 2008; Kurth et al., 2014; Salla et al., 2016).
Plant roots are colonized by vast amount of microbes, some of which contribute to biological control (Whipps, 2001; Hardoim et al., 2015). The complex community of microbes produces a variety of compounds and develops interactions, including the competition between BCAs and plant pathogens (Raaijmakers et al., 2009). The rhizosphere—a layer of the soil surrounding the root surface including rhizoplane—harbors an array of microorganisms, whose composition is influenced by root exudates (Hiltner, 1904; Lugtenberg and Kamilova, 2009). Rhizosphere competence is a prerequisite for a BCA to establish beneficial relationship with the host. In fact, some rhizobacteria successfully colonizing rhizosphere protected the host from soil borne fungal pathogens (Kloepper et al., 2004; Haas and Defago, 2005; Weller, 2007). Nowadays, several genetic markers are available for the identification and quantification of microorganisms in the rhizosphere as well as in the endorhiza—the plant inner root area. Among these, antibiotic resistance has been used as a marker to quantify the colonization dynamics of microbes in the plant root system (Gamalero et al., 2003; Adesina et al., 2009; Angelopoulou et al., 2014; Schreiter et al., 2014; Bonaldi et al., 2015). At the same time, fluorescent proteins, such as the green fluorescent protein (GFP), provide appropriate tool to monitor the colonization patterns of BCAs on plants. Enhanced GFP (EGFP), a modified version of GFP, has numerous silent nucleotide substitutions to maximize its expression in mammalian cells (Haas et al., 1996), and is also suitable for use in Streptomyces spp. because of a similar codon usage (Sun et al., 1999). GFP tagging was frequently used to determine colonization of host by beneficial Bacillus and Pseudomonas species (Krzyzanowska et al., 2012; Li et al., 2013; Subramanian et al., 2015). However, up to now, very few studies have addressed the plant colonization by EGFP-tagged Streptomyces spp. The strain EN 27 colonized the inner seed area of wheat at early stage of development (Coombs and Franco, 2003) and the pathogenic strain S. turgidiscabies Car8 colonized several-day-old radish seedlings (Joshi et al., 2007). For BCAs, the viability and persistence in rhizosphere and endorhiza are pre-requisites for their application against soil borne pathogens. In fact, certain biocontrol rhizobacteria showed stable and long-term colonization of the root surface, as well as endophytic colonization (Compant et al., 2005; Berg, 2009). Therefore, determining the rhizosphere competence and endophytic colonization of the host by tagged Streptomyces will unravel part of the mechanisms involved in Streptomyces-mediated biocontrol. Moreover, the evidence of disease suppression by beneficial microbes in vivo encourages their development into bio-products for large-scale applications. However, the inconsistency between the biocontrol performance of BCAs in laboratory and in field occurred frequently and is considered one of the restraining factors of the biocontrol products (Velivellil et al., 2014). In addition, the application timing and method, as well as the concentration of BCAs play crucial roles in their biocontrol efficacy in vivo (Bonaterra et al., 2003; Fravel, 2005; Fernando et al., 2007; Müller and Berg, 2008).
In our previous study, two Streptomyces strains, S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I, showed high in vitro inhibition of S. sclerotiorum (Bonaldi et al., 2015). The objective of this work was to evaluate their in vivo biological control activity against S. sclerotiorum on lettuce, assessing two different cell concentrations and two application timings in growth chamber, and subsequently their activity in field. Their performance in greenhouse and in field experiments was compared to S. lydicus WYEC 108, isolated from the commercial product Actinovate®. Simultaneously, we determined the colonization patterns of the EGFP-tagged Streptomyces on lettuce rhizoplane, using confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) and we performed scanning electron microscopy (SEM) observations to verify the endophytic colonization of lettuce roots by EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W, the most promising strain. Finally, we determined the colonization dynamics by quantifying its concentration in lettuce rhizosphere and endorhiza at different times after lettuce inoculation.
Materials and methods
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum inoculum preparation
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum strain FW598 from the Plant Pathology Laboratory fungi repository, Department of Food, Environmental and Nutritional Sciences (DeFENS), University of Milan, was grown for 3 days at 20°C on Malt Extract Agar (MEA) medium (30 g/L Malt Extract, Difco, 15 g/L agar, Applichem). Then, ten agar-mycelium discs (6 mm diameter) were taken from the edge of an actively growing colony and transferred into a 300 mL flask containing 25 g of sterilized wheat kernels and 50 mL distilled water (Budge and Whipps, 2001). The flask was incubated for 3 weeks at 20°C and was regularly shaken. Afterwards, the pathogen-colonized wheat kernels were blended with 100 mL of sterilized water to obtain the “S. sclerotiorum slurry”. One gram of S. sclerotiorum slurry was diluted in an adequate volume of water to facilitate the distribution and added to 100 g of non-sterile Irish and Baltic peat-based growing substrate (Vigorplant, Piacenza, Italy). The inoculum density of S. sclerotiorum was estimated by plating serial dilutions on MEA medium. The plates were incubated at 20°C for 2 days, the number of colonies was counted and the inoculum density was calculated as CFU/g of slurry.
Streptomyces biological control of lettuce drop in growth chamber experiment
Biological activity of the two Streptomyces strains, S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I against S. sclerotiorum was first investigated in vivo in a growth chamber (24°C, 55% relative humidity and 15 h photoperiod) using plastic pots (Sterivent, Duchefa, Italy), 10 × 10 × 10 cm, filled with 200 g of inoculated growing substrate as mentioned above. S. sclerotiorum inoculum was ca. 3 × 104 CFU/g of slurry. One mL of each Streptomyces strain spore suspensions (104 CFU/mL or 106 CFU/mL) was sprayed on the growing substrate immediately after the pathogen inoculation. Lettuce seeds, Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci”, (Semeurop, Italy) were sterilized in 2 mL of 0.7% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) for 5 min and were rinsed three times with sterilized water. Thirty seeds were sown in three rows in each pot at two different times. In the experiment A, lettuce was sown on the same day of substrate inoculation with Streptomyces strains and the pathogen. In the experiment B, lettuce was sown 7 days after the inoculation of Streptomyces strains and pathogen inoculation. Streptomyces lydicus WYEC 108, isolated from commercial product Actinovate® (Natural Industries, Inc. Houston), was used as the reference strain. The pot inoculated only with S. sclerotiorum was used as the inoculated control. The pot inoculated neither with S. sclerotiorum nor Streptomyces was used as the non-inoculated control. For experiments A and B, eight trials were prepared in three replicates: (1) non-inoculated control; (2) S. sclerotiorum inoculated control; (3) S. exfoliatus FT05W-104 CFU/mL; (4) S. exfoliatus FT05W-106 CFU/mL; (5) S. cyaneus ZEA17I-104 CFU/mL; (6) S. cyaneus ZEA17I-106 CFU/mL; (7) S. lydicus WYEC 108-104 CFU/mL; (8) S. lydicus WYEC 108-106 CFU/mL. Dead plants were counted from the emergence up to 18 days for the experiment A, and up to 25 days for the experiment B. Disease incidence was calculated as the percent of dead plants over the plants germinated in the non-inoculated control.
Streptomyces biological control of lettuce drop in field experiment
Field experiment was carried out in Travacò Siccomario (Pavia, Italy), characterized by loamy soil. Lettuce, Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” was grown in polystyrene seed trays (84 cells—48 cm3 each), filled with the non-sterile Irish and Baltic peat-based growing substrate described above. One seed was sown in each cell added with 0.5 mL of Streptomyces spore suspension (104 CFU/mL) uniformly distributed on the growing substrate. Each tray was first covered with a thin layer of the growing substrate and then with coarse perlite. Two weeks later, the same amount of Streptomyces spore suspension was added to each cell. Three weeks after sowing, each cell was inoculated with 1 mL of S. sclerotiorum slurry (ca. 3 × 104 CFU/g of slurry) prepared as described above. One day after the pathogen inoculation, the lettuce plants were transplanted into the field under plastic tunnel (width 1.2 m), at a density of 5.5 plants/m2. Five trials were prepared following a completely randomized block design in four replicates: (1) non-inoculated control; (2) S. sclerotiorum inoculated control; (3) S. exfoliatus FT05W; (4) S. cyaneus ZEA17I; (5) S. lydicus WYEC 108. Each trial consisted of 20 plants. Dead plants were counted at 3-week intervals, from the day the disease symptoms appeared until the end of the experiment. Disease incidence was calculated as the percent of dead plants over the number of transplanted plants.
CLSM observations of lettuce root colonization by EGFP-Streptomyces strains
A Leica TCS SPE Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (Leica Microsystems, Mannheim, Germany) equipped with solid state lasers for excitation was used to unravel lettuce root colonization patterns by the two Streptomyces strains, EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W and EGFP- S. cyaneus ZEA17I. Plant colonization assays were carried out at the Institute of Environmental Biotechnology, Graz University of Technology, Austria. The lettuce seeds were sterilized and bacterized with EGFP-tagged Streptomyces as previously described (Bonaldi et al., 2015). Subsequently, nine bacterized seeds were sown in three rows in a seed tray filled with 640 g of a mixture of autoclaved quartz sand (Scherf GmbH & Co. KG, Austria) and peat soil (“Gramoflor Profi-Substrat-Topfpikier M+Ton+Fe” GBC, Kalsdorf, Austria) in 1:3 ratio (w/w), and 200 mL of sterilized tap water were added. In two trays, no seeds were planted to monitor the soil moisture (≥25%) by a moisture analyzer (MB35 Halogen, Ohaus, USA). Nine surface sterilized non-bacterized seeds were sown in seed trays prepared in the same way and were used as non-inoculated control. After sowing, the seed trays were incubated in a growth chamber (24°C, 55% relative humidity and 14 h photoperiod). Two- and three-day-old seedlings and 2-week-old plants were used to verify the ability of EGFP-Streptomyces to colonize lettuce. At each interval, the roots of three bacterized plants, taken from a different seed tray, and one non-bacterized plant (negative control) were cleaned in sterile water and cut into 0.5 cm long sections for CLSM observation. Filter settings were adjusted to achieve the maximum signal from EGFP and low background autofluorescence of the plant tissues. The EGFP was excited with a 488 nm laser beam and the detection window was optimized for every field of view, in order to gain a better discrimination between the signal and the noise. Plant tissues were excited with a 635 nm laser beam and the autofluorescence emitted in the range 650–690 nm was recorded. The fluorescence signals from EGFP and from plant tissues were acquired sequentially. For each field of view, maximum projections of an appropriate number optical slices were acquired with a Z-step of 0.15–0.5 μm (“confocal stacks”) and the software Imaris 7.3 (Bitplane, Zurich, Switzerland) was used for post-processing (Erlacher et al., 2015).
SEM observations of Streptomyces endophytic colonization
To further verify the endophytic Streptomyces colonization of lettuce roots, we carried out SEM observations (Leo Electron Microscopy, Cambridge, UK) at DeFENS, University of Milan, Italy, using the representative strain EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W, whose wild-type strain showed promising biocontrol potential. Inoculated and non-inoculated control lettuce seeds were grown in sterile conditions as described for CLSM observations with minor modification. Each seed was sown individually in a closed 200 mL box containing 80 g of a mixture of autoclaved sandy substrate (“Sabbia Vagliata” Gras Calce s.p.a., Italy) and peat soil (Vigorplant, Piacenza, Italy) in 1:3 ratio (w/w), and 20 mL sterilized tap water. Root samples from 1-, 2- and 3-week-old plants were harvested from two inoculated plants and one control plant. Root fragments, 1 cm long, were cut: in the proximity of soil surface, in the middle, and at the root apex. The fragments were rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen, broken into pieces with the aid of two forceps (cryo-fractured) in order to expose the internal tissues, and prepared for SEM observations (Sardi et al., 1992; Rocchi et al., 2010). In total, 22 samples from 6 inoculated plants and 11 samples from three control plants were observed.
Colonization dynamics in lettuce rhizosphere and endorhiza
To understand the competence of EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W to colonize lettuce rhizosphere and endorhiza, we exploited the introduced apramycin resistance marker to quantify the amount (as colony forming units, CFU) in sterile conditions as described by Bonaldi et al. (2015) for non-sterile conditions. Briefly: lettuce plants, obtained as described above for SEM observations, were collected at 1, 2, and 3 weeks after sowing. Seedlings with the whole root system were carefully extracted from the growth substrate and the bulk soil was removed by gently shaking the plants. Excised roots were immersed in 50 mL Falcon tubes containing 8–18 mL (volume varying according to plant age) of sterilized washing solution containing 0.9% NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, United States) and 0.02% Silwet L-77 (Chemtura Manufacturing, Italy) and vortexed two-times for 15 s. The roots were removed and kept for inner root tissue analysis. The rhizosphere suspension was filtered through a 100 μm nylon mesh placed on the top of a Falcon tube, and centrifuged for 60 s to remove any remaining washing solution from the nylon mesh. The rhizosphere soil retained on the nylon mesh was collected and its dry weight was determined. The suspension was centrifuged at 10,600 g for 10 min and the pellet was resuspended in 2.5 mL of washing solution and plated in serial dilutions on Water Agar (WA) medium (15 g/L agar) added with 50 mg/L apramycin, 50 mg/L cycloheximide, and 50 mg/L nystatin. The plates were incubated at 24°C for 7 days. Streptomyces colonies were counted and the concentration was expressed as CFU/g of rhizosphere dry weight. For inner root tissues analysis, the roots were surface sterilized with propylene oxide for 1 h. Afterwards, they were washed in 2–3 mL of washing solution, depending on plant age, and 0.5 mL of the total volume of washing solution was plated on WA medium to verify the absence of contaminants. Subsequently, the roots were finely homogenized in the washing solution, left to macerate for 1 h and plated in serial dilutions on WA medium. The Streptomyces concentration was determined as described above and expressed as CFU/g of roots dry weight.
Statistical analyses
All analyses were done using R software, version R3.0.2. (R_Core_Team, 2013). The data of the in vivo biological control experiments, concerning the activity of Streptomyces strains against S. sclerotiorum, were submitted to survival analysis by the survival package (Therneau, 2014). First, the time-to-death of lettuce plants untreated and treated with the streptomycetes was computed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Then, the estimated survivor curve of each Streptomyces-inoculated group was compared to the inoculated control via log-rank test (P = 0.05). Finally, the effect of each strain was quantified using the Cox proportional hazard model (Kleinbaum and Klein, 2012). This model computes the hazard h at time t, as follows: where Xi are the explanatory variables and ßi are the coefficients for each variable included in the model. The effect of each treatment was quantified as Hazard Ratio (HR) expressed as where X* is the covariate for one group, generally the one with the larger hazard, and X for the group with the smaller hazard. The HR values equal to 1 were interpreted as no effect of Streptomyces-treated trial over Streptomyces non-treated control, HR > 1 means that the Streptomyces non-treated plants have a higher risk of lettuce drop and HR < 1 the opposite. The rhizosphere and endorhiza colonization dynamics data were submitted to ANOVA, followed by a Tukey post hoc test for multiple comparison (P = 0.05), using the TukeyC package (Faria et al., 2013).
Results
Streptomyces biological control of lettuce drop in growth chamber experiment
The germination rate of lettuce, calculated from the non-inoculated control, was 86.7%. When lettuce was sown the same day of the pathogen and Streptomyces inoculation (experiment A), the number of dead plants was recorded from the 4th day after sowing to the 18th day after sowing (Supplementary Table 1). The disease incidence of S. sclerotiorum inoculated control at the end of the experiment was 85% and none of the Streptomyces strains showed significant protection against lettuce drop according to both log-rank test and Cox model analysis (Table 1).
Table 1.
Biological control of Streptomyces strains against lettuce drop, when Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” was sown the same day of S. sclerotiorum and Streptomyces co-inoculation.
| Trial | Disease Incidence (%) | Protection (%) | Log-rank test | Cox model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | βc | HRd | Pe | |||
| S. sclerotiorum inoculated control | 84.6 | /a | / | / | / | / |
| S. exfoliatus FT05W (104 CFU/mL) | 92.3 | −9.09 | 0.0952 | −0.273 | 0.761 (0.544–1.065) | 0.111 |
| S. exfoliatus FT05W (106 CFU/mL) | 79.5 | 6.06 | 0.847 | 0.0171 | 1.017 (0.721–1.436) | 0.923 |
| S. cyaneus ZEA17I (104 CFU/mL) | 75.6 | 10.6 | 0.336 | 0.142 | 1.152 (0.812–1.635) | 0.428 |
| S. cyaneus ZEA17I (106 CFU/mL) | 83.3 | 1.52 | 0.864 | 0.0226 | 1.023 (0.727–1.439) | 0.896 |
| S. lydicus WYEC 108 (104 CFU/mL) | 76.9 | 9.09 | 0.399 | −0.183 | 0.833 (0.594–1.168) | 0.290 |
| S. lydicus WYEC 108 (106 CFU/mL) | 88.5 | −4.55 | 0.213 | −0.233 | 0.792 (0.565–1.111) | 0.177 |
No value.
P-value of the log-rank test.
β is the coefficient for the treatment covariate in the Cox model.
Hazard Ratio (95% confidence interval).
P-value of the Cox model.
When lettuce was sown 7 days after the pathogen and Streptomyces inoculation (experiment B), the dead plants were recorded from the 4th day after sowing to the 25th day after sowing (Supplementary Table 2). Disease incidence of the S. sclerotiorum inoculated control was 74.4% at the end of the experiment. The Streptomyces strains showed 25.7–51.7% protection of lettuce against S. sclerotiorum, which was statistically significant based on survival curves analyzed by log-rank test, except for S. lydicus WYEC 108 applied at the lower dose (104 CFU/mL; P = 0.175). According to Cox regression model, S. exfoliatus FT05W, at both spore concentrations, significantly reduced the risk of lettuce drop disease, compared to the S. sclerotiorum inoculated control (HR = 2.078 and HR = 2.172, respectively). S. cyaneus ZEA17I was less effective than S. exfoliatus FT05W at both spore concentrations (HR = 1.595 and HR = 1.784, respectively). S. lydicus WYEC 108 applied at 106 CFU/mL reduced the most the risk of lettuce drop (HR = 2.462), whereas when applied at 104 CFU/mL, it was ineffective, which was in accordance with log-rank test analysis (HR = 1.261, P = 0.24, Table 2).
Table 2.
Biological control of Streptomyces strains against lettuce drop, when Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” was sown one week after S. sclerotiorum and Streptomyces co-inoculation.
| Trial | Disease Incidence (%) | Protection (%) | Log-rank test | Cox model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | βc | HRd | Pe | |||
| S. sclerotiorum inoculated control | 74.4 | /a | / | / | / | / |
| S. exfoliatus FT05W (104 CFU/mL) | 41.0 | 44.8 | 0.000942 | 0.731 | 2.078 (1.366–3.161) | 0.000634 |
| S. exfoliatus FT05W (106 CFU/mL) | 42.3 | 43.1 | 0.000337 | 0.776 | 2.172 (1.427–3.307) | 0.000296 |
| S. cyaneus ZEA17I (104 CFU/mL) | 53.9 | 27.6 | 0.0242 | 0.467 | 1.595 (1.072–2.372) | 0.0212 |
| S. cyaneus ZEA17I (106 CFU/mL) | 53.9 | 27.6 | 0.00523 | 0.579 | 1.784 (1.200–2.653) | 0.00422 |
| S. lydicus WYEC 108 (104 CFU/mL) | 55.1 | 25.7 | 0.175 | 0.232 | 1.261 (0.856–1.857) | 0.24 |
| S. lydicus WYEC 108 (106 CFU/mL) | 35.9 | 51.7 | 5.08E-05 | 0.901 | 2.462 (1.589–3.812) | 5.43E-05 |
No value.
P-value of the log-rank test.
β is the coefficient for the treatment covariate in the Cox model.
Hazard Ratio (95% confidence interval).
P-value of the Cox model.
Streptomyces biological control of lettuce drop in field experiment
Under field conditions, the number of dead plants was recorded from the 10th to the 142nd day after transplanting (Supplementary Table 3). At the end of the experiment, drop incidence of the S. sclerotiorum inoculated control was 50.0% and treatments with S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I showed respectively 40.0% and 10.0% protection against lettuce drop (Supplementary Figure 1). Survival curves of lettuce treated with S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I were not significantly different from the S. sclerotiorum inoculated control according to the log-rank test (Table 3). However, the HR used to estimate the effect of S. exfoliatus FT05W was 2.178, therefore the model estimated a risk of lettuce drop about two-times lower than that of the S. sclerotiorum inoculated control (P = 0.120). The survival curve of lettuce treated with S. lydicus WYEC 108 was significantly different from the S. sclerotiorum inoculated control (P = 0.0305), but with a negative protection of 30%. The HR of S. lydicus WYEC 108 was 0.448, confirming that plants inoculated only with S. sclerotiorum had significantly lower risk of drop compared to those treated with the S. lydicus WYEC 108 (P = 0.0309, Table 3).
Table 3.
Biological control of Streptomyces strains against lettuce drop of Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” under field conditions, Travacò Siccomario (Pavia, Italy).
| Trial | Disease incidence (%) | Protection (%) | Log-rank test | Cox model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | βc | HRd | Pe | |||
| S. sclerotiorum inoculated control | 50.0 | /a | / | / | / | / |
| S. exfoliatus FT05W | 30.0 | 40.0 | 0.802 | 0.779 | 2.178 (1.366–3.161) | 0.120 |
| S. cyaneus ZEA17I | 45.0 | 10.0 | 0.939 | 0.0626 | 1.065 (1.427–3.307) | 0.884 |
| S. lydicus WYEC 108 | 65.0 | −30.0 | 0.0305 | −0.804 | 0.448 (1.072–2.372) | 0.0309 |
No value.
P-value of the log-rank test.
β is the coefficient for the treatment covariate in the Cox model.
Hazard Ratio (95% confidence interval).
P-value of the Cox model.
CLSM observations of lettuce root colonization by EGFP-Streptomyces strains
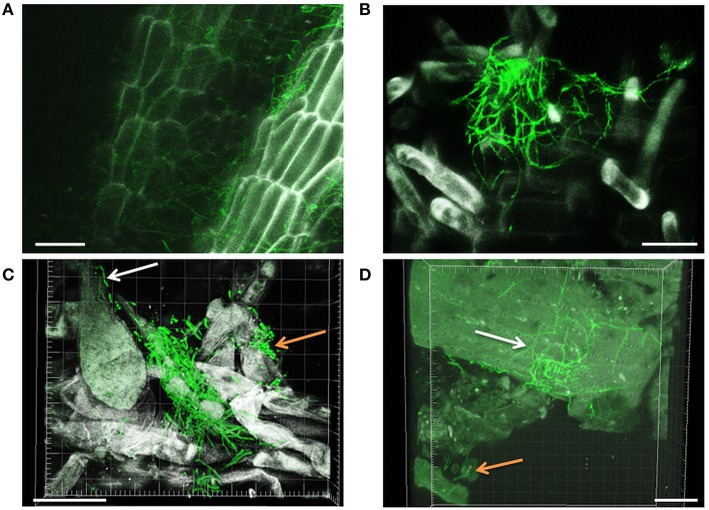
Filamentous growth of EGFP-Streptomyces was frequently observed on the surface of 2- and 3-day-old lettuce roots (Figure 1) and the mycelium of EGFP-S. cyaneus ZEA17I colonized abundantly the lettuce rhizoplane (Figure 1A). The colonization by EGFP- S. cyaneus ZEA17I was observed mostly in the zone of cellular maturation of the main and lateral roots, and particularly on or in the proximity of root hairs (Figure 1B). Moreover, germinated spores grouped together in an area close to the root hair zone (Figure 1C). Interestingly, a piece of soil substrate that remained attached to the lettuce root tissue showed that EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W colonized more extensively the lettuce root surface than the soil particle (Figure 1D). We also observed EGFP-Streptomyces colonization on 2-week-old lettuce roots. In general, Streptomyces at different stages of their life cycle appeared concurrently at some sites of lettuce roots. Spores, single hyphae, spore chains, and mycelium of EGFP- S. cyaneus ZEA17I were observed on the root surface (Figure 2). We only rarely detected colonization on the root cap and elongation zone of the roots.
Figure 1.
CLSM observations of lettuce radicle colonization by EGFP-Streptomyces, two and three days after lettuce sowing. Filamentous growth of EGFP- S. cyaneus ZEA17I at rhizoplane (A), root hair zone (B), and area close to the root hair zone (C). The white arrow points to a single hypha, the orange arrow points to a group of germinating spores, (D) EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W colonizing lettuce root tissue with a soil particle attached (orange arrow). The white arrow points to the mycelium on the root surface, which is more abundant than that on the soil particle. Scale bar equals to 30 μm, for Figures (A–D).
Figure 2.
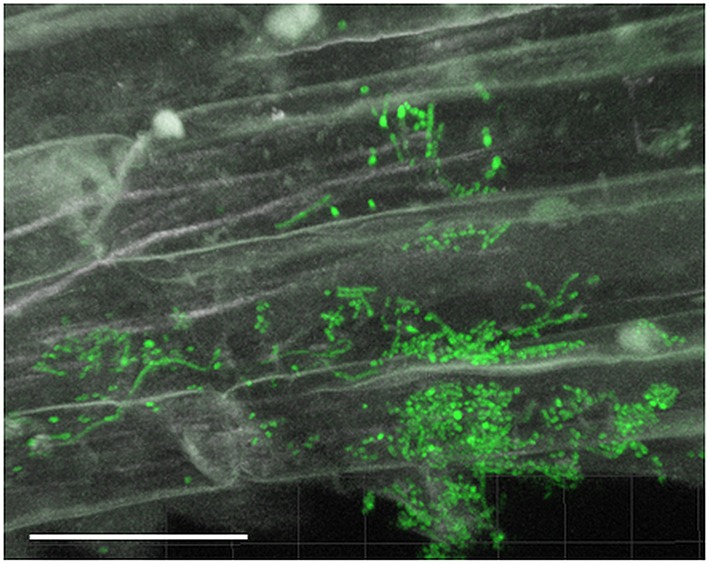
CLSM observations of lettuce root colonization by EGFP-Streptomyces two weeks after lettuce sowing. Root surface colonization by EGFP-S. cyaneus ZEA17I. Scale bar equals to 30 μm.
SEM observations of lettuce root endophytic colonization by Streptomyces strains
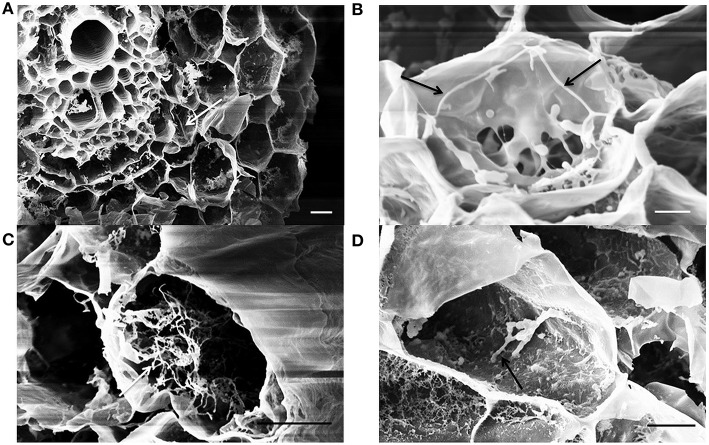
Following sample cryo-fracturation, 88 sections were obtained and observed. Mycelium of EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W was frequently observed on the root surface of inoculated plants (micrograph not shown). Endophytic colonization of lettuce roots by EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W was observed in 99% of root sections from all samples from 1- to 3-week-old roots. Generally, several cells were colonized in each section (Figure 3). Along the entire length of the root, both close to the collar and near the apex, single hyphae were frequently detected inside cortical cells in 1-week-old (Figure 3A), and 2-week-old roots (Figure 3B), but not inside the vascular cylinder. In a few cases, mainly in 3-week-old roots, the hyphae grew abundantly inside cortical cells forming a tangled structure (Figure 3C). Hyphae growing inside cortical cells had a diameter of about 0.2 μm, half the size the ones grown on the root surface or in vitro cultures. EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W mainly colonized the endorhiza of lettuce as vegetative hyphae and rarely short spore chains were found (Figure 3D).
Figure 3.
SEM observations of lettuce root colonization by EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W, one to three weeks after lettuce sowing. Arrows indicate the hyphae inside one-week-old roots (A), two-week-old roots (B), 3-week-old roots (C), a spore chain in the 3-week-old roots (D). Scale bar equals to 10 μm (A,C,D) and 3 μm (B).
Streptomyces colonization dynamics in lettuce rhizosphere and endorhiza
EGFP- S. exfoliatus FT05W showed stable concentration up to three weeks, both in lettuce rhizosphere and endorhiza, ranging from 1.72 × 106 to 5.49 × 106 CFU/g rhizosphere dry weight and from 1.10 × 105 to 7.36 × 106 CFU/g root dry weight, respectively (Table 4). There were no statistically significant differences in its concentration based on plant age both in rhizosphere and in endorhiza.
Table 4.
Colonization dynamics of EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W in Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” rhizosphere and endorhiza.
| EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W (CFU/g dry weight) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 week | 2 weeks | 3 weeks | |
| Rhizosphere | 1.72 × 106nsa | 2.45 × 106ns | 5.49 × 106ns |
| Endorhiza | 4.31 × 105ns | 7.36 × 106ns | 1.10 × 105ns |
ANOVA analysis, means in a row were not significantly different (P = 0.05).
Discussion
Biological control strategies are gaining popularity in agriculture as a way to address some of the concerns about food security. Studies exploring novel biocontrol microorganisms and investigating their mechanisms of action have consistently increased. However, we are still facing significant fluctuations in the efficiency of biocontrol microorganisms, which represent a critical limitation to a more general and broader use in agriculture as plant protection products. The variable performance of BCAs could be due to the limited knowledge about their mode of action and about their ability to survive and establish stable relation with plant host (Compant et al., 2005; Cuppels et al., 2013). Even when they successfully establish symbiosis with the host, e.g., in the rhizosphere, another challenge is whether the beneficial microbes can compete and suppress the pathogens. Nowadays, tremendous efforts are increasingly done to investigate the colonization patterns of BCAs on plants and their biocontrol against pathogens in vivo (Chen et al., 2013; Xue et al., 2013; Maldonado-Gonzalez et al., 2015a,b; Santiago et al., 2015).
In this work we have studied in vivo biocontrol activity of two promising Streptomyces strains against S. sclerotiorum as a follow up of a previous study, in which we obtained excellent in vitro activity against this pathogen (Bonaldi et al., 2015). S. lydicus WYEC 108, reisolated from the commercial product Actinovate®, recommended for the management of several soil borne fungal pathogens including S. sclerotiorum (Yuan and Crawford, 1995; Leisso et al., 2009; Zeng et al., 2012), was incorporated to our growth chamber and field experiments as the reference strain. In growth chamber experiments, we tested two different timings of Streptomyces application and two different spore concentrations. Both microorganisms, the pathogen and the Streptomyces strains, were inoculated at the same time of lettuce sowing, or 7 days before the lettuce sowing. The obtained results clearly showed that the timing of Streptomyces application has a significant impact on their biocontrol activity. In particular, both S. exfoliatus FT05W and S. cyaneus ZEA17I significantly reduced S. sclerotiorum lettuce drop when they were applied 7 days before the plant sowing. In contrast, when application of S. sclerotiorum and Streptomyces was postponed until sowing, neither strain was able to reduce disease incidence and improve lettuce survival. The importance of application timing on biocontrol activity of BCAs against apple diseases was also reported for blue mold, bitter rot, and apple scab, as well as for brown rot of cherries and plums (Teixido et al., 1999; Poleatewich et al., 2012; Rungjindamai et al., 2014). For Streptomyces, the production of biocontrol related secondary metabolites is induced or increased when the aerial hyphae appear and sporulation starts (Hopwood, 1988; Chater, 1996; Pope et al., 1996). Therefore, we hypothesize that Streptomyces need time after application to perform biocontrol activity. We also observed that the efficacy of some strains was positively correlated to the application rate, as for the reference strain S. lydicus WYEC 108, whose protection reached 51.7% when applied at 106 CFU/mL. In the field experiment, the three Streptomyces strains showed different biological control activity against S. sclerotiorum and the results were not always consistent with those observed in the greenhouse. S. exfoliatus FT05W was able to reduce drop incidence by 40%, which can be considered a promising biocontrol performance compared to other studies. For instance, application of S. padanus SS-07 resulted in 17% reduction of Rhizoctonia damping-off on Chinese cabbage, while four Streptomyces spp. strains showed 2 to 9.8% reduction of Verticillium wilt on eggplant (Chung et al., 2005; Bubici et al., 2013). On the contrary, S. lydicus WYEC 108 had a surprisingly negative effect on lettuce drop incidence in the field, opposite to the 51.7% protection obtained in the growth chamber experiment. One possible explanation could be that in the rhizosphere, the microbes respond to the many metabolites released by plant roots, as well as to the natural microflora producing a variety of compounds (Morgan et al., 2005). Such complex interactions, especially under field conditions, may result in positive, neutral, and negative effects on plant growth, health, and survival (Bouwmeester et al., 2007; Berg, 2009). Negative effect of S. lydicus WYEC 108 was previously reported for tomato bacterial spot as well as for tomato early blight in Canada (Cuppels et al., 2013). However, in the same study, a combined application of S. lydicus WYEC108 and P. fluorescens A506 resulted in a good protection against the two diseases. Similarly, S. lydicus WYEC 108 applied to control Fusarium wilt of watermelon resulted in increased disease severity in American soils, whereas the combination of green manure and S. lydicus WYEC 108 mitigated the negative effect. S. lydicus inefficacy was probably due to its lack of survival on watermelon roots in those specific conditions (Himmelstein et al., 2014). Another hypothesis might be that under certain environmental conditions S. lydicus WYEC 108 produces fungal growth promoting secondary metabolites, which enhance the pathogen growth and promote the infection of the host plant. Fungal growth promotion was shown for Streptomyces sp. strain AcH 505 producing auxofuran, a molecule which improved mycelial growth of the ectomycorrhizal fungus, Amanita muscaria, and its interaction with spruce (Schrey et al., 2005; Riedlinger et al., 2006).
The beneficial plant-microbe interactions occurring at specific sites usually require the microbe competence for host colonization (Berg et al., 2015; Hardoim et al., 2015). It has been hypothesized that the Streptomyces-mediated disease suppression is linked to the production of active secondary metabolites and their ability to colonize plant roots (Tokala et al., 2002; Franco et al., 2007). In this study, we investigated Streptomyces lettuce colonization as one of the characters underlying Streptomyces-mediated biocontrol. The use of fluorescent proteins to study plant colonization by BCAs such as Bacillus and Pseudomonas spp. has been widely reported (Buddrus-Schiemann et al., 2010; De-Bashan et al., 2010; Krzyzanowska et al., 2012; Sun et al., 2014). However, very few studies investigated Streptomyces colonization patterns on plants using fluorescent proteins in combination with CLSM. Coombs and Franco (2003) demonstrated that the EGFP-tagged endophytic Streptomyces sp. strain EN27 rapidly colonized the wheat embryo, as it was detected in developing seeds as early as 24 h after inoculation, but long-term rhizosphere competence and root colonization were not investigated. Similarly, Joshi et al. (2007) labeled a pathogenic strain of S. turgidiscabies with EGFP, and it was detected mainly on the surface of several-day-old radish seedlings, without any further monitoring. In our study, both EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W and EGFP-S. cyaneus ZEA17I were able to rapidly colonize the lettuce root system, and establish interactions with the host from early stages of seed germination and root development. Although it is not known if the localization of Streptomyces regulates their activity for biological control of pathogens, it has been hypothesized that endophytic bacteria form more stable interactions with plants than rhizospheric or epiphytic bacteria (Ryan et al., 2008; Compant et al., 2010; Malfanova et al., 2011). Using CLSM, we were able to detect EGFP-Streptomyces extensively colonizing the rhizoplane, and the SEM analyses confirmed the presence of EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W on the root surface and revealed the endophytic colonization in the root cortex. To our knowledge, this is the first study, which describes the observation of lettuce epiphytic and endophytic colonization by EGFP-tagged Streptomyces up to three weeks. In addition, we consistently recovered high concentration of EGFP-S. exfoliatus FT05W (105-106 CFU/g dry weight) from both, lettuce rhizosphere and endorhiza, up to three weeks after seed inoculation. This evidence allows us to conclude that S. exfoliatus FT05W is both rhizospheric and endophytic in lettuce roots.
The ability of microorganisms to colonize plant roots enables them to establish long-term beneficial interactions including biocontrol against plant pathogens (Adesina et al., 2009; Schreiter et al., 2014). The ability of S. exfoliatus FT05W to produce chitinases, to solubilize phosphates and to synthesize IAA (Bonaldi et al., 2015) coupled with its stable rhizosphere competence and endophytic colonization of lettuce roots determined in this study, could explain its biocontrol activity against S. sclerotiorum. When S. exfoliatus FT05W was applied 1 week before plant sowing, it showed significant protection against lettuce drop in growth chamber, data that have been confirmed in field. Studying the colonization patterns of Streptomyces on lettuce in the presence of the pathogen will give us insight into whether and how Streptomyces spp. compete with plant pathogens, leading to better understanding of Streptomyces-mediated biocontrol. In addition, studies evaluating S. exfoliatus FT05W activity against other soil borne fungal pathogens (e.g., Fusarium, Pythium, Rhizoctonia, or Verticillium spp.) and its ability to establish stable interactions with other hosts are needed to make it more attractive for its development into a commercial biocontrol product.
Author contributions
XC performed the CLSM observations, promoted the SEM and colonization dynamics studies, and drafted the manuscript. CP evaluated the colonization dynamics data and conducted the statistical analyses. MB performed the biocontrol experiments in greenhouse and in field. MS performed SEM sample preparation, observations and acquired SEM pictures. AE contributed to the CLSM observations and post-processed the CLSM photos. AK participated to the discussions of each section of experiments, and improved the manuscript. GB hosted and supported XC in her lab to perform the CLSM observations with assistance of AE. PC designed the outline of the study and partly supported the research. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Flavia Marinelli (University of Insubria, Italy), for providing the donor strain E. coli ET12567 and the reference strain S. coelicolor A3(2) and Prof. Mervyn Bibb (John Innes Centre, UK), for kindly providing the plasmid pIJ8641. The authors also thank Dr. Tomislav Cernava and Mr. Tobija Glawogger, from Graz University of Technology, Austria, for their technical assistance during the acquisition of CLSM photos, and their helpful advice and discussion regarding the experiments done in Graz. This research was supported in part by research program “Dote ricerca applicata” funded by Lombardy Region and Sipcam Italia Spa.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00714
Survival of lettuce plants (Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci”) in the field experiment (ca. 60 days after transplanting) inoculated with (A) Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (inoculated control); (B) S. sclerotiorum + S. exfoliatus FT05W; (C) S. sclerotiorum + S. cyaneus ZEA17I; and (D) S. sclerotiorum + S. lydicus WYEC 108.
Number of lettuce dead plants recorded for the experiment A, when Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” was sown the same day of S. sclerotiorum and Streptomyces co-inoculation.
Number of lettuce dead plants recorded for the experiment B, when Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” was sown one week after S. sclerotiorum and Streptomyces co-inoculation.
Number of Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” dead plants recorded for field experiment, Travacò Siccomario (Pavia, Italy).
References
- Adesina M. F., Grosch R., Lembke A., Vatchev T. D., Smalla K. (2009). In vitro antagonists of Rhizoctonia solani tested on lettuce: rhizosphere competence, biocontrol efficiency and rhizosphere microbial community response. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 69, 62–74. 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00685.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agbessi S., Beauséjour J., Déry C., Beaulieu C. (2003). Antagonistic properties of two recombinant strains of Streptomyces melanosporofaciens obtained by intraspecific protoplast fusion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 62, 233–238. 10.1007/s00253-003-1256-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulou D. J., Naska E. J., Paplomatas E. J., Tjamos S. E. (2014). Biological control agents (BCAs) of verticillium wilt: influence of application rates and delivery method on plant protection, triggering of host defence mechanisms and rhizosphere populations of BCAs. Plant Pathol. 63, 1062–1069. 10.1111/ppa.12198 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Berg G., Rybakova D., Grube M., Koberl M. (2015). The plant microbiome explored: implications for experimental botany. J. Exp. Bot. 67, 995–1002. 10.1093/jxb/erv466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg G. (2009). Plant-microbe interactions promoting plant growth and health: perspectives for controlled use of microorganisms in agriculture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 84, 11–18. 10.1007/s00253-009-2092-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldi M., Kunova A., Saracchi M., Sardi P., Cortesi P. (2014). Streptomycetes as biological control agents against basal drop, in VIII International Symposium on Chemical and Non-Chemical Soil and Substrate Disinfestation, Vol. 1044 (Torino: ). [Google Scholar]
- Bonaldi M., Chen X. Y. L., Kunova A., Pizzatti C., Saracchi M., Cortesi P. (2015). Colonization of lettuce rhizosphere and roots by tagged Streptomyces. Front. Microbiol. 6:25 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonaterra A., Mari M., Casalini L., Montesinos E. (2003). Biological control of Monilinia laxa and Rhizopus stolonifer in postharvest of stone fruit by Pantoea agglomerans EPS125 and putative mechanisms of antagonism. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 84, 93–104. 10.1016/S0168-1605(02)00403-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwmeester H. J., Roux C., Lopez-Raez J. A., Becard G. (2007). Rhizosphere communication of plants, parasitic plants and AM fungi. Trends Plant Sci. 12, 224–230. 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubici G., Marsico A. D., D'amico M., Amenduni M., Cirulli M. (2013). Evaluation of Streptomyces spp. for the biological control of corky root of tomato and Verticillium wilt of eggplant. Appl. Soil Ecol. 72, 128–134. 10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.07.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Buddrus-Schiemann K., Schmid M., Schreiner K., Welzl G., Hartmann A. (2010). Root colonization by Pseudomonas sp. DSMZ 13134 and impact on the indigenous rhizosphere bacterial community of barley. Microb. Ecol. 60, 381–393. 10.1007/s00248-010-9720-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budge S. P., Whipps J. M. (2001). Potential for integrated control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in glasshouse lettuce using Coniothyrium minitans and reduced fungicide application. Phytopathology 91, 221–227. 10.1094/PHYTO.2001.91.2.221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chater K. F. (1996). Regulation of bacterial antibiotic production, in Products of Secondary Metabolism, ed Kleinkauf H., von Dohren H. (Weinheim: Biotechnology VCH; ), 57–105. [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Yan F., Chai Y. R., Liu H. X., Kolter R., Losick R. (2013). Biocontrol of tomato wilt disease by Bacillus subtilis isolates from natural environments depends on conserved genes mediating biofilm formation. Environ. Microbiol. 15, 848–864. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02860.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung W. C., Huang J. W., Huang H. C. (2005). Formulation of a soil biofungicide for control of damping-off of Chinese cabbage (Brassica chinensis) caused by Rhizoctonia solani. Biol. Contr. 32, 287–294. 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2004.10.011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. F., Yamasaki H., Mazzola M. (2005). Brassica napus seed meal soil amendment modifies microbial community structure, nitric oxide production and incidence of Rhizoctonia root rot. Soil Biol. Biochem. 37, 1215–1227. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.11.027 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Compant S., Duffy B., Nowak J., Clement C., Barka E. A. (2005). Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 4951–4959. 10.1128/AEM.71.9.4951-4959.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compant S., Clement C., Sessitsch A. (2010). Plant growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizo- and endosphere of plants: their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 42, 669–678. 10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Conn V. M., Walker A. R, Franco C. M. M. (2008) Endophytic Actinobacteria induce defense pathways in Arabidopsis 37 thaliana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact 21:208–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs J. T., Franco C. M. M. (2003). Visualization of an endophytic Streptomyces species in wheat seed. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 4260–4262. 10.1128/AEM.69.7.4260-4262.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppels D. A., Higham J., Traquair J. A. (2013). Efficacy of selected streptomycetes and a streptomycete plus pseudomonad combination in the management of selected bacterial and fungal diseases of field tomatoes. Biol. Contr. 67, 361–372. 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2013.09.005 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- De-Bashan L. E., Hernandez J. P., Bashan Y., Maier R. M. (2010). Bacillus pumilus ES4: candidate plant growth-promoting bacterium to enhance establishment of plants in mine tailings. Environ. Exp. Bot. 69, 343–352. 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.04.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlacher A., Cardinale M., Grube M., Berg G. (2015). Biotic stress shifted structure and abundance of Enterobacteriaceae in the lettuce microbiome. PLoS ONE 10:e0118068 10.1371/journal.pone.0118068 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faria J. C., Jelihovschi E. G., Allaman I. B. (2013). Conventional Tukey Test. (Ilheus: Test.UESC; ). [Google Scholar]
- Fernando W. G. D., Nakkeeran S., Zhang Y., Savchuk S. (2007). Biological control of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary by Pseudomonas and Bacillus species on canola petals. Crop Prot. 26, 100–107. 10.1016/j.cropro.2006.04.007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Franco C., Michelsen P., Percy N., Conn V., Listiana E., Moll S. (2007). Actinobacterial endophytes for improved crop performance. Australas. Plant Pathol. 36, 524–531. 10.1071/AP07067 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fravel D. R. (2005). Commercialization and implementation of biocontrol. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 43, 337–359. 10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.032904.092924 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamalero E., Lingua G., Berta G., Lemanceau P. (2003). Methods for studying root colonization by introduced beneficial bacteria. Agronomie 23, 407–418. 10.1051/agro:2003014 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Haas D., Defago G. (2005). Biological control of soil-borne pathogens by fluorescent pseudomonads. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3, 307–319. 10.1038/nrmicro1129 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J., Park E.-C., Seed B. (1996). Codon usage limitation in the expression of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Curr. Biol. 6, 315–324. 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00482-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardoim P. R., Van Overbeek L. S., Berg G., Pirttila A. M., Compant S., Campisano A. (2015). The hidden world within plants: ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 79, 293–320. 10.1128/MMBR.00050-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiltner (1904). Über neuere Erfahrungen und Probleme auf dem Gebiete der Bodenbakteriologie unter besonderer Berücksic. Arb. Dtsch. Landwirt. Ges. 98, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Himmelstein J. C., Maul J. E., Everts K. L. (2014). Impact of five cover crop green manures and Actinovate on Fusarium wilt of watermelon. Plant Dis. 98, 965–972. 10.1094/PDIS-06-13-0585-RE [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A. (1988). The Leeuwenhoek Lecture, 1987. towards an understanding of gene switching in Streptomyces, the basis of sporulation and antibiotic production. Proc, R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 235, 121–138. 10.1098/rspb.1988.0067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell C. R. (2003). Mechanisms employed by Trichoderma species in the biological control of plant diseases: the history and evolution of current concepts. Plant Dis. 87, 4–10. 10.1094/PDIS.2003.87.1.4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii H. (2006). Impact of fungicide resistance in plant pathogens on crop disease control and agricultural environment. Jarq Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 40, 205–211. 10.6090/jarq.40.205 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen B. J., Zidack N. K., Larson B. J. (2004). The role of Bacillus-based biological control agents in integrated pest management systems: plant diseases. Phytopathology 94, 1272–1275. 10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.11.1272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi M., Rong X., Moll S., Kers J., Franco C., Loria R. (2007). Streptomyces turgidiscabies secretes a novel virulence protein, Nec1, which facilitates infection. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 20, 599–608. 10.1094/MPMI-20-6-0599 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanini G. S., Katsifas E. A., Savvides A. L., Karagouni A. D. (2013). Streptomyces rochei ACTA1551, an indigenous Greek isolate studied as a potential biocontrol agent against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp lycopersici. Biomed Res. Int. 2013:387230. 10.1155/2013/387230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkel L. L., Schlatter D. C., Bakker M. G., Arenz B. E. (2012). Streptomyces competition and co-evolution in relation to plant disease suppression. Res. Microbiol. 163, 490–499. 10.1016/j.resmic.2012.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinbaum D. G., Klein M. (eds.). (2012). Evaluating the proportional hazards assumption, in Survival Analysis: A Self-Learning Text, 3rd Edn (New York, NY: Springer; ), 161–200. 10.1007/978-1-4419-6646-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kloepper J. W., Ryu C. M., Zhang S. A. (2004). Induced systemic resistance and promotion of plant growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology 94, 1259–1266. 10.1094/PHYTO.2004.94.11.1259 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler H. R., Triebskorn R. (2013). Wildlife ecotoxicology of pesticides: can we track effects to the population level and beyond? Science 341, 759–765. 10.1126/science.1237591 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzyzanowska D., Obuchowski M., Bikowski M., Rychlowski M., Jafra S. (2012). Colonization of potato rhizosphere by GFP-Tagged Bacillus subtilis MB73/2, Pseudomonas sp. P482 and Ochrobactrum sp. A44 shown on large sections of roots using enrichment sample preparation and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Sensors 12, 17608–17619. 10.3390/s121217608 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurth F., Mailänder S., Bönn M., Feldhahn L., Herrmann S., Große I., et al. (2014). Streptomyces-induced resistance against oak powdery mildew involves host plant responses in defense, photosynthesis, and secondary metabolism pathways. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 27, 891–900. 10.1094/MPMI-10-13-0296-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeda D. P., Goodfellow M., Brown R., Ward A. C., Lanoot B., Vanncanneyt M., et al. (2012). Phylogenetic study of the species within the family Streptomycetaceae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101, 73–104. 10.1007/s10482-011-9656-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamberth C., Jeanmart S., Luksch T., Plant A. (2013). Current challenges and trends in the discovery of agrochemicals. Science 341, 742–746. 10.1126/science.1237227 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehr N. A., Schrey S. D., Hampp R., Tarkka M. T. (2008). Root inoculation with a forest soil streptomycete leads to locally and systemically increased resistance against phytopathogens in Norway spruce. New Phytol. 177, 965–976. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02322.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehtonen M. J., Rantala H., Kreuze J. F., Bang H., Kuisma L., Koski P., et al. (2004). Occurrence and survival of potato scab pathogens (Streptomyces species) on tuber lesions: quick diagnosis based on a PCR-based assay. Plant Pathol. 53, 280–287. 10.1111/j.0032-0862.2004.01009.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Leisso R. S., Miller P. R., Burrows M. E. (2009). The influence of biological and fungicidal seed treatments on chickpea (Cicer arietinum) damping off. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 31, 38–46. 10.1080/07060660909507570 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Jiang Y., Ning P., Zheng L., Huang J., Li G., et al. (2011). Suppression of Magnaporthe oryzae by culture filtrates of Streptomyces globisporus JK-1. Biol. Contr. 58, 139–148. 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2011.04.013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. Q., Zhang N., Zhang Z. H., Luo J., Shen B., Zhang R. F., et al. (2013). Antagonist Bacillus subtilis HJ5 controls Verticillium wilt of cotton by root colonization and biofilm formation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 49, 295–303. 10.1007/s00374-012-0718-x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Loria R., Kers J., Joshi M. (2006). Evolution of plant pathogenicity in Streptomyces. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 44, 469–487. 10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.032905.091147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Kamilova F. (2009). Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 63, 541–556. 10.1146/annurev.micro.62.081307.162918 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado-Gonzalez M. M., Bakker P. A., Prieto P., Mercado-Blanco J. (2015a). Arabidopsis thaliana as a tool to identify traits involved in Verticillium dahliae biocontrol by the olive root endophyte Pseudomonas fluorescens PICF7. Front. Microbiol. 6:266. 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00266 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado-Gonzalez M. M., Schiliro E., Prieto P., Mercado-Blanco J. (2015b). Endophytic colonization and biocontrol performance of Pseudomonas fluorescens PICF7 in olive (Olea europaea L.) are determined neither by pyoverdine production nor swimming motility. Environ. Microbiol. 17, 3139–3153. 10.1111/1462-2920.12725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfanova N., Kamilova F., Validov S., Shcherbakov A., Chebotar V., Tikhonovich I., et al. (2011). Characterization of Bacillus subtilis HC8, a novel plant-beneficial endophytic strain from giant hogweed. Microb. Biotechnol. 4, 523–532. 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2011.00253.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzola M., Zhao X. (2010). Brassica juncea seed meal particle size influences chemistry but not soil biology-based suppression of individual agents inciting apple replant disease. Plant Soil 337, 313–324. 10.1007/s11104-010-0529-5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Bending G. D., White P. J. (2005). Biological costs and benefits to plant-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere. J. Exp. Bot. 56, 1729–1739. 10.1093/jxb/eri205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H., Berg G. (2008). Impact of formulation procedures on the effect of the biocontrol agent Serratia plymuthica HRO-C48 on Verticillium wilt in oilseed rape. Biocontrol 53, 905–916. 10.1007/s10526-007-9111-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Palaniyandi S. A., Yang S. H., Zhang L., Suh J. W. (2013). Effects of actinobacteria on plant disease suppression and growth promotion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 9621–9636. 10.1007/s00253-013-5206-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulitz T. C., Belanger R. R. (2001). Biological control in greenhouse systems. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 39, 103–133. 10.1146/annurev.phyto.39.1.103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poleatewich A. M., Ngugi H. K., Backman P. A. (2012). Assessment of application timing of Bacillus spp. to suppress pre- and postharvest diseases of apple. Plant Dis. 96, 211–220. 10.1094/PDIS-05-11-0383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope M. K., Green B. D., Westpheling J. (1996). The bld mutants of Streptomyces coelicolor are defective in the regulation of carbon utilization, morphogenesis and cell-cell signalling. Mol. Microbiol. 19, 747–756. 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.414933.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prapagdee B., Kuekulvong C., Mongkolsuk S. (2008). Antifungal potential of extracellular metabolites produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus against phytopathogenic fungi. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 4, 330–337. 10.7150/ijbs.4.330 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R_Core_Team (2013). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. (Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; ).htigung der Gründüngung und Brache. Arb. Dtsch. Landwirtsch. Ges 98. [Google Scholar]
- Raaijmakers J. M., Paulitz T. C., Steinberg C., Alabouvette C., Moenne-Loccoz Y. (2009). The rhizosphere: a playground and battlefield for soilborne pathogens and beneficial microorganisms. Plant Soil 321, 341–361. 10.1007/s11104-008-9568-6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rabeendran N., Jones E. E., Moot D. J., Stewart A. (2006). Biocontrol of Sclerotinia lettuce drop by Coniothyrium minitans and Trichoderma hamatum. Biol. Contr. 39, 352–362. 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2006.06.004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Riedlinger J., Schrey S. D., Tarkka M. T., Hampp R., Kapur M., Fiedler H. P. (2006). Auxofuran, a novel metabolite that stimulates the growth of fly agaric, is produced by the mycorrhiza helper bacterium Streptomyces strain AcH 505. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 3550–3557. 10.1128/AEM.72.5.3550-3557.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi F., Quaroni S., Sardi P., Saracchi M. (2010). Studies on Anthostoma decipiens involved in Carpinus betulus decline. J. Plant Pathol. 92, 637–644. 10.4454/jpp.v92i3.308 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rungin S., Indananda C., Suttiviriya P., Kruasuwan W., Jaemsaeng R., Thamchaipenet A. (2012). Plant growth enhancing effects by a siderophore-producing endophytic streptomycete isolated from a Thai jasmine rice plant (Oryza sativa L. cv. KDML105). Antonie van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. Gen. Mol. Microbiol. 102, 463–472. 10.1007/s10482-012-9778-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungjindamai N., Jeffries P., Xu X. M. (2014). A novel strategy to reduce overwintering inoculum of Monilinia laxa. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 140, 591–596. 10.1007/s10658-014-0473-y [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R. P., Germaine K., Franks A., Ryan D. J., Dowling D. N. (2008). Bacterial endophytes: recent developments and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 278, 1–9. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00918.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salla T. D., Astarita L. V., Santarém E. R. (2016). Defense responses in plants of Eucalyptus elicited by Streptomyces and challenged with Botrytis cinerea. Planta 243, 1055–1070. 10.1007/s00425-015-2460-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago T. R., Grabowski C., Rossato M., Romeiro R. S., Mizubuti E. S. G. (2015). Biological control of Eucalyptus bacterial wilt with rhizobacteria. Biol. Contr. 80, 14–22. 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2014.09.007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sardi P., Saracchi M., Quaroni S., Petrolini B., Borgonovi G. E., Merli S. (1992). Isolation of endophytic Streptomyces strains from surface-sterilized roots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 2691–2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiter S., Sandmann M., Smalla K., Grosch R. (2014). Soil type dependent rhizosphere competence and biocontrol of two bacterial inoculant strains and their effects on the rhizosphere microbial community of field-grown lettuce. PLoS ONE 9:e103726. 10.1371/journal.pone.0103726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrey S. D., Schellhammer M., Ecke M., Hampp R., Tarkka M. T. (2005). Mycorrhiza helper bacterium Streptomyces AcH 505 induces differential gene expression in the ectomycorrhizal fungus Amanita muscaria. New Phytol. 168, 205–216. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01518.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrey S. D., Tarkka M. T. (2008). Friends and foes: streptomycetes as modulators of plant disease and symbiosis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 94, 11–19. 10.1007/s10482-008-9241-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spadaro D., Gullino M. L. (2004). State of the art and future prospects of the biological control of postharvest fruit diseases. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 91, 185–194. 10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00380-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao K. V. (1998). Progress toward integrated management of lettuce drop. Plant Dis. 82, 1068–1078. 10.1094/PDIS.1998.82.10.1068 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian P., Mageswari A., Kim K., Lee Y., Sa T. (2015). Psychrotolerant endophytic Pseudomonas sp strains OB155 and OS261 induced chilling resistance in tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum Mill.) by activation of their antioxidant capacity. Mol. Plant Microbe Inter. 28, 1073–1081. 10.1094/MPMI-01-15-0021-R [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J. H., Kelemen G. H., Fernandez-Abalos J. M., Bibb M. J. (1999). Green fluorescent protein as a reporter for spatial and temporal gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 145, 2221–2227. 10.1099/00221287-145-9-2221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun K., Liu J., Gao Y. Z., Jin L., Gu Y. J., Wang W. Q. (2014). Isolation, plant colonization potential, and phenanthrene degradation performance of the endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas sp. Ph6-gfp. Sci. Rep. 4:5462. 10.1038/srep05462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkka M., Hampp R. (2008). Secondary metabolites of soil streptomycetes in biotic interactions, in Secondary Metabolites in Soil Ecology, ed Karlovsky P. (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; ), 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Teixido N., Usall J., Vinas I. (1999). Efficacy of preharvest and postharvest Candida sake biocontrol treatments to prevent blue mould on apples during cold storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 50, 203–210. 10.1016/S0168-1605(99)00105-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Therneau T. (2014). A Package for Survival Analysis in S. R package version 2.37-7. Avaliable online at: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival
- Tian X. L., Zheng Y. B. (2013). Evaluation of biological control agents for Fusarium wilt in Hiemalis begonia. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 35, 363–370. 10.1080/07060661.2013.812580 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tokala R. K., Strap J. L., Jung C. M., Crawford D. L., Salove M. H., Deobald L. A., et al. (2002). Novel plant-microbe rhizosphere interaction involving Streptomyces lydicus WYEC108 and the pea plant (Pisum sativum). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 2161–2171. 10.1128/AEM.68.5.2161-2171.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejo-Estrada S. R., Sepulveda I. R., Crawford D. L. (1998). In vitro and in vivo antagonism of Streptomyces violaceusniger YCED9 against fungal pathogens of turfgrass. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 14, 865–872. 10.1023/A:1008877224089 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beneden S., Pannecoucque J., Debode J., De Backer G., Hofte M. (2009). Characterisation of fungal pathogens causing basal rot of lettuce in Belgian greenhouses. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 124, 9–19. 10.1007/s10658-008-9385-z [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Bergh J. C. J. M., Rietveld P. (2004). Reconsidering the limits to world population: meta-analysis and meta-prediction. Bioscience 54, 195–204. 10.1641/0006-3568(2004)054[0195:RTLTWP]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Velivellil S. L. S., De Vos P., Kromann P., Declerck S., Prestwich B. D. (2014). Biological control agents: from field to market, problems, and challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 32, 493–496. 10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma V. C., Singh S. K., Prakash S. (2011). Bio-control and plant growth promotion potential of siderophore producing endophytic Streptomyces from Azadirachta indica A. Juss. J. Basic Microbiol. 51, 550–556. 10.1002/jobm.201000155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh U. F., Morrissey J. P., O'gara F. (2001). Pseudomonas for biocontrol of phytopathogens: from functional genomics to commercial exploitation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12, 289–295. 10.1016/S0958-1669(00)00212-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller D. M. (2007). Pseudomonas biocontrol agents of soilborne pathogens: looking back over 30 years. Phytopathology 97, 250–256. 10.1094/PHYTO-97-2-0250 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipps J. M. (2001). Microbial interactions and biocontrol in the rhizosphere. J. Exp. Bot. 52, 487–511. 10.1093/jexbot/52.suppl_1.487 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue Q. Y., Ding G. C., Li S. M., Yang Y., Lan C. Z., Guo J. H., et al. (2013). Rhizocompetence and antagonistic activity towards genetically diverse Ralstonia solanacearum strains - an improved strategy for selecting biocontrol agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 1361–1371. 10.1007/s00253-012-4021-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan W. M., Crawford D. L. (1995). Characterization of Streptomyces lydicus WYEC108 as a potential biocontrol agent against fungal root and seed rots. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 3119–3128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng W. T., Kirk W., Hao J. J. (2012). Field management of Sclerotinia stem rot of soybean using biological control agents. Biol. Contr. 60, 141–147. 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2011.09.012 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao S., Du C.-M., Tian C.-Y. (2012). Suppression of Fusarium oxysporum and induced resistance of plants involved in the biocontrol of Cucumber Fusarium Wilt by Streptomyces bikiniensis HD-087. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28, 2919–2927. 10.1007/s11274-012-1102-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Survival of lettuce plants (Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci”) in the field experiment (ca. 60 days after transplanting) inoculated with (A) Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (inoculated control); (B) S. sclerotiorum + S. exfoliatus FT05W; (C) S. sclerotiorum + S. cyaneus ZEA17I; and (D) S. sclerotiorum + S. lydicus WYEC 108.
Number of lettuce dead plants recorded for the experiment A, when Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” was sown the same day of S. sclerotiorum and Streptomyces co-inoculation.
Number of lettuce dead plants recorded for the experiment B, when Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” was sown one week after S. sclerotiorum and Streptomyces co-inoculation.
Number of Lactuca sativa var. capitata, “Regina dei ghiacci” dead plants recorded for field experiment, Travacò Siccomario (Pavia, Italy).