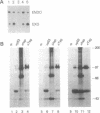
Abstract
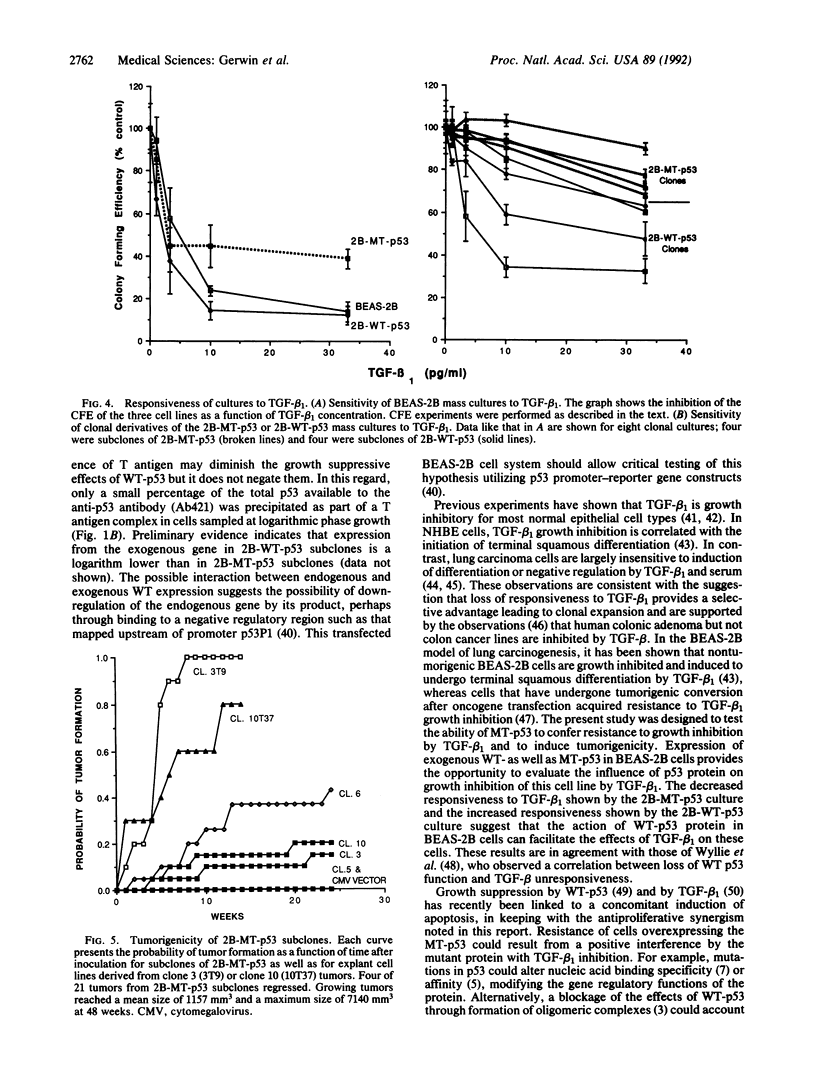
Loss of normal functions and gain of oncogenic functions when the p53 tumor suppressor gene is mutated are considered critical events in the development of the majority of human cancers. Human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) provide an in vitro model system to study growth, differentiation, and neoplastic transformation of progenitor cells of lung carcinoma. When wild-type (WT) or mutant (MT; codon 143Val-Ala) human p53 cDNA was transfected into nontumorigenic BEAS-2B cells, we observed that (i) transfected WT p53 suppresses and MT p53 enhances the colony-forming efficiency of these cells, (ii) MT p53 increases resistance to transforming growth factor beta 1, and (iii) clones of MT p53 transfected BEAS-2B cells are tumorigenic when inoculated into athymic nude mice. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that certain mutations in p53 may function in multistage lung carcinogenesis by reducing the responsiveness of bronchial epithelial cells to negative growth factors.
Full text
PDF
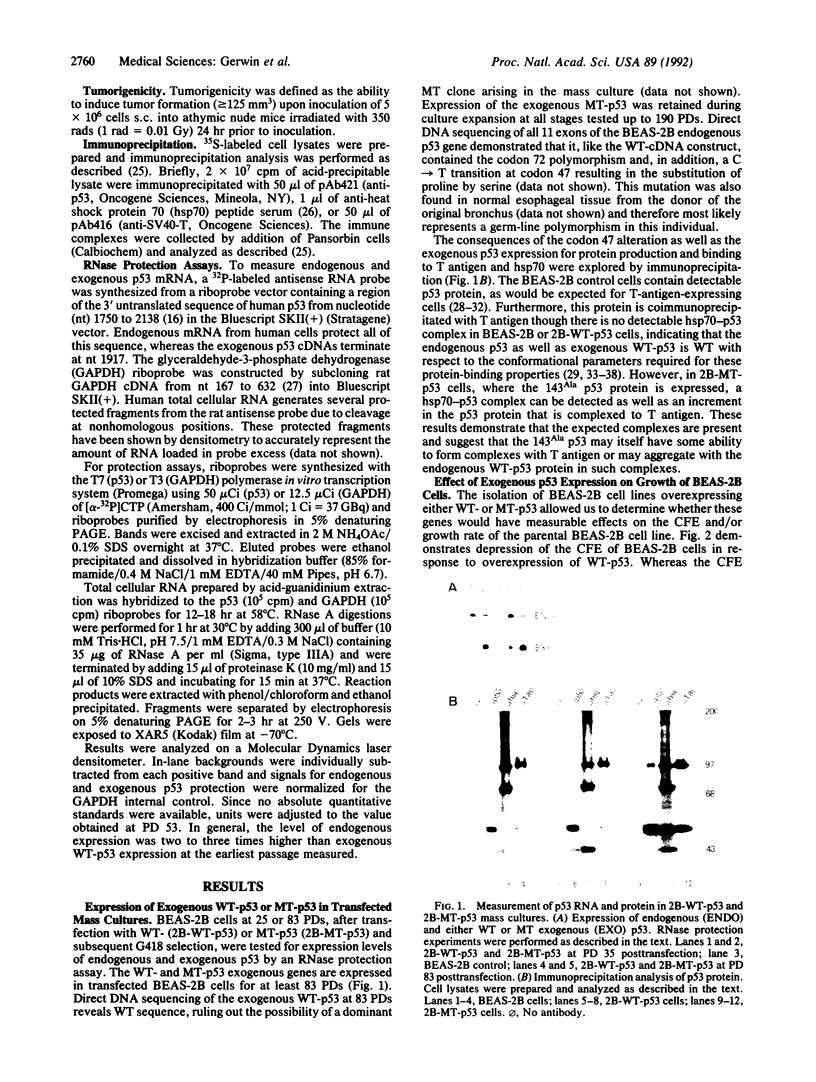
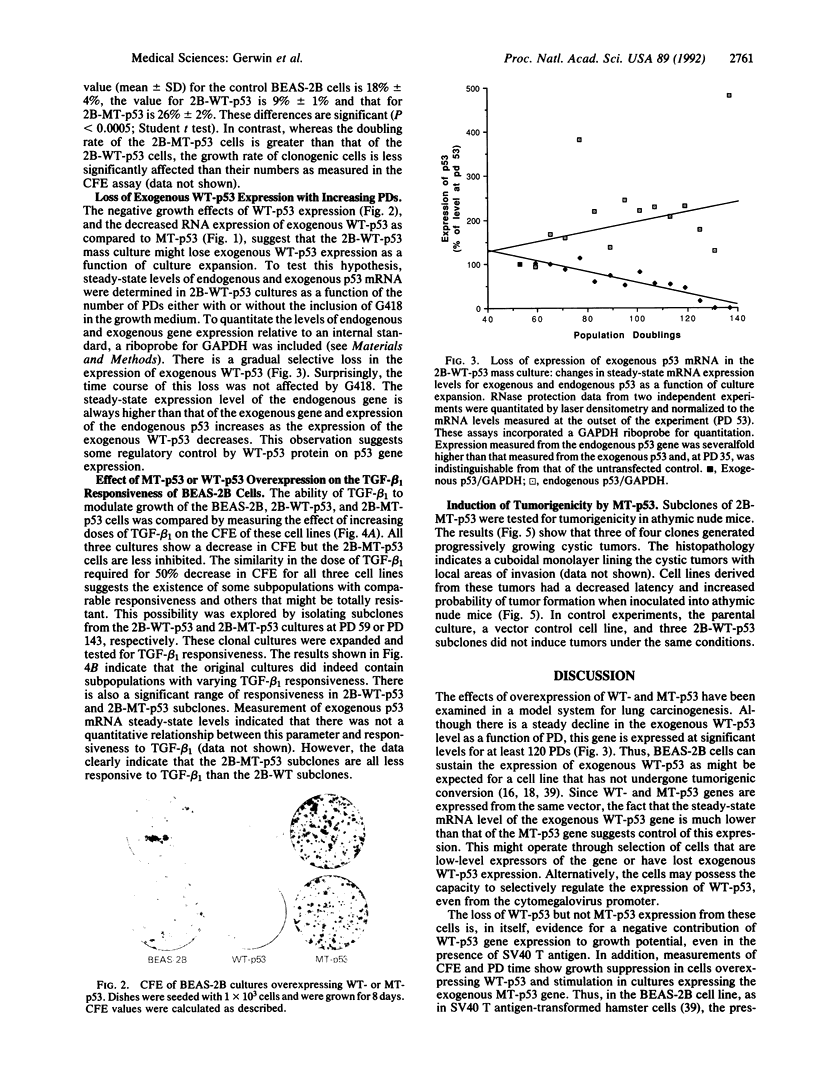

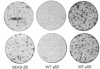
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Jenkins J. R. Ability of p53 and the adenovirus E1b 58-kilodalton protein to form a complex is determined by p53. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1792–1799. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1792-1799.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash D. E., Reddel R. R., Quanrud M., Yang K., Farrell M. P., Harris C. C. Strontium phosphate transfection of human cells in primary culture: stable expression of the simian virus 40 large-T-antigen gene in primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2031–2034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Bascom C. C., Sipes N. J., Graves-Deal R., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Selective inhibition of growth-related gene expression in murine keratinocytes by transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3088–3093. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey R. J., Jr, Sipes N. J., Bascom C. C., Graves-Deal R., Pennington C. Y., Weissman B. E., Moses H. L. Growth modulation of mouse keratinocytes by transforming growth factors. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 15;48(6):1596–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diller L., Kassel J., Nelson C. E., Gryka M. A., Litwak G., Gebhardt M., Bressac B., Ozturk M., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5772–5781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrhart J. C., Duthu A., Ullrich S., Appella E., May P. Specific interaction between a subset of the p53 protein family and heat shock proteins hsp72/hsc73 in a human osteosarcoma cell line. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):595–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy O., Michalovitz D., Oren M. Different tumor-derived p53 mutants exhibit distinct biological activities. Science. 1990 Oct 5;250(4977):113–116. doi: 10.1126/science.2218501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Frey A. B., Levine A. J. Immunological evidence for the association of p53 with a heat shock protein, hsc70, in p53-plus-ras-transformed cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2863–2869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Chumakov P., Addison C., Stürzbecher H. W., Wade-Evans A. Two distinct regions of the murine p53 primary amino acid sequence are implicated in stable complex formation with simian virus 40 T antigen. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3903–3906. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3903-3906.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke Y., Gerwin B. I., Ruskie S. E., Pfeifer A. M., Harris C. C., Lechner J. F. Cell density governs the ability of human bronchial epithelial cells to recognize serum and transforming growth factor beta-1 as squamous differentiation-inducing agents. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):833–843. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke Y., Reddel R. R., Gerwin B. I., Miyashita M., McMenamin M., Lechner J. F., Harris C. C. Human bronchial epithelial cells with integrated SV40 virus T antigen genes retain the ability to undergo squamous differentiation. Differentiation. 1988 Jun;38(1):60–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Baker S. J., Nigro J. M., Rotter V., Levine A. J., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Mutant p53 proteins bind DNA abnormally in vitro. Oncogene. 1991 Jan;6(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Benchimol S. p53: oncogene or anti-oncogene? Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):1–8. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. A., Bennett W. P., Metcalf R. A., Welsh J. A., Ecker J., Modali R. V., Ullrich S., Romano J. W., Appella E., Testa J. R. p53 mutations, ras mutations, and p53-heat shock 70 protein complexes in human lung carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4090–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning A. M., Williams A. C., Game S. M., Paraskeva C. Differential sensitivity of human colonic adenoma and carcinoma cells to transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta): conversion of an adenoma cell line to a tumorigenic phenotype is accompanied by a reduced response to the inhibitory effects of TGF-beta. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1471–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui T., Wakefield L. M., Lechner J. F., LaVeck M. A., Sporn M. B., Harris C. C. Type beta transforming growth factor is the primary differentiation-inducing serum factor for normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2438–2442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Ullrich S. J., Romano J. W. Wild type human p53 is antiproliferative in SV40-transformed hamster cells. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):973–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Romano J. W., Ullrich S. J. Negative growth regulation in a glioblastoma tumor cell line that conditionally expresses human wild-type p53. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6166–6170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Medcalf E. A. Cotranslation of activated mutant p53 with wild type drives the wild-type p53 protein into the mutant conformation. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):765–774. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90384-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Yang E. Y., Pietenpol J. A. TGF-beta stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation: new mechanistic insights. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke R. W., Miller C. W., Kato G. J., Simon K. J., Chen D. L., Dang C. V., Koeffler H. P. A potential transcriptional activation element in the p53 protein. Oncogene. 1990 Dec;5(12):1829–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer A. M., Lechner J. F., Masui T., Reddel R. R., Mark G. E., Harris C. C. Control of growth and squamous differentiation in normal human bronchial epithelial cells by chemical and biological modifiers and transferred genes. Environ Health Perspect. 1989 Mar;80:209–220. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8980209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Holt J. T., Stein R. W., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factor beta 1 suppression of c-myc gene transcription: role in inhibition of keratinocyte proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3758–3762. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietenpol J. A., Stein R. W., Moran E., Yaciuk P., Schlegel R., Lyons R. M., Pittelkow M. R., Münger K., Howley P. M., Moses H. L. TGF-beta 1 inhibition of c-myc transcription and growth in keratinocytes is abrogated by viral transforming proteins with pRB binding domains. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90188-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddel R. R., Ke Y., Gerwin B. I., McMenamin M. G., Lechner J. F., Su R. T., Brash D. E., Park J. B., Rhim J. S., Harris C. C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Greenberg M., Rotter V. Human p53 oncogene contains one promoter upstream of exon 1 and a second, stronger promoter within intron 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5146–5150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:107–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronen D., Rotter V., Reisman D. Expression from the murine p53 promoter is mediated by factor binding to a downstream helix-loop-helix recognition motif. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4128–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotello R. J., Lieberman R. C., Purchio A. F., Gerschenson L. E. Coordinated regulation of apoptosis and cell proliferation by transforming growth factor beta 1 in cultured uterine epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3412–3415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samet J. M. Radon and lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989 May 10;81(10):745–757. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.10.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaulsky G., Goldfinger N., Rotter V. Alterations in tumor development in vivo mediated by expression of wild type or mutant p53 proteins. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5232–5237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slingerland J. M., Benchimol S. Transforming activity of mutant human p53 alleles. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Sep;148(3):391–395. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmeyer K., Deppert W. DNA binding properties of murine p53. Oncogene. 1988 Nov;3(5):501–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Addison C., Jenkins J. R. Characterization of mutant p53-hsp72/73 protein-protein complexes by transient expression in monkey COS cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3740–3747. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Chumakov P., Welch W. J., Jenkins J. R. Mutant p53 proteins bind hsp 72/73 cellular heat shock-related proteins in SV40-transformed monkey cells. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):201–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Friedman P. N., Prives C. The murine p53 protein blocks replication of SV40 DNA in vitro by inhibiting the initiation functions of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey J. C., Harris C. C. Cellular and molecular biological aspects of human bronchogenic carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1990;10(2):181–209. doi: 10.1016/1040-8428(90)90006-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie F. S., Dawson T., Bond J. A., Goretzki P., Game S., Prime S., Wynford-Thomas D. Correlated abnormalities of transforming growth factor-beta 1 response and p53 expression in thyroid epithelial cell transformation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1991 Apr;76(1-3):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(91)90255-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., van Oostwaard T. M., de Laat S. W. Transforming growth factor-beta and retinoic acid modulate phenotypic transformation of normal rat kidney cells induced by epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5003–5009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]